Your HTC Aria
User guide
Choose a rate plan wisely
Charge the battery
Before you do anything else, please read this
Know about privacy laws
Trademarks and copyrights
Conventions used in this guide
Contents
Phone calls
People
Messages
Setting text and multimedia message options
Keyboard
Accounts and sync
Social
Calendar 108
Clock and Weather 117
Internet 126
Bluetooth 139
Camera 145
Photos 153
Music 160
Maps and location 165
More apps 176
Settings 193
Security 191
Update and reset 202
Specifications 204 Index 205
Your Phone
Basics
Inside the box
Front panel
Back panel
Home
Top panel
Left panel
Bottom panel
Removing the back cover
Before turning on your phone
Back cover
Replacing the back cover
SIM card
Storage card
Battery
Inserting the battery
Inserting the storage card
Removing the battery
Charging the battery
Finger gestures
Turning on your phone
Setting up your phone for the first time
Getting started
Turning off your phone
Basics
Waking up from Sleep mode
Sleep mode
Switching to Sleep mode
Unlocking the screen
Navigating the Home screen
Home screen
Extended Home screen
Directly going to a particular screen
Phone status and notifications
Phone status icons
Notification icons
Basics
Checking notifications
Opening the Notifications panel
Closing the Notifications panel
Adjusting the volume
Adjusting the ringer volume
Adjusting the media volume
Connecting your phone to a computer
Copying files to and from the storage card
Setting Web and Quick Search Box options
Searching the Web and your phone using the Quick Search Box
Searching your phone and the Web
Personalizing
Making your phone truly yours
Changing the ringtone
Customizing and saving a scene
Using a preset scene
Personalizing your phone with scenes
Renaming or deleting a scene
Changing your wallpaper
Changing your Home screen or lock screen wallpaper
Personalizing your Home screen with widgets
Adding a widget to your Home screen
Downloading HTC widgets
Personalizing
Adding folders on your Home screen
Creating a new folder and adding items to it
Renaming a folder
Moving a widget or icon
Removing a widget or icon
Making calls
Calling somebody using your phone
Phone calls
Smart Dial
Calling a phone number in an email
Calling a speed dial number
Calling a phone number in a text message
Adding a contact to speed dial
Making an emergency call
Receiving calls
Answering an incoming call
Muting the ringing sound without rejecting the call
Editing the default message
Rejecting an incoming call
Rejecting a call and sending a text message
Using in-call options
Handling multiple calls
Muting the microphone during a call
Setting up a conference call
Putting a call on hold
Turning the speakerphone on or off during a call
Using call history
Adding a new phone number to your contacts from call history
Checking a missed call
Clearing the call history list
Call services
Turning Airplane mode on or off
People
About People
Ways of getting contacts into your phone
Setting up My contact card
People screen
Your contacts list
Adding a new contact
Merging contact information
Importing contacts from your SIM card
Importing contacts from online directories
Manually merging contact information
Backing up your contacts to the storage card
Editing a contact’s information
Searching for a contact
Importing contacts from the storage card
Deleting contacts
Sending contact information as a vCard via MMS
Sending your contact information as a vCard via MMS
Deleting a group
Contact groups
Creating a group and adding contacts
Adding or removing contacts from a group
Sending an SMS/MMS message or email to a group
Contact information and conversations
People widget
Setting the default communication method
Changing the default communication method
Adding the People widget
Keyboard
Using the onscreen keyboard
Using the landscape onscreen keyboard
Changing the onscreen keyboard layout
Entering text
Entering words with predictive text
Adding a word to the predictive text dictionary
Editing or deleting a word in the user dictionary
Adjusting touch input settings
Text input
Phone keypad & compact Qwerty
Other settings
Finger touch precision
Sending text and multimedia messages
Messages
About Messages
Sending a text message
Sending a multimedia MMS message
Saving and resuming a draft message
New message notifications
WAP push messages
Opening the link contained in a WAP push message
Viewing all your WAP push messages
Viewing a multimedia message
Managing message conversations
Reading a text message
Replying to a text or multimedia message
Deleting several message threads
Protecting a message from deletion
Deleting a message thread
Deleting a single message
MMS settings
Setting text and multimedia message options
SMS settings
Received messages
Adding the Messages widget
Sent messages
Adding a social network account
Accounts and sync
Synchronizing with online accounts
Synchronizing with a Google Account
Synchronizing with a Microsoft Exchange ActiveSync account
Changing general sync settings
Changing account settings
Managing your accounts
Removing an account
Using HTC Sync
Setting up HTC Sync to recognize your phone
Setting up synchronization
Setting up more sync options
Synchronizing your phone with your computer automatically
Downloading the latest HTC Sync upgrade
Synchronizing your phone
Synchronizing your phone with your computer manually
Installing apps from your computer to your phone
Using the Facebook application
Social
Facebook for HTC Sense
Adding the Facebook widget
Twittering on your phone
Peep screen
Sending a tweet
Sending a direct message
Setting Peep options
Searching for Twitter users to follow
Unfollowing a Twitter user
Adding the Twitter widget
Using Friend Stream
Friend Stream screen
Updating your status
Adding the Friend Stream widget
Chatting in Google Talk
Signing in to Google Talk
Chatting with friends
Changing your online status and picture
Managing your Friends list
Making a friend popular
Changing Google Talk settings
Setting notifications for new Google Talk messages
Blocking a friend
Showing or hiding the mobile indicator to friends
Setting whether you sign into Google Talk automatically
Using Gmail/Google Mail
Viewing your Gmail/Google Mail inbox
Switching to another Google Account
Reading your messages
Replying to or forwarding an email message
Muting a conversation
Reporting a conversation as spam
Sending a message
Adding a signature to your messages
Managing conversations and messages
Changing Gmail/Google Mail settings
Changing Gmail/Google Mail synchronization settings
Working with conversations in batches
Page
Mail
Adding a POP3/IMAP email account
Viewing your email inbox
Sorting email messages
Inbox filter tabs
Refreshing an email account
Deleting an email message
Exchange ActiveSync email
Setting out of the office status
Setting the priority for an email message
Sending a meeting request
Composing and sending an email message
Deleting an email account
Editing email account settings
Viewing and replying to an email message
Adding the Mail widget
Calendar
About Calendar
Creating a calendar event
Inviting guests to your event Google Account only
Set the reminder time
Changing calendar views
Month view
Day and Agenda views
Week view
Viewing, editing or deleting an event
Viewing and editing an event
Deleting an event
Calendar event reminders
Viewing, dismissing, or snoozing event reminders
Stop synchronizing a Google Calendar
Displaying and synchronizing calendars
Showing or hiding calendars
Adding a Google Calendar to sync with
Changing Calendar settings
Reminder settings
Calendar view settings
Sending a vCalendar
About the Calendar widget
Clock and Weather
About the HTC Clock widget
About the Clock application
Using Desk Clock
Using World Clock
Setting your home city
Setting the time zone, date, and time
Adding a city to the World Clock screen
Setting the alarm clock
Setting an alarm
Deleting an alarm
Changing alarm sound settings
Checking weather
Adding a city to the Weather screen
Deleting cities from the Weather screen
About the Weather widget
Changing the order of cities on the Weather screen
Changing weather options
Internet
Data connection
Wi-Fi
Turning Wi-Fi on and connecting to a wireless network
Connecting to a Wi-Fi network with EAP-TLS security
Checking the wireless network status
Connecting to another Wi-Fi network
Adding the Data connection and Wi-Fi widgets
Setting up secure credential storage
Connecting to a virtual private network VPN
Connecting to a VPN
Preparing your phone for VPN connection
Disconnecting from a VPN
Opening the browser
Using your phone’s web browser
Setting your home
Going to a web
Browsing full versions of all web sites
Navigating on a web
Zooming in or out on a web
Selecting a link in a web
Opening a new browser window
Downloading applications from the web
Switching between browser windows
Finding text within a web
Viewing your downloads
Copying text, looking up information, and sharing
Selecting text
Viewing bookmarks and previously visited pages
Setting browser options
Turning Bluetooth on or off
Bluetooth
Using Bluetooth
Changing the phone name
Connecting a Bluetooth headset or car kit
Reconnecting a headset or car kit
Disconnecting or unpairing from a Bluetooth device
Disconnecting a Bluetooth device
Unpairing from a Bluetooth device
Sending and receiving information using Bluetooth
Receiving information from another device
Adding the Bluetooth received folder to the Home screen
Camera
Camera basics
Viewfinder screen
Using the optical trackball as the shutter release
Review screen
Zooming
Taking a photo
Capturing a video
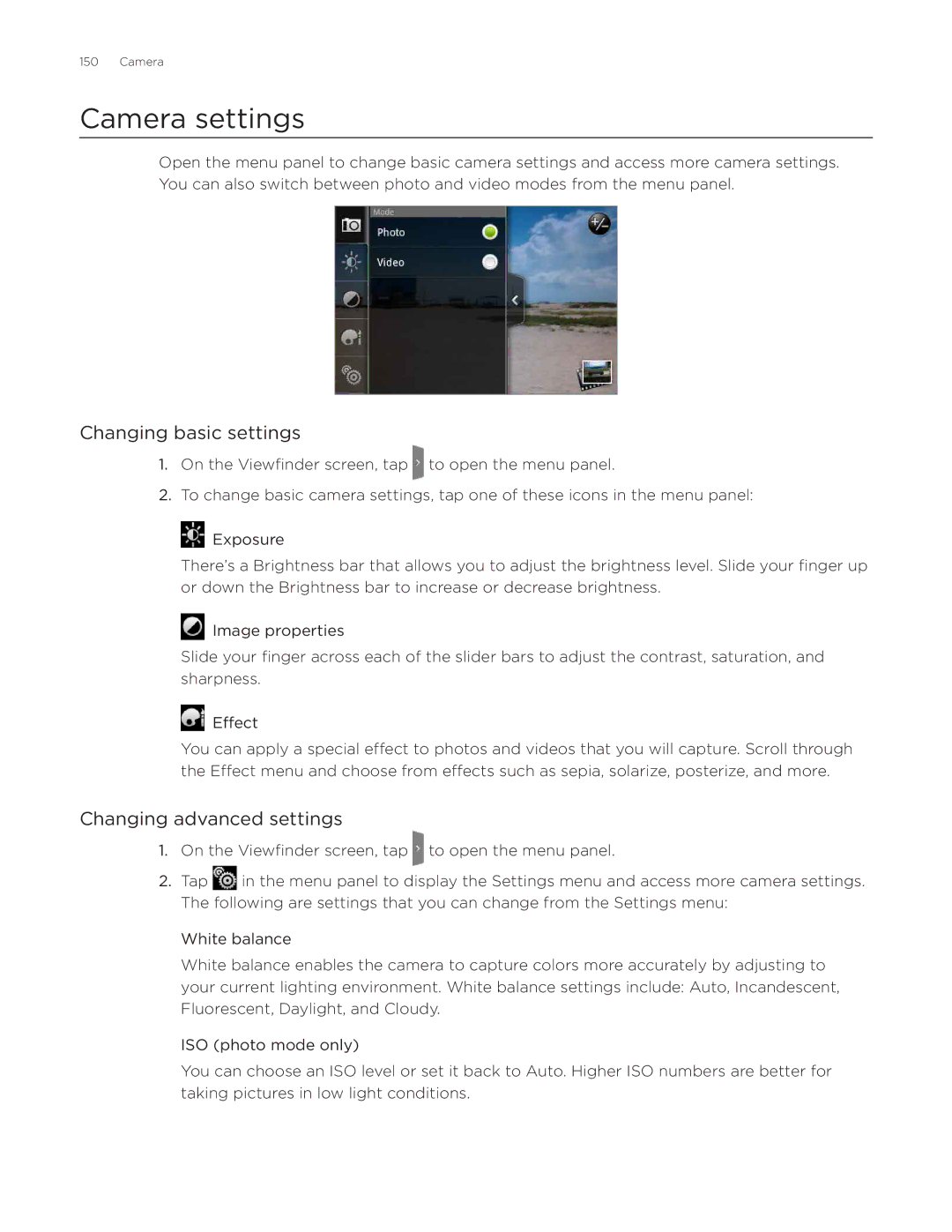
Camera settings
Changing basic settings
Changing advanced settings
Camera
Camera
Photos
About the Photos application
Selecting an album
Viewing photos and videos
Browsing in filmstrip or grid view
Viewing a photo in landscape orientation
Zooming in or out on a photo
Watching video
Viewing photos in your social networks
Viewing photos on Facebook
Viewing photos on Flickr
Working with photos
Rotating and saving a photo
Cropping a photo
Sending photos or videos by email
Sending photos or videos using Bluetooth
Sharing
Sending a photo or video by MMS
Sharing photos on Picasa
Sharing photos on Facebook
Sharing photos on Flickr
Sharing videos on YouTube
Music
About the Music application
Playing music
Browsing music in the Library
Managing playlists
Creating a playlist
Playing the songs in a playlist
Adding more songs to a playlist
Rearranging songs in a playlist
Deleting songs from a playlist
Deleting playlists
About the Music widget
Setting a song as ringtone
Sending music using Bluetooth
Checking if the song was added as a ringtone
Using Google Maps
Maps and location
Viewing locations
Looking at a location in Street View
Clearing the map
Viewing map layers
Searching for a location
Tap . The search results are displayed on the map
Getting directions
Joining Latitude
Inviting friends to share their locations
Responding to an invitation
Connecting with and managing friends
Viewing your friends’ locations
Changing privacy settings
Using HTC Footprints
Creating a footprint
Revisiting a footprint
Editing or deleting a footprint
Exporting your footprints
Importing footprints
Adding the Footprints widget
Watching videos
More apps
Watching videos on YouTube
Searching for videos
Sharing a video link
Capturing a video and sharing it on YouTube
More apps
Viewing documents, presentations, and spreadsheets
Changing the stock list order
Keeping track of your stocks
Adding a stock quote or stock market index
Deleting stock quotes and indices
Setting stock information update frequency
Manually updating stock information
Adding the Stocks widget
Listening to the radio
Listening to an FM station
Adding station names
Minimizing or turning off FM Radio
Recording your voice
Setting a voice clip as a ringtone
Recording your voice
Sharing a voice clip
Finding and installing apps from Android Market
Finding and installing an application
Creating a Google Checkout account
Requesting a refund for an application
Opening an installed application
Uninstalling an application
Getting help
Reading news feeds
News screen
Subscribing to a news channel from a list
Reading a story
Setting update frequency for stories
Subscribing to a news channel by entering a URL
Starring a story
Adding a keyword
Adding the News widget
Security
Protecting your SIM card with a PIN
Restoring a SIM card that has been locked out
Protecting your phone with a screen lock
Settings
Settings on your phone
Settings
Changing display settings
Switching animation effects on or off
Enabling or disabling touch tones
Changing sound settings
Setting a sound profile
Choosing the notification sound
Changing the phone language
Optimizing your phone’s battery life
Checking the power usage of applications
Managing memory
Checking information about your phone
Update and reset
Checking for phone system software updates manually
Updating your phone’s system software
Performing a hard/factory reset
Performing a factory reset via settings
Performing a factory reset using phone buttons
Specifications
GPS
Symbols
Index
Index
Index