Handbook for
across the aperture of your telescope and point the instrument high in the sky, to avoid any gradient in the light near the horizon. Now take several images with exposure times adjusted to give a bright, but not overloaded, picture. Averaging flat field together is a good way to reduce their noise contribution and so recording 4, or more, images is a good idea.
To use your flat fields, they must first have a dark frame subtracted. Although this may appear to be unimportant with such brightly lit and short exposures, there is the ‘bias offset’ of the camera in each image and this can produce an error in the final correction. As we are mainly interested in the bias, any very short exposure dark frame will give a good result. The dark subtracted images should then be averaged together before use.
After the above procedures have been executed, the flat field will be ready for use. Load up your image for processing, subtract the dark frame and then select ‘Apply flat field’ in the ‘Merge’ menu. The result should be an image with very little sign of the original artefacts.
********************************************************************
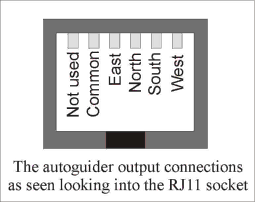
The accessory ports
The
The high density parallel port socket provides both control and power for the
Using the built-in serial ports
The
20