AT&T
Page
Contents
DS1 Transmission and Cabling
Need for Synchronization Synchronization Hierarchy
Digital Loss Plan
Synchronization of Digital Facilities
LOSS-PLAN Implementation and Provisioning
Administration Options and Requirements
Port TYPES/INSTALLATION Compatibilities
Generic
System 75 R1V2 and R1V3
Maintenance and Alarms
Procedure
Administrative Procedure Summary
Index
AB-1
Glossary
GL-1
List of Figures
Contents
Xiv Contents
Procedure 012 Word 1 Name Database Generic
Figure A-1 DS1 Circuit Pack Screen
Bccos
List of Tables
User-to-User IE Opcodes
Purpose
About this Document
Prerequisite Skills and Knowledge
Intended Audiences
HOW this Document is Organized
Abbreviations Glossary Index
Appendixes
About this Document
Trademarks and Service Marks
HOW to USE this Document
Related Sources
AT&T
HOW to Make Comments about this Document
Xxiv about this Document
Introduction
Fundamentals of DS1 Signals
2INTRODUCTION
Introduction
Layer
4INTRODUCTION
Megacom
Introduction
6INTRODUCTION
Channels
8INTRODUCTION
Voice Voice-grade data Digital data
Channels
Channel Backup Generic
10INTRODUCTION
Circuit-Switched Versus Packet-Switched Channels
Framing Formats
D4 Framing
D4 Framing
ESF Framing
Data Link Signal Frame Sync Pattern
Bits Robbed BIT Optional
DS1 Signal, Framing Format, and ESF Superframe 24 Frames
14INTRODUCTION
Signaling Types
Robbed-Bit Signaling
24th-Channel Signaling
ESF
Signaling Superframe
Superframe Frame No
Alternate Mark Inversion
Line-Coding Formats
16INTRODUCTION
Zero Code Suppression and Bipolar with 8 Zero Substitution
1s-Density Requirement
Unrestricted or Clear Channel
Restricted Channel
18INTRODUCTION
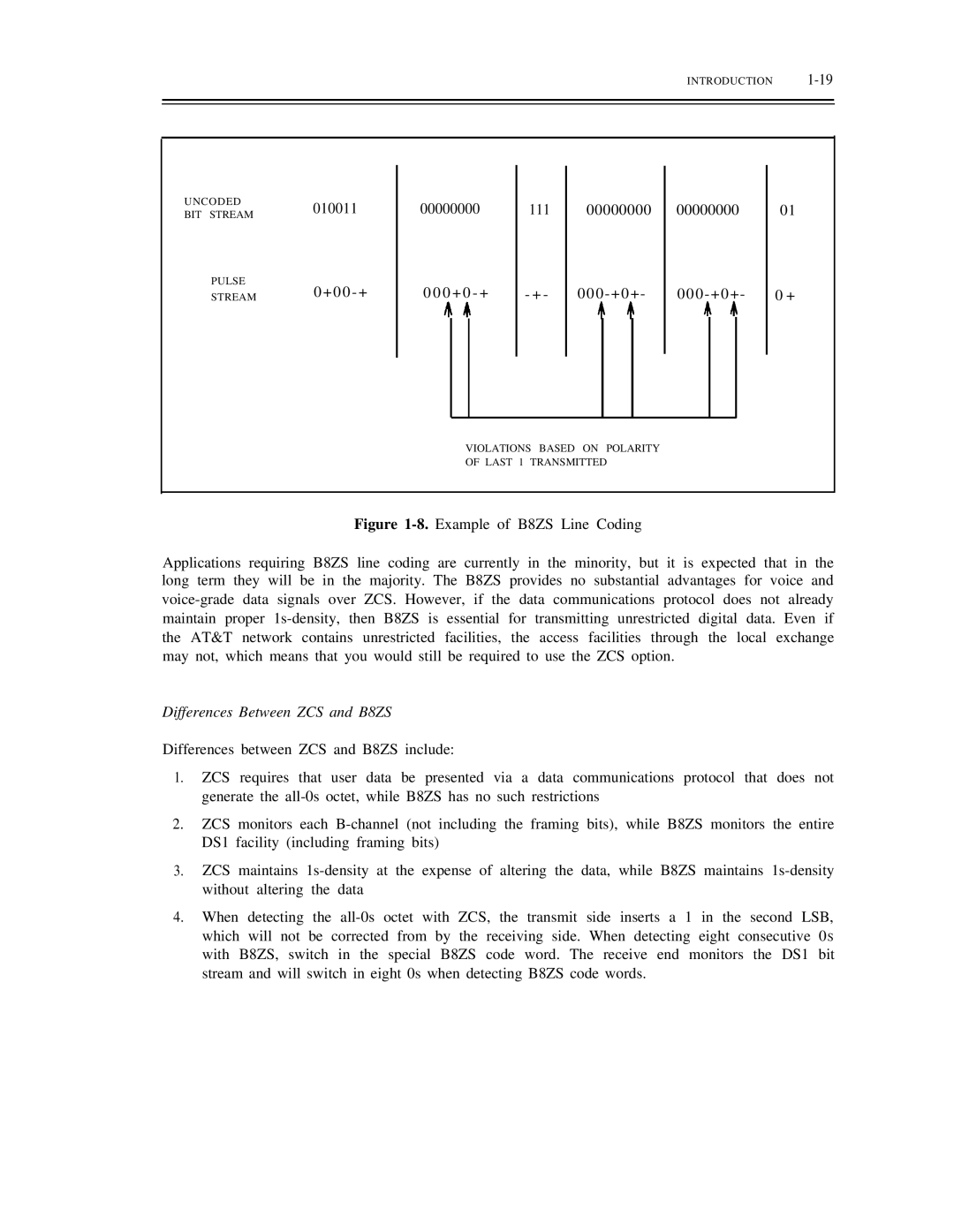
Introduction Uncoded BIT Stream Pulse
Differences Between ZCS and B8ZS
Violations Based on Polarity Last 1 Transmitted
Communication Protocols and 1s-Density Requirement
Bipolar Violations
20INTRODUCTION
DMI
Data
22INTRODUCTION
Common-Channel Signaling
Important Concepts
Alternate Voice/Data AVD Trunks
System 85 R2V4
Bearer Capability BC
24INTRODUCTION
Generic
Outgoing Calls
Switch Parameter Default Value
Bccos
Isdn Call Processing
Summary
Incoming Calls
26INTRODUCTION
Introduction
System 85 R2V4/Generic 2 CBC Implementation
CBC Service Selection
28INTRODUCTION
Networking Restrictions and ISDN-PRI Limitations
Generic 1 Implementation
30INTRODUCTION
Introduction
32INTRODUCTION
Hyperactivity
Network Difficulties
Glare
2NETWORK Connections and Configurations
DS1/DMI PRIVATE-NETWORK Connections
Network Connections and Configurations
Host Computer to Another System
4NETWORK Connections and Configurations
Other Vendor Digital Switch to Another System
IBM Idnx Multiplexer to Another System
OPS to Another System Via a D4-Channel Bank
Analog Switch to Another System
DS1/DMI PUBLIC-NETWORK Connections
4ESS to Another System Special-Access Connection
Synchronization
Screening Intra-LATA Calls
5ESS to Another System
Dacs to Another System
8NETWORK Connections and Configurations
Analog CO to Another System Via a D4-Channel Bank
CDM
DS1/DMI TERMINAL-EQUIPMENT Connections
CEM to a BCM32000
10NETWORK Connections and Configurations
Network Connections and Configurations
ISDN-PRI PRIVATE-NETWORK Connections
12NETWORK Connections and Configurations
System 85 R2 to a System 85 R2V4, Generic 1, or Generic
System 85 R2V4, Generic 1, and Generic 2 to a 4ESS
ISDN-PRI PUBLIC-NETWORK Connections
User-to-User Information transfer
Backup D-Channel
14NETWORK Connections and Configurations
Codeset
System 85 or Generic 2 ISDN-PRI to a 5ESS
Network Specific Facility
Synchronization
System 85 R2V4, Generic 1, or Generic 2 to a Dacs
16NETWORK Connections and Configurations
DS1 Transmission and Cabling
2DS1 Transmission and Cabling
Metallic Cabling Options
DSX-1 Distance Limitations
Network Channel Terminating Equipment Ncte
Direct Under 1310 Feet
On-Premises Cabling
DS1 Transmission and Cabling
Greater Than 4310 Feet
Between 1310 and 4310 Feet
4DS1 Transmission and Cabling
Maximum Distance of 4311 or More
Off-Premises Cabling
Maximum FT or Less
Maximum DSX-1 DS1
Maximum
Nonmetallic Cabling Options
6DS1 Transmission and Cabling
DSX-1 T E DS1
DS1/DMI DSX-1
CEM and CDM Cabling Configurations
ANY DS1 DSX-1 Channel Bank Transmission
CDM DSX-1 Or D4 Channel
Media Dedicated Channel Units Applications CDM only
OFF
Line Equalizer and Compensation Settings
System 85 Traditional Modules
AWG Abam & 24 AWG PDS
10DS1 Transmission and Cabling
Digital Loss Plan
Generic
LOSS-PLAN Implementation and Provisioning
2THE Digital Loss Plan
Digital Loss Plan
Encode Loss-Plan Function ANSI/EIA/TIA-464-A-1989 Designator
PORT-TO-PORT Loss Values
Loss plan
Digital conn
Loss
Transmit Receive Direction
Analog Facility DS1/DMI Digital Switch Channel Bank N K ONS
A L
CO did Trunk Ports
DS1/DMI/ISDN-PRI Port Losses
Terminating a DS1 AT a Channel Bank
Tie Trunk Ports
OPS Ports
8THE Digital Loss Plan
Need for Synchronization
Synchronization of Digital Facilities
Bank Transmit Digital BIT Stream
2SYNCHRONIZATION of Digital Facilities
Transmit
Channel Analog Bank Receive
Synchronization of Digital Facilities
Synchronization Hierarchy
4SYNCHRONIZATION of Digital Facilities
Page
6SYNCHRONIZATION of Digital Facilities
System 85 and Generic 2 Synchronization Architecture
Page
System 85 and Generic 2 Synchronization Software Operation
RED
Primary Secondary Reference Indicators
Indicators
Blue YEL Good LOS Misf
System 75 and Generic 1 Synchronization Architecture
System 75 and Generic 1 Synchronization Software Operation
Criteria for Switching Back to the Primary Reference
Criteria for Switching to the Secondary Reference
14SYNCHRONIZATION of Digital Facilities
External Synchronization Clock
Synchronization of Digital Facilities
16SYNCHRONIZATION of Digital Facilities
External-Clock Interface
Network Synchronization and Engineering
Selecting a Timing Source for the Switch
18SYNCHRONIZATION of Digital Facilities
Rule
Internal Reference Selection Rules
Digital Transmission Facilities Primary Frequency Reference
20SYNCHRONIZATION of Digital Facilities
13.Proper Use of Backup Facilities
Page
15.Optimal Diverse Routing
16.Less Than Optimal Diverse Routing
17.Excessive Cascading
26SYNCHRONIZATION of Digital Facilities
19.Excessive Synchronization from One Node
Rules 2 Through
External-Reference Selection Rules
28SYNCHRONIZATION of Digital Facilities
Availability of Synchronization Sources
Misconception
Fact
ISDN-PRI Trunk Facilities ANN35 or TN767 with TN755
Line-Only Mode DS1/DMI-BOS ANN11 or TN767
Conclusions on Synchronization
USE of Generic 2 AS a System Clock Reference
Trunk-Mode ISDN-PRI TN767
Line+Trunk Mode DS1/DMI-BOS ANN35 or TN767 with TN555
DMI-MOS ANN35 or TN767 with TN755
USE of Generic 1 AS a System Clock Reference
Trunk-Mode DS1/DMI-MOS TN767
Line-Only Mode DS1/DMI-BOS TN767
32SYNCHRONIZATION of Digital Facilities
Port TYPES/INSTALLATION Compatibilities
FX, Wats
2PORT TYPES/INSTALLATION Compatibilities
DMI-BOS E
Port TYPES/INSTALLATION Compatibilities
Supported Port Types
Operating Mode
4PORT TYPES/INSTALLATION Compatibilities
Generic 1 DS1/DMI-BOS
System 85 DS1, Traditional Modules ANN11
Line-Only Mode
DMI Trunks
Generic 1 ISDN-PRI
6PORT TYPES/INSTALLATION Compatibilities
Line+Trunk Mode
Port TYPES/INSTALLATION Compatibilities
Others
OPS Other Circuit Packs OPS PORTS/CARRIER Slot
Port TYPES/INSTALLATION Compatibilities Carrier Slots P T Y
10PORT TYPES/INSTALLATION Compatibilities
Line+Trunk Mode Port Grouping Rules
Did Trunk
DMI-BOS Trunks
Ground-Start CO Trunk
Transparent Ports
12PORT TYPES/INSTALLATION Compatibilities
Loop-Start CO Trunk
Of-Premises Stations
System 85 DS1 or DMI-MOS, Traditional Modules ANN35
Port Grouping Rules
14PORT TYPES/INSTALLATION Compatibilities
Administration Options and Requirements
2ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements
Field
Procedure 275 Word 4 Isdn Service Enable/Disable
Administration Options and Requirements System
System 85 R2V1 Through R2V4
Display only
Procedure 276 Word 1 Other Feature Groups
Procedure 250 Word 1 DS1 Carrier Designation
4ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
Position
V1-V4
Module Control
Procedure 260 Word 1 DS1/DMI/ISDN-PRI Physical Interface
Slot numbers 0, 5, 13, or 18 for line-only operation
Service or Facility Options
Can be assigned
V1-V2
V3-V4
Voice/data AVD
10ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
Criteria for Switching Back to the Primary Facility
Criteria for Switching to the Secondary Facility
12ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
DS1/OPS Related Translations
DS1 Channel Slot/Circuit
14ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
V4 Only
DS1/DMI-BOS applications should be administered with a
Supported. Therefore, option one is not applicable
PRI Parameters
Procedure 262 Word 1 Isdn Board Parameters
16ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
Fields
Field
Procedure 354 Word 3 NPA-NXX Digits Assignment
Enhanced Mode Procedure 354, Word NPA-NXX Assignment
Procedure 000 Word 4 NPA-NXX Index Designator
20ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
Range of 1 through
22ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
Field
Enhanced Mode Procedure 100, Word Trunk Group Translation
24ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
Dial Access CODE/TRUNK ID Code
Wats
Trunk Description Type
Did
Isdn TIE
Administration Options and REQUIREMENT’S System
Procedure 100 Word 2 Trunk Group Data Translations
Sychronous Duplex
Procedure 100 Word 3 Isdn Trunk Group Signaling Options
Modem Pooling
Data Rate
28ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
Field
Isdn network features is desired
Field 1 Field
Fields Fields 9-11 Field
32ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
This field is ignored by Isdn software
34ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
Procedure 116 Word 1 DS1/DMI/ISDN-PRI Trunk Assignments
36ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
DS1/ISDN-PRI Administration Channel Versus Trunk Assignments
38ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
Procedure 012 Word 1 Name Database
Through 99999, for extension and directory numbers
Procedure 012 Word 2 Name Database
Enhanced Mode Procedure 012, Word Name Database Entry
Procedure 012 Word 3 Name Database
Charater Encodes
Enhanced Mode Procedure 012, Word Name Database Compaction
42ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
IXC Isdn
Enhanced Mode Procedure 309, Word ARS Route Tables
Bearer Capability
44ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
Isdn
Network Service/Feature Options, shows the relationships
Network Service or
Network Feature Value Trunk Type
46ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
AAR System 85 R2V4, depicts the procedure
Enhanced Mode Procedure 321, Word AAR Route Tables
Bearer Capability
TNS
Procedure Word Field
NSF IXC
NSF
TTL Telephone Digits
23. Procedure
Terminating Test Line Telephone Digits
Attendant Release Loop Operation
Administration Options and Requirements Generic
Maximum Preemption Level Administrable Alarms
Generic
SNC
52ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Procedure 250 Word 1 SC/DS1 Carrier Designation
Field Fields
54ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
SC Information Connected to CC0 ON-LINE Enter command
ISDN-PRI
Equipment Traditional Universal Parameter Module
That
Zero Code Suppression ZCS
Criteria for Switching to the Secondary
Criteria for Switching Back to the Primary
Field
62ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Field
133 to 90 to 266 to 180 to 399 to 270 to 532 to 360 to
Distance to Midpoint Compensation Or Endpoint FT
PRI and BRI Layer 2 Parameters
BRI Only
Depending on the particular facility
NFAS-PRI Only
Procedure 262 Word 2 ISDN-PRI D-Channel Backup
Backup Channel Equipment Location
68ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Primary D-CHANNEL Equipment Location
Procedure 262 Word 3 ISDN-PRI Codeset Map Assignments
Performance
Mapped from CODESET/INFORMATION Element
Enhanced Mode Procedure 280, Word Isdn Codeset Mapping
Mapped to CODESET/INFORMATION Element
Field Field 6 Field IE Name Codeset
NPA
Enhanced Mode Procedure 354, Word
NXX
74ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
34.Procedure 000 Word 4 NPA-NXX Index Designator
LDN
Enhanced Mode Procedure 210, Word
NPA-NXX
Differences Between System 85 R2V4 and Generic
Procedure 014 Word 1 Bccos Routing Options
Call Types and Action Taken
COS Default Capabilities
78ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Procedure 014 Word 2 Bccos Data Options
Or is not 0 supported
80ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
38.Procedure 010 Word 4 Terminal COS Restrictions Generic
Field
Enhanced Mode Procedure 100, Word
82ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Isdn
DMI
84ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
40. Procedure
86ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Not applicable For
Whether access to other Isdn network features is desired
Assigns whether the trunk group has 1 or does not have
Procedure 103 Word 1 Network Trunk Group Translations
AAR/ARS
Channel Versus Trunk Assignments
92ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
DS1 Channel Slot/Circuit
94ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
45.Procedure 012 Word 1 Name Database Generic
From 1 to
Character Encodes
96ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
47.Procedure 012 Word 3 Name Database Generic Field
Parameters
98ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Enhanced Mode Procedure 279, Word NETWORK-SPECIFIC Facility
Isdn Network Definition
Coding Value Binary
Network Parameterized Feature Facility
11. Network
Name
100ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Procedure 309 Word 1 ARS Route Tables
Enhanced Mode Procedure 309, Word
Procedure 309 Word 5 ARS-ISDN Bccos
Procedure 321 Word 1 AAR Tables Generic
Services/Network Features, for the appropriate encode
102ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Enhanced Mode Procedure 321, Word
104ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Procedure 321 Word 5 AAR-ISDN and Other Feature Parameters
53.Procedure 107 Word 1 Atms TTL Assignment System 85 R2V4
106ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Procedure 108 Word 1 Isdn Trunk Group TTL Number Digits
DS1 Circuit Pack
Service/Facility Options
DMI-BOS? Maintenance Parameters
System 75 R1V2 and R1V3
Compensation Value Distance Feet
108ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
109
Loop
Slip
Detection
Remote
DS1 Circuit Packs
Synchronization Plan
Trunk Group/Trunk Group Members
112ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
Mode
Delay
Port
Name
Call
114ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements System
ACA
AAR/ARS
116ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
60.DS1 Circuit Pack Screen, Common-Channel Signaling
Line
Location
118ADINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Interface
120ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
DTT
Trunk Group/Trunk Group Members DS1 Trunk Applications
Call COR
STT
In/out
122ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
BCC
Avd or data
PBX ID
Trunk Group ACA
Night
With auto Mode
Processor Interface Data Module ISDN-PRI Applications
Processor Channel Assignments ISDN-PRI Applications
Data Extension
Physical
Channel
Chan Priority
Proc Chan
Appl
Link
DTE/DCE
Trunking Considerations ISDN-PRI Applications
128ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Advantages of CBC Trunking
NETWORK-FACILITIES
Feature
Either a feature 0, or service
Network Facilities ISDN-PRI Applications
Trunk Group ISDN-PRI Trunk Applications
Coding
COR TAC
Options access, tie
Dial Access
Service
Service Type
Message Size
Send
Display/TCM
Max
SID?
Trunk Features
SID/ANI
134ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Application Example #1
Del
Application Example #2
Case
Insert
Per Call
SID/ANI
Application for Case 2 being selected
Application for Case 1 being selected most restrictive
Application for Case 3 being selected
Application for Case 4 being selected
138ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
PBX
Applications for Cases
Example Screen Entries for Cases
Trunk Group Usage Allocation ISDN-PRI Applications
Plan
140ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Usage
Allocation
An Example Application for Usage Allocation Plans
Min# Chan Max# Chan
CBC Trunk Group Usage Allocation Plan Assignment Schedule
142ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Fixed
Number Scheduled
75.Trunk Group Screen, Page 5 ISDN-PRI
Trunk Group Member Assignments ISDN-PRI Trunk Applications
SID Prefix
144ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Name Night
SID Prefix Table ISDN-PRI Applications
SID Prefix
Ext Code
An Example Application that uses SID
Routing Patterns ISDN-PRI Applications
146ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
FRL
Pattern
Number
Grp No
Inserted
148ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
No. Del
Digits
Hunt Group ISDN-PRI Applications
Band
ACD?
150ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Terminating Extension Group ISDN-PRI Applications
Hunt Group
Terminating Extension Group
152ADMINISTRATION Options and Requirements Generic
Generic 2 Maintenance Capabilities and Concerns
Generic 1 and Generic 2 ISDN-PRI Maintenance Philosophy
2MAINTENANCE and Alarms
Generic 2 Maintenance Procedures
Maintenance and Alarms
4MAINTENANCE and Alarms
Summary of Generic 2 Maintenance Capabilities
Generic 1 Maintenance Procedures
Generic 1 Maintenance Capabilities and Concerns
6MAINTENANCE and Alarms
Yellow LED
Summary of Generic 1 Maintenance Capabilities
Alarms
Circuit Pack Alarms
8MAINTENANCE and Alarms
Facility Alarms
Excessive Misframe and CRC Errors
LFA Alarm
Loss of Signal Alarm
Remote Frame Alarm
10MAINTENANCE and Alarms
Blue Alarm
Major and Minor Alarms
Framing Mode Alarm Type Conversion
Administration Requirements
Megacom COR
2ADMINISTRATION Requirements
PBX ID ACA
Administration Requirements
4ADMINISTRATION Requirements
DCS? PBX ID
Figure A-5.Trunk Group Screen, Page 1 SDN
Facilities, for details
6ADMINISTRATION Requirements
Dacs
TRANSLATIONS-BASED Problems
Transmission Facility
2SAMPLE Installation and Maintenance Problems
Trunks and Trunk Groups
Sample Installation and Maintenance Problems
Type
4SAMPLE Installation and Maintenance Problems
DS1 or DMI
CDMs
CEMs
System
6SAMPLE Installation and Maintenance Problems
D4-Channel Banks
Sample Installation Maintenance Problems
8SAMPLE Installation and Maintenance Problems
SYNCHRONIZATION-RELATED Problems
Leavenworth Loop
Loss of or No Synchronization
Figure B-10.Leavenworth Loop on the Primary Reference
D4 Synchronization Problems
Sample Installation and Maintenance Problems
12SAMPLE Installation and Maintenance Problems
Digital CO Synchronization Problems
Dacs
Figure B-15.Synchronization from Dacs Node
Typical Physical Interface Connection Problems
Initial System 85 DS1 or DMI Pinout for 50-PIN Connector
14SAMPLE Installation and Maintenance Problems
System Intracabinet
Installation Maintenance Problems
CABLE/CONNECTORS Initial or OLD PDS Compatible System
C6C To WIRE-LUGS
16SAMPLE Installation and Maintenance Problems
Specific Cabling Options
Permitted Cabling Combinations
18SAMPLE Installation and Maintenance Problems
Using cable GR-380
Permitted Cabling Combinations Using PDS
20SAMPLE Installation and Maintenance Problems
Permitted Cabling Combinations Using PDS
22SAMPLE Installation and Maintenance Problems
Voice
Procedure 000 Word 3 Generic 2 Only
2ADMINISTRATIVE Procedure Summary
Mode Voice Grade Data Unknown Digital Analog Mode 3/2
Isdn Routing Parameters System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Procedure 000 Word 4 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Procedure 010 Word 4 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Administrative Procedure Summary
BC System 85 R2V4 Only
4ADMINISTRATIVE Procedure Summary
Voice or Voice Grade Data
Procedure 100 Word 1 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Procedure 012 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
6ADMINSTRATIVE Procedure Summary
Procedure 100 Word 2 Generic 2 Only
Rules for Trunk Type 120 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Procedure
Procedure 100 Word 3 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
TCM
For international calls that is, a dial Calls For ARS calls
Procedure 107 Word 1 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
8ADMINISTRATIVE Procedure Summary
Called-Party Number IE System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Procedure 260 Word 1 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Procedure 108 Word 1 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Procedure 116 Word 1 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Procedure 210 Word 2 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
10ADMINISTRATIVE Procedure Summary
Procedure 280 Word 1 Generic 2 Only
Procedure 262 Word 3 Generic 2 Only
Procedure 275 Word 4 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Procedure 279 Word 1 Generic 2 Only
Information Element IE Name Opcode Value
12ADMINISTRATIVE Procedure Summary
IE Opcode Value
Information Element IE Name R2V4
Field 5, Network Service Value
Procedure 309 Word 5 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Field 4, Isdn Trunk Type
Megacom NSF
14ADMINISTRATIVE Procedure Summary
NSF IE System 85 R2V4
Through 288 Outwats Band NSFs SDN NSF
NSF IE Generic
Wats NSF Accunet via encode
BC System 85 R2V4 and Generic
16ADMINISTRATIVE Procedure Summary
Fields 6-10 System 85 R2V4
Procedure 354 Word 3 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Procedure 321 Word 5 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Field 6 Generic
18ADMINISTRATIVE Procedure Summary
Procedure 420 System 85 R2V4 & Generic
Administrative Procedure Summary
20ADMINISTRATIVE Procedure Summary
Trunk/Signaling Cross-references
Trunk Type and Signaling Type Compatibility Tables
Aplt
2TRUNK Type and Signaling Type Compatibility Tables
TIE
Trunk Type and Signaling Type Compatibility Tables
Wats
Did
MAIN/SAT
CAS
ISDN/PRI
NDM-I
R2V4 G2 Equiv Type Sig. Type
6TRUNK Type and Signaling Type Compatibility Tables
Trunk
EQU
Trunk Type and Signaling Type Compatibility Tables
ANN11
8TRUNK Type and Signaling Type Compatibility Tables
S BC BCC Bccos bps
AAR F T C Afrl Aiod ALU ANI ARS Autovon AVD AWG
CBC Ccitt CCR Ccsa CDM CEM COR COS CRC CSU
AB-2ABBREVIATIONS
Dacs dB
Abbreviations AB-3
AB-4ABBREVIATIONS
Adftc Afrl Aiod
Accunet
Megacom
Tandem
Data transmission
GL-2GLOSSARY
B8ZS
AWG
Ports, packet switching,
Binary service
Parameterized service format
Bit error rate Burstiness
Glossary GL-5
See network channel-terminating equipment
See cyclic redundancy check
Cross coupling
Unrestricted digital data
Q.931
DTE
Dnis
DMI-MOS
DS1
Epscs
GL-9
EIA
ETN
Hdlc
GRS
Inads
GL-12GLOSSARY
See Integrated Services Digital Network
Isdn network- See Isdn network identifier. service value
Clock reference
See loss of frame alignment
Loss of signal
Isdn SID-ANI Lata LFA
Station identification number
Ncte
Mpdm
Glossary GL-15
OPS OPX
Digital Network primary rate interface
Network primary rate interface
PRI
PAD
PAM PC/PBX
PCM PDM PDS
PCM
PAM
See Software Defined Network
Robbed-bit signaling
See remote frame alarm See Remote Group
SDN
SS7
Transport mode
Switch TMS
Multiplexed switch
See time-multiplexed switch
ZCS
Zero code
Adftc
Network 7-84,7-88nodal services
Accunet 6-3,C-16code
Equal 7-43,7-47,7-101,7-103ISDN
Violation 1-18,1-20,3-3
AVD 1-22,7-9
BC 1-22,C-16 BC code 7-23,7-81
Bccos 1-24,C-1
9delta
Ccitt
CEM
9bank D4 1-1,2-5D-type1-1
CRC 1-12,1-14CRV CSU xix, 1-20,3-2customer
COR 7-112,7-125,A-2
DCE 1-21,7-127D-channel
Index IN-5
NPA-NXX7-28,7-72
BOS
I -Contd BOS-Contd
EIA
IN-6 Index
DS1- Contd
DTE 2-18
FXS
D4 1-10,2-5,2-7
Index IN-7
Lapd 1-3,7-17LATA 2-7layer 1 1-3layer 2
IN-8 Index
LEC
Index IN-9
Misframe 1-11,1-14MO
Voice 1-23,7-33voice-grade data 1-23,1-24ZCS
CDM
Ncte
IN-10 Index
NPA-NNX C-17
Channel1-5,1-9,7-57facility 7-11,7-59
OPS
Ports 4-7,6-6
PCM 1-8,5-1PCM data
RNX 1-27robbed-bit signaling
9sources
SS7 7-30,7-88
Index IN-13
CEM 2-10terminating
IN-14 Index
TMS
108
CO 2-8,7-13combination tie 2-5,6-4DID 6-11,7-13
FX 2-8,7-13ground-start CO 6-11group
Members 7-35,7-92Generic 1
IN-16 Index