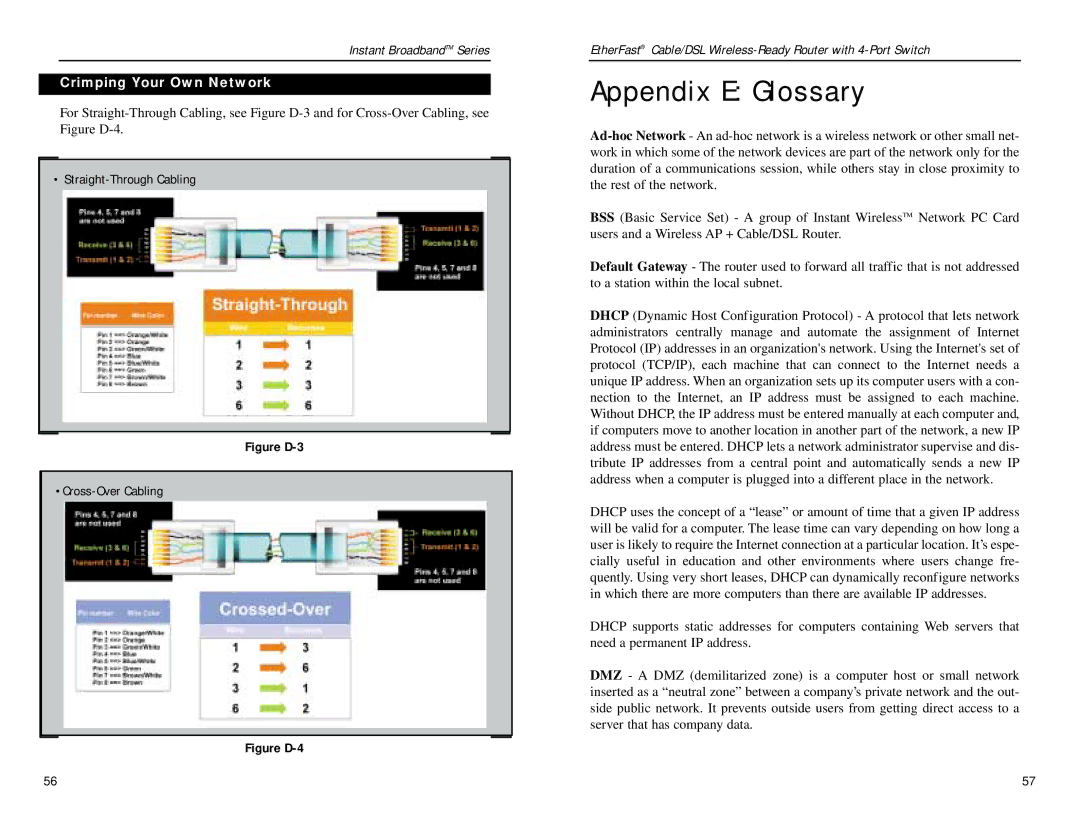
BEFSR41W specifications
The Linksys BEFSR41W is a versatile wireless broadband router that has been a popular choice for both home and small office environments since its introduction. Designed to offer reliable internet connectivity, the BEFSR41W combines wired and wireless capabilities, ensuring that users can connect multiple devices efficiently.One of the standout features of the Linksys BEFSR41W is its integrated 4-port 10/100 Ethernet switch, which allows users to connect their wired devices directly. This is particularly useful for users who require stable connections for activities such as gaming or streaming high-definition content. The router supports the IEEE 802.3 and 802.3u standards, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of devices.
In terms of wireless capabilities, the BEFSR41W operates on the 802.11b and 802.11g standards, providing maximum wireless data rates of up to 54 Mbps. This enables users to experience reasonably fast wireless internet speeds for everyday online activities such as browsing and emailing. The router's built-in antenna offers decent coverage, making it suitable for smaller homes and office spaces.
Security is a key consideration for any network device, and the Linksys BEFSR41W incorporates several features to help safeguard users' data. It supports Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) encryption methods, allowing users to set up secure connections and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Additionally, the router includes a built-in firewall to help prevent external attacks and threats.
Another significant characteristic of the BEFSR41W is its easy setup process. The router comes with a user-friendly web-based interface that simplifies the configuration process. Users can easily set up their network, configure security settings, and manage connected devices without needing specialized technical skills.
Additionally, the router is designed for longevity, with robust build quality ensuring reliability over time. It is also backward compatible with older wireless standards, which provides flexibility for users who have legacy devices in their network.
In conclusion, the Linksys BEFSR41W is a solid option for anyone seeking a dependable routing solution that balances both wired and wireless connectivity. With its blend of features, ease of use, and security options, it remains a relevant choice for users looking to establish a basic home or small office network.