Chapter 2 GETTING STARTED
POWER REQUIREMENTS:
The RS232/RS485 Converter can be powered using any voltage less than 32 volts. The converter consumes 75 mA. From the converter, a 6 wire line carries the data to and from the remote stations. Two wires send data, two wires receive data, one additional line is connected to the computer's ground and one wire is connected to the power supply input (before the converter's voltage regulator). This way, unregulated power can be carried to the remote stations.
The RS232/RS485 converter is NOT optoisolated. Optoisolation must be provided independently in each station along the network as is the case with the RS485 Data Acquisition and Control line of boards.
LINE CONNECTIONS AND TERMINATION:
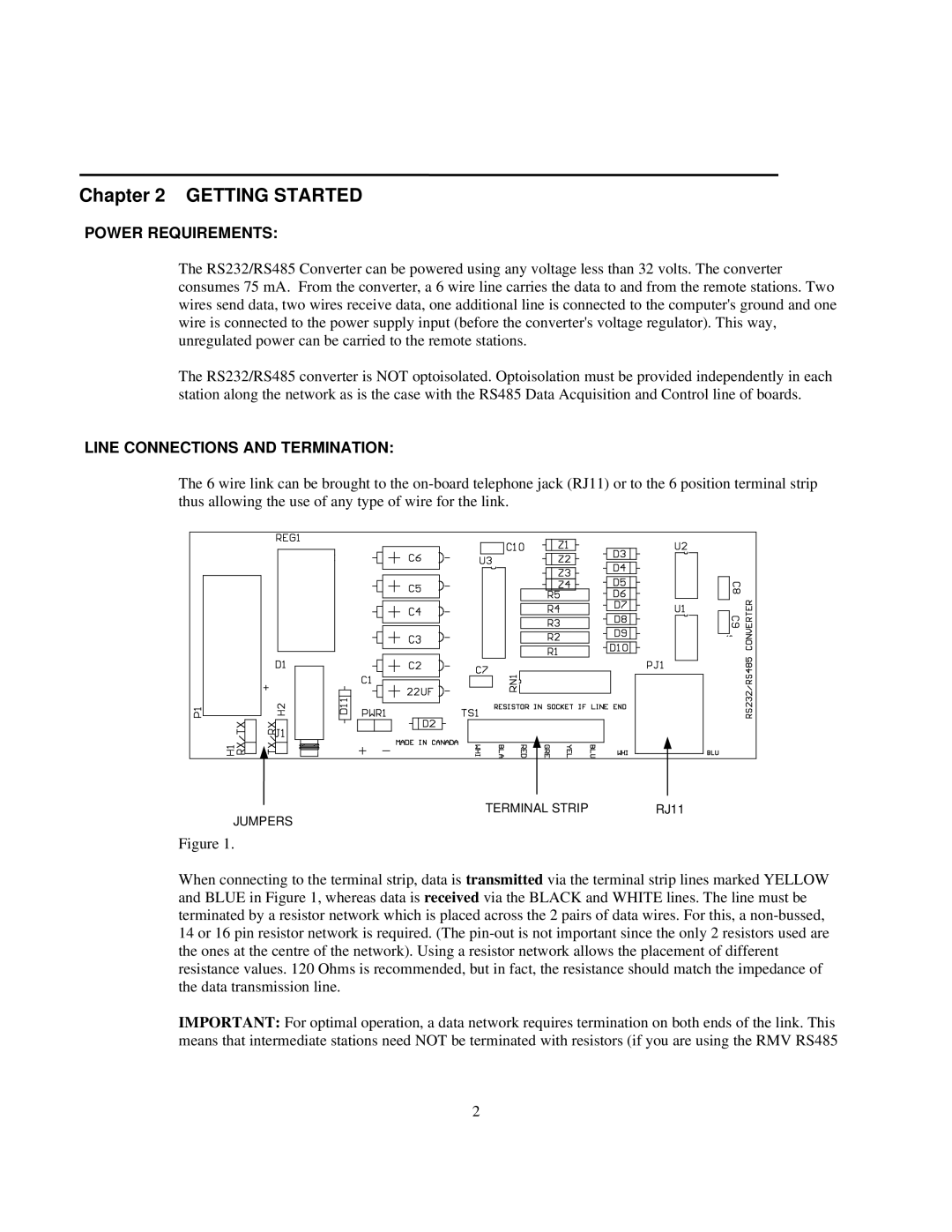
The 6 wire link can be brought to the
TERMINAL STRIP | RJ11 |
JUMPERS |
|
Figure 1.
When connecting to the terminal strip, data is transmitted via the terminal strip lines marked YELLOW and BLUE in Figure 1, whereas data is received via the BLACK and WHITE lines. The line must be terminated by a resistor network which is placed across the 2 pairs of data wires. For this, a
IMPORTANT: For optimal operation, a data network requires termination on both ends of the link. This means that intermediate stations need NOT be terminated with resistors (if you are using the RMV RS485
2