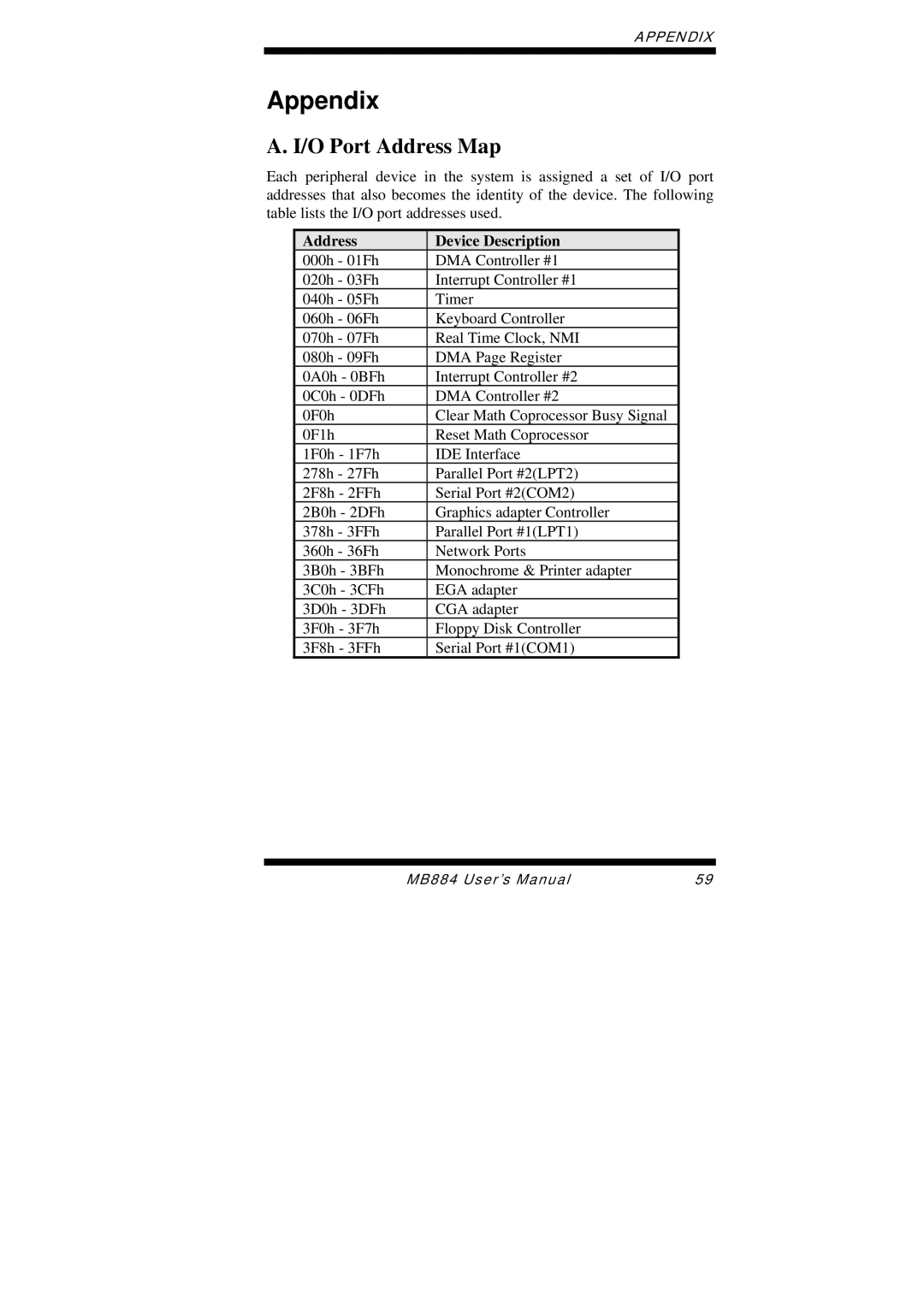
MB884 specifications
The Intel MB884 is a versatile and efficient microcontroller that has garnered attention for its range of features and innovative technologies. Built to enhance various applications, the MB884 microcontroller is particularly favored in automotive, industrial, and consumer electronics domains.One of the standout features of the Intel MB884 is its robust architecture. It integrates a high-performance CPU that supports various instruction sets, allowing for flexibility in programming and application development. The microcontroller typically operates at clock speeds that facilitate swift processing capabilities, crucial for real-time applications.
The MB884 comes equipped with a range of input/output interfaces, which enable seamless communication with peripheral devices. This includes support for serial communication protocols such as SPI, I2C, and UART. These features allow developers to connect sensors, displays, and other components effortlessly, simplifying the design of complex systems.
In terms of memory, the MB884 includes both volatile and non-volatile options, providing developers with ample space for code and data storage. This dual-memory approach ensures that critical data is preserved during power outages or system resets, making it a reliable choice for long-term applications.
Additionally, the MB884 microcontroller integrates various built-in peripherals, which can include analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), timers, and PWM outputs. These components reduce the need for external chips, resulting in cost savings and a more compact design. The inclusion of high-resolution ADCs is particularly useful for gathering precise sensor data, essential in applications requiring accurate measurements.
Another key characteristic of the Intel MB884 is its power management features. The microcontroller is designed to operate efficiently, with low power modes that can significantly extend the battery life of portable devices. This energy efficiency is critical in industries where sustainability and energy conservation are priorities.
Moreover, the Intel MB884 is supported by a range of development tools and software, making it easier for engineers to prototype and implement their designs. Comprehensive documentation and community support further enhance the user experience, empowering developers to leverage the full potential of this microcontroller.
In summary, the Intel MB884 microcontroller stands out for its robust performance, versatile features, and efficiency. With its comprehensive set of peripherals, flexible communication interfaces, and strong power management capabilities, it remains a top choice for engineers looking to build innovative and efficient electronic systems. As technology continues to evolve, the MB884 is likely to maintain its relevance in the ever-growing field of microcontroller applications.