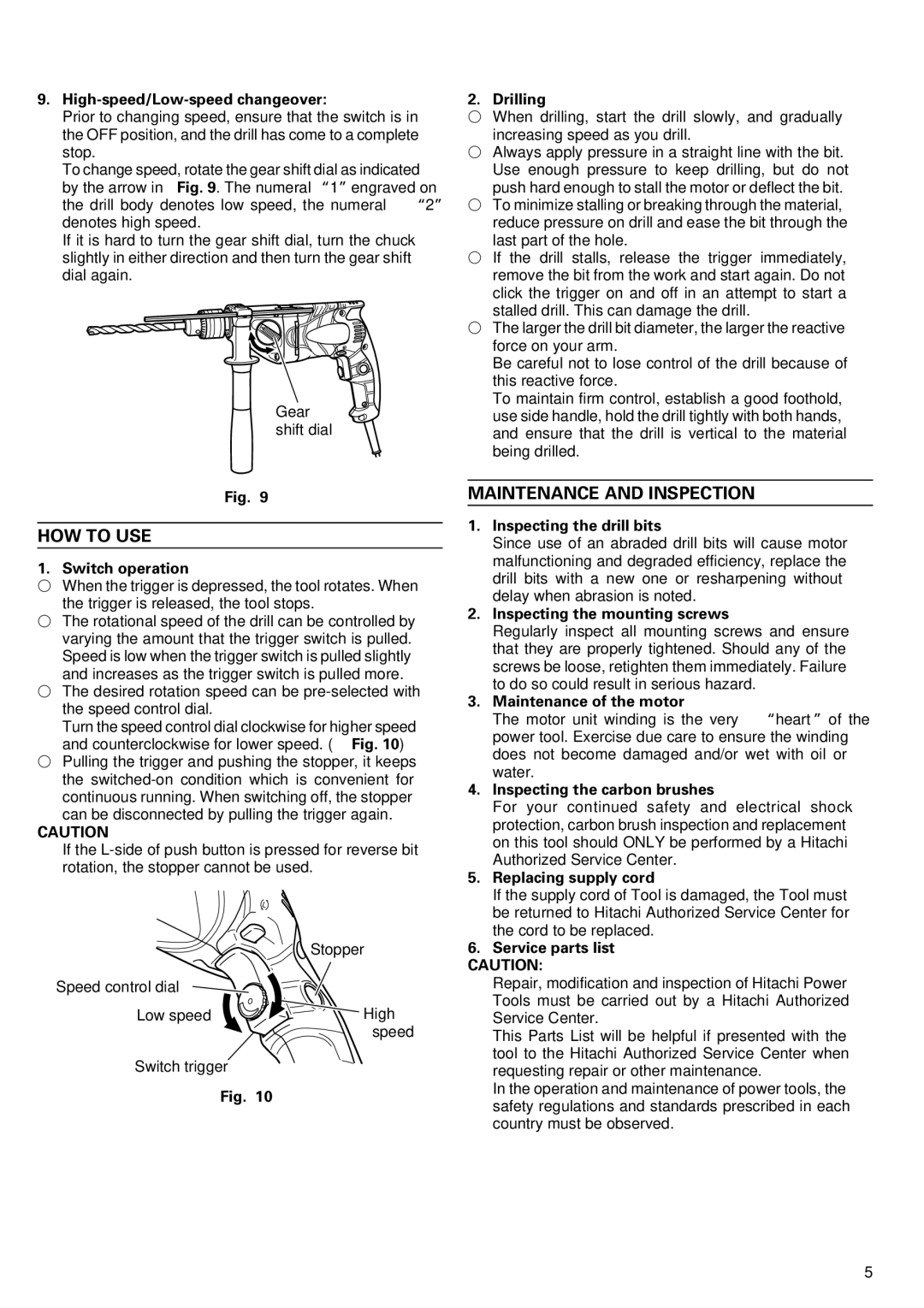
9.High-speed/Low-speed changeover:
Prior to changing speed, ensure that the switch is in the OFF position, and the drill has come to a complete stop.
To change speed, rotate the gear shift dial as indicated by the arrow in Fig. 9. The numeral “1” engraved on the drill body denotes low speed, the numeral “2” denotes high speed.
If it is hard to turn the gear shift dial, turn the chuck slightly in either direction and then turn the gear shift dial again.
Gear shift dial
Fig. 9
HOW TO USE
1. Switch operation
◯When the trigger is depressed, the tool rotates. When the trigger is released, the tool stops.
◯The rotational speed of the drill can be controlled by varying the amount that the trigger switch is pulled. Speed is low when the trigger switch is pulled slightly and increases as the trigger switch is pulled more.
◯The desired rotation speed can be
Turn the speed control dial clockwise for higher speed and counterclockwise for lower speed. (Fig. 10)
◯Pulling the trigger and pushing the stopper, it keeps the
can be disconnected by pulling the trigger again.
CAUTION
If the
| Stopper |
Speed control dial |
|
Low speed | High |
| speed |
Switch trigger |
|
Fig. | 10 |
2. Drilling
◯When drilling, start the drill slowly, and gradually increasing speed as you drill.
◯Always apply pressure in a straight line with the bit. Use enough pressure to keep drilling, but do not push hard enough to stall the motor or deflect the bit.
◯To minimize stalling or breaking through the material, reduce pressure on drill and ease the bit through the last part of the hole.
◯If the drill stalls, release the trigger immediately, remove the bit from the work and start again. Do not click the trigger on and off in an attempt to start a stalled drill. This can damage the drill.
◯The larger the drill bit diameter, the larger the reactive force on your arm.
Be careful not to lose control of the drill because of this reactive force.
To maintain firm control, establish a good foothold, use side handle, hold the drill tightly with both hands, and ensure that the drill is vertical to the material being drilled.
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
1.Inspecting the drill bits
Since use of an abraded drill bits will cause motor malfunctioning and degraded efficiency, replace the drill bits with a new one or resharpening without delay when abrasion is noted.
2.Inspecting the mounting screws
Regularly inspect all mounting screws and ensure that they are properly tightened. Should any of the screws be loose, retighten them immediately. Failure to do so could result in serious hazard.
3.Maintenance of the motor
The motor unit winding is the very “heart” of the power tool. Exercise due care to ensure the winding does not become damaged and/or wet with oil or water.
4.Inspecting the carbon brushes
For your continued safety and electrical shock protection, carbon brush inspection and replacement on this tool should ONLY be performed by a Hitachi Authorized Service Center.
5.Replacing supply cord
If the supply cord of Tool is damaged, the Tool must be returned to Hitachi Authorized Service Center for the cord to be replaced.
6.Service parts list
CAUTION:
Repair, modification and inspection of Hitachi Power Tools must be carried out by a Hitachi Authorized Service Center.
This Parts List will be helpful if presented with the tool to the Hitachi Authorized Service Center when requesting repair or other maintenance.
In the operation and maintenance of power tools, the safety regulations and standards prescribed in each country must be observed.
5