Installation (continued)
8.Install branch circuit wires
Determine the proper wire size for each branch circuit using the guidelines in step 4. Verify that the standard 15 ampere circuit breakers installed in the panel are large enough for each branch circuit. Remove and replace with a higher amperage any that are undersized.
Connect the positive (red) branch circuit wires to the load terminals of each circuit breaker.
Connect each negative (black or yellow) branch circuit wire to the DC negative bus. DO NOT CONFUSE THE DC NEGATIVE BUS WITH THE DC GROUNDING BUS.
9.Optional - install grounding system wire
The grounding wire (bare, green or green with yellow stripe and normally
In Boatowner’s Illustrated Handbook of Wiring, Charlie Wing identifies three purposes of DC grounding:
1.Holding conductive housings of low voltage (under 50 volts) DC devices at ground potential by providing a low resistance return path for currents accidentally coming into contact with the device cases.
2.Providing a low resistance return path for electrical current, preventing stray currents that may cause corrosion.
3.Grounding metal electrical cases to prevent emission from inside or absorption from outside of radio frequency interference (RFI).
ABYC requires that grounding wires be sized no smaller than one wire size under that required for current carrying conductors supplying the device to which the grounding wire is connected.
A full treatment of this subject is not possible within the scope of these instructions and there is controversy surrounding the general subject of DC bonding, of which DC grounding is a component. It is suggested that installers not familiar with this subject consult one of the reference books listed elsewhere in these instructions.
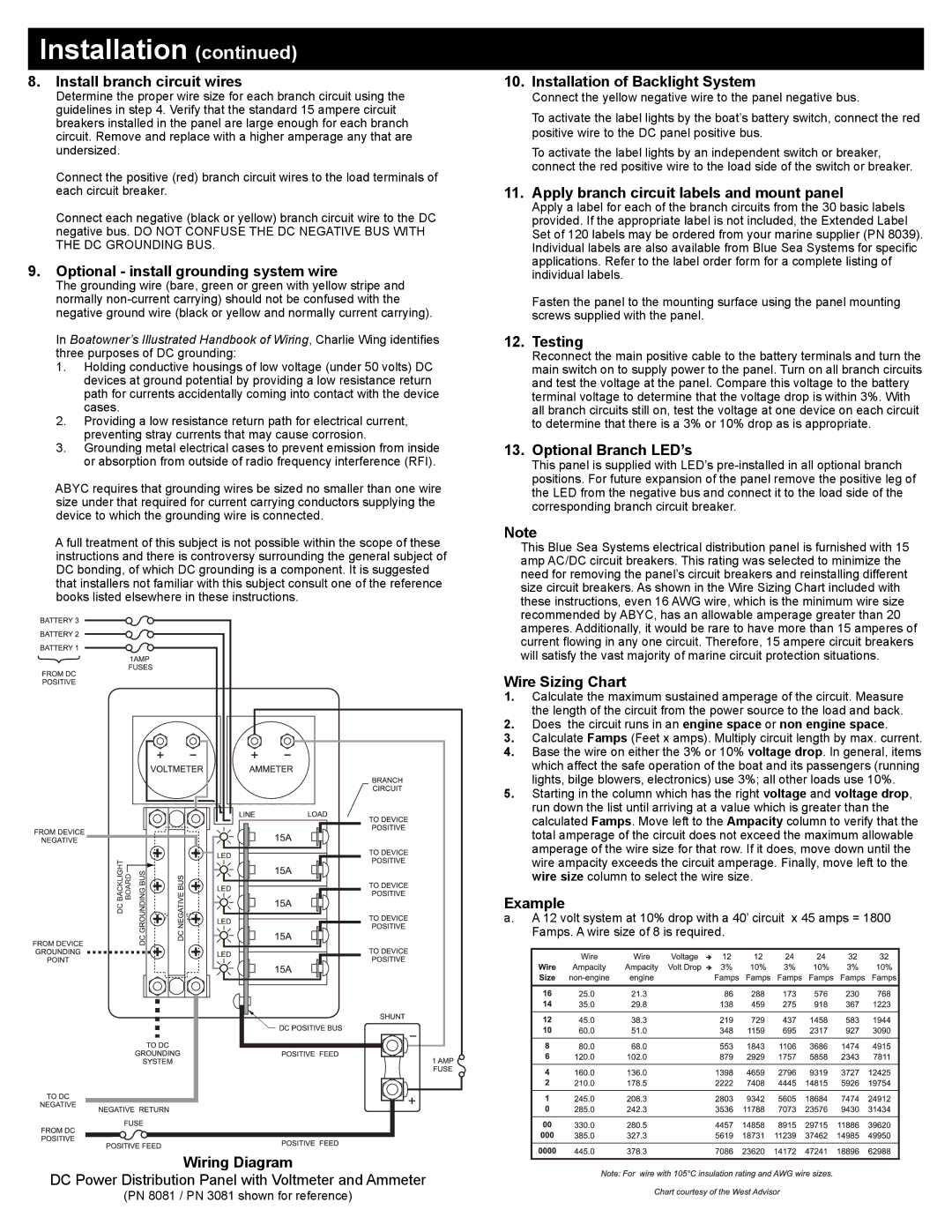
Wiring Diagram
DC Power Distribution Panel with Voltmeter and Ammeter
10. Installation of Backlight System
Connect the yellow negative wire to the panel negative bus.
To activate the label lights by the boat’s battery switch, connect the red
positive wire to the DC panel positive bus.
To activate the label lights by an independent switch or breaker, connect the red positive wire to the load side of the switch or breaker.
11. Apply branch circuit labels and mount panel
Apply a label for each of the branch circuits from the 30 basic labels provided. If the appropriate label is not included, the Extended Label Set of 120 labels may be ordered from your marine supplier (PN 8039). Individual labels are also available from Blue Sea Systems for specific applications. Refer to the label order form for a complete listing of individual labels.
Fasten the panel to the mounting surface using the panel mounting screws supplied with the panel.
12. Testing
Reconnect the main positive cable to the battery terminals and turn the main switch on to supply power to the panel. Turn on all branch circuits and test the voltage at the panel. Compare this voltage to the battery terminal voltage to determine that the voltage drop is within 3%. With all branch circuits still on, test the voltage at one device on each circuit to determine that there is a 3% or 10% drop as is appropriate.
13. Optional Branch LED’s
This panel is supplied with LED’s
Note
This Blue Sea Systems electrical distribution panel is furnished with 15 amp AC/DC circuit breakers. This rating was selected to minimize the need for removing the panel’s circuit breakers and reinstalling different size circuit breakers. As shown in the Wire Sizing Chart included with these instructions, even 16 AWG wire, which is the minimum wire size recommended by ABYC, has an allowable amperage greater than 20 amperes. Additionally, it would be rare to have more than 15 amperes of current flowing in any one circuit. Therefore, 15 ampere circuit breakers will satisfy the vast majority of marine circuit protection situations.
Wire Sizing Chart
1.Calculate the maximum sustained amperage of the circuit. Measure the length of the circuit from the power source to the load and back.
2.Does the circuit runs in an engine space or non engine space.
3.Calculate Famps (Feet x amps). Multiply circuit length by max. current.
4.Base the wire on either the 3% or 10% voltage drop. In general, items which affect the safe operation of the boat and its passengers (running lights, bilge blowers, electronics) use 3%; all other loads use 10%.
5.Starting in the column which has the right voltage and voltage drop, run down the list until arriving at a value which is greater than the calculated Famps. Move left to the Ampacity column to verify that the total amperage of the circuit does not exceed the maximum allowable amperage of the wire size for that row. If it does, move down until the wire ampacity exceeds the circuit amperage. Finally, move left to the wire size column to select the wire size.
Example
a.A 12 volt system at 10% drop with a 40’ circuit x 45 amps = 1800 Famps. A wire size of 8 is required.
(PN 8081 / PN 3081 shown for reference)