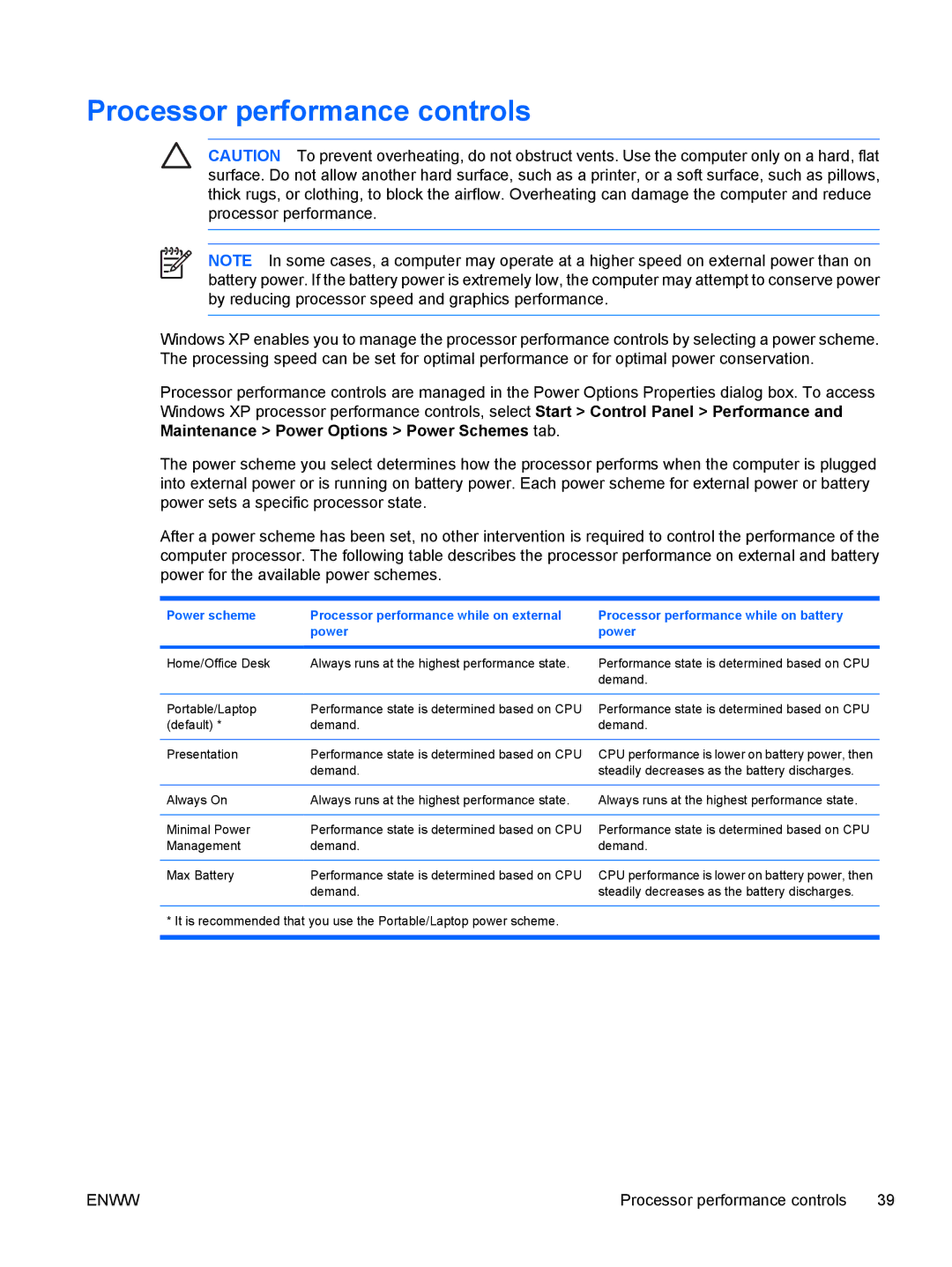
C318LA, C310EU, C350EU, C302NR, C300EU specifications
The HP C305LA, C310EA, C399XX, C300, and C303NR are part of HP's diverse lineup of laptops, catering to different user needs with their unique features and specifications. Each model offers a blend of power, performance, and portability, making them suitable for various applications, from casual use to more demanding tasks.Starting with the HP C305LA, this model is a well-rounded laptop that targets the everyday user with solid performance and reliable functionality. It features a powerful Intel processor, ensuring that multitasking and routine applications run smoothly. With its vibrant display and integrated graphics, the C305LA is suitable for streaming media and light gaming. Additionally, it boasts a durable design, making it an excellent choice for students and professionals who require a dependable machine for daily use.
Next, the HP C310EA brings a bit more to the table with its enhanced specifications. It is equipped with an upgraded processor, providing users with faster performance and improved efficiency. The C310EA also features an ergonomic keyboard and a spacious touchpad, providing an enhanced user experience for both typing and navigation. With its increased storage capacity, users can store their files, documents, and media without worrying about running out of space.
The C399XX stands out with its sleek design and portability. This model is ideal for users on the go, featuring a lightweight chassis and a dependable battery life. Performance-wise, the C399XX comes with advanced technology that supports robust applications, thus catering to creative professionals and casual users alike. The high-definition display ensures clear and vibrant visuals, making it perfect for multimedia consumption.
Meanwhile, the HP C300 is tailored for budget-conscious consumers who still require functionality. Equipped with essential features, the C300 is designed for basic tasks like web browsing, document editing, and media playback. Its compact design makes it easy to take anywhere, while its reliable performance ensures that common usage scenarios are adequately covered.
Finally, the HP C303NR offers a balance of performance and affordability, making it a great option for students and families. This model provides good processing power coupled with sufficient RAM, allowing for smooth operation of everyday software. The C303NR's long-lasting battery life appeals to users who require extended usability without frequent recharging.
In conclusion, the HP C305LA, C310EA, C399XX, C300, and C303NR each present a variety of features tailored to meet diverse user needs. Whether for personal, educational, or professional use, these models highlight HP's commitment to providing reliable and innovative computing solutions.