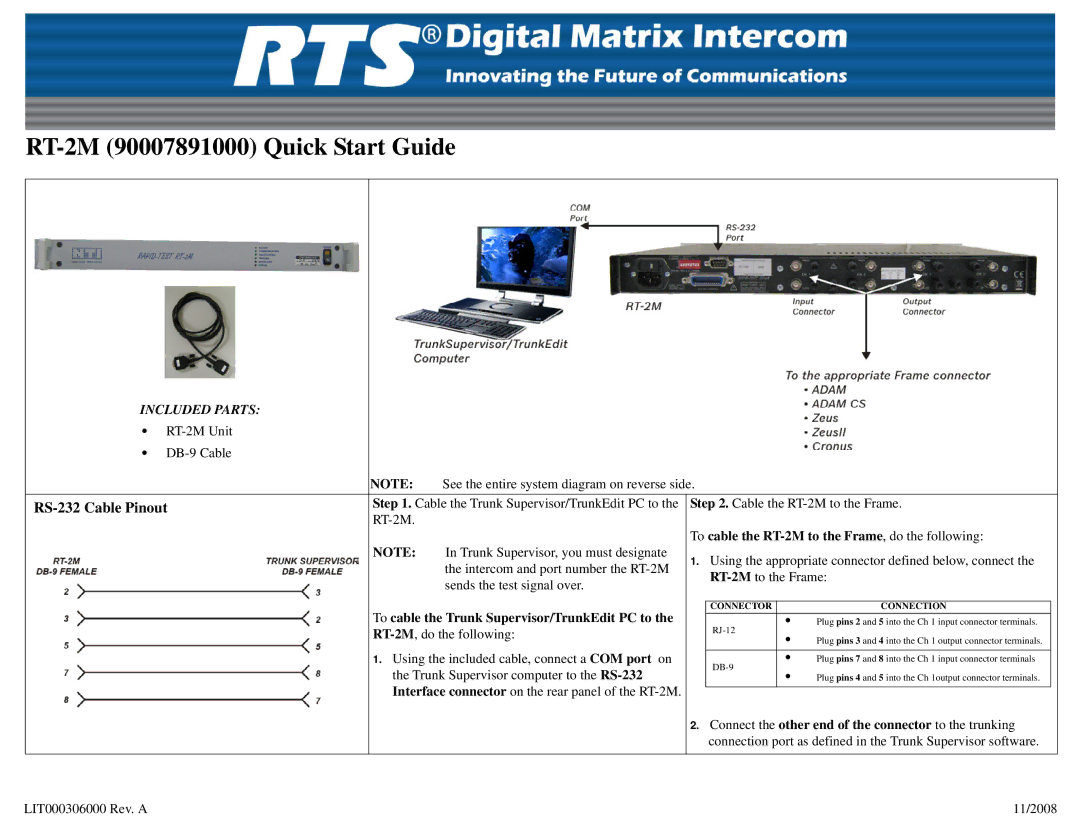
RT-2M specifications
The RTS RT-2M, also known as the RSD-10 Pioneer, is an intercontinental ballistic missile system developed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. Its design signifies significant advancements in military technology and reflects the strategic needs of the era. Introduced in the early 1970s, the RT-2M was developed to enhance the Soviet Union's nuclear deterrent capability, serving as a critical component of the nation’s strategic military arsenal.One of the main features of the RTS RT-2M is its road-mobile platform, which allows for increased survivability and flexibility in deployment. Unlike fixed missile silos that are vulnerable to first-strike attacks, the mobile capabilities of the RT-2M enable it to be relocated quickly, making it difficult for enemy forces to target. The system is mounted on large, heavy-duty trucks, facilitating movement across diverse terrains and enhancing its operational readiness.
The RT-2M boasts a range of approximately 10,000 kilometers, allowing for strikes against distant targets while remaining within the borders of the Soviet Union. It is equipped with a three-stage solid-fuel rocket motor, which contributes to its reliability and decreased launch preparation time compared to liquid-propellant systems. The missile features Multiple Independently targetable Reentry Vehicles (MIRV) technology, allowing it to carry multiple nuclear warheads and strike several targets simultaneously, increasing its lethality and effectiveness.
Another noteworthy characteristic of the RTS RT-2M is its advanced guidance system. The missile utilizes inertial guidance coupled with terminal guidance capabilities, enhancing its accuracy and enabling precise strikes. This precision reduces the number of warheads needed to ensure target destruction, optimizing the strategic positioning of nuclear forces.
Through the years, the RTS RT-2M has undergone various upgrades to improve its performance and responsiveness. It served as an essential part of the Soviet Union's strategic deterrence throughout the Cold War and into the post-Soviet era. Its legacy continues to influence modern ballistic missile systems and reflects the intricate balance of power that characterized global military strategies during its operational lifetime. Overall, the RTS RT-2M encapsulates a pivotal moment in the evolution of military technology and strategic defense.