2610003213
Assembly
Preparing the Saw
BLADE SELECTION
No one blade can be efficient on all cutting jobs. Different materials require specially designed blades. Since your reciprocating saw can cut so many materials, many types of BOSCH blades are available. Be sure to use the proper blade to insure proper cutting performance.
INSTALLING A BLADE
!WARNING Disconnect battery pack from tool before making
any assembly, adjustments or changing accessories.
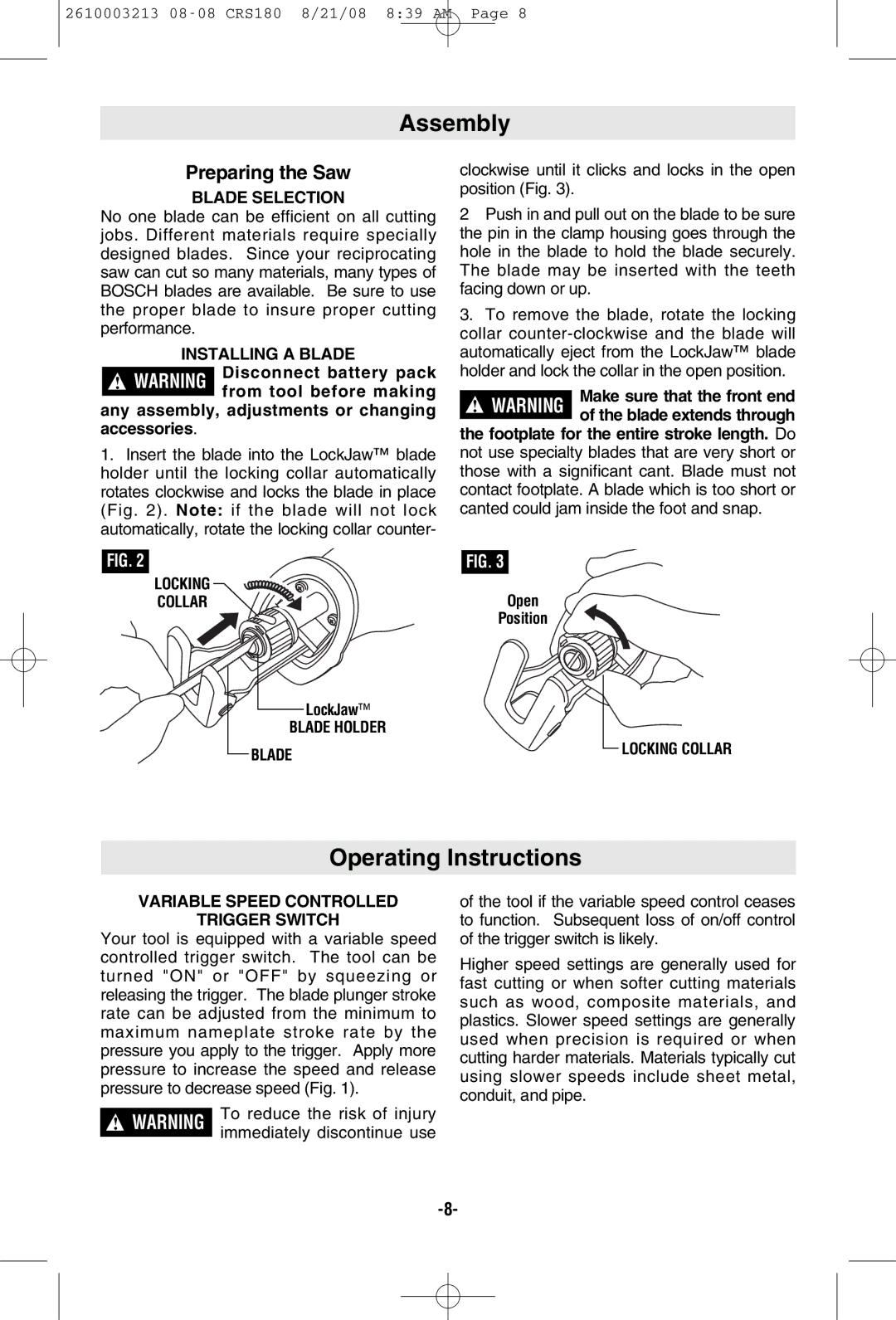
1.Insert the blade into the LockJaw™ blade holder until the locking collar automatically rotates clockwise and locks the blade in place (Fig. 2). Note: if the blade will not lock automatically, rotate the locking collar counter-
clockwise until it clicks and locks in the open position (Fig. 3).
2Push in and pull out on the blade to be sure the pin in the clamp housing goes through the hole in the blade to hold the blade securely. The blade may be inserted with the teeth facing down or up.
3.To remove the blade, rotate the locking collar
!Make sure that the front end WARNING of the blade extends through
the footplate for the entire stroke length. Do not use specialty blades that are very short or those with a significant cant. Blade must not contact footplate. A blade which is too short or canted could jam inside the foot and snap.
FIG. 2 | FIG. 3 |
LOCKING | Open |
COLLAR | |
| Position |
LockJaw™
BLADE HOLDER
BLADE
LOCKING COLLAR
Operating Instructions
VARIABLE SPEED CONTROLLED
TRIGGER SWITCH
Your tool is equipped with a variable speed controlled trigger switch. The tool can be turned "ON" or "OFF" by squeezing or releasing the trigger. The blade plunger stroke rate can be adjusted from the minimum to maximum nameplate stroke rate by the pressure you apply to the trigger. Apply more pressure to increase the speed and release pressure to decrease speed (Fig. 1).
!WARNING To reduce the risk of injury immediately discontinue use
of the tool if the variable speed control ceases to function. Subsequent loss of on/off control of the trigger switch is likely.
Higher speed settings are generally used for fast cutting or when softer cutting materials such as wood, composite materials, and plastics. Slower speed settings are generally used when precision is required or when cutting harder materials. Materials typically cut using slower speeds include sheet metal, conduit, and pipe.