Drive Specifications | www.seagate.com |
During Standby mode, the drive accepts commands, but the drive is not spinning, and the servo and read/ write electronics are in
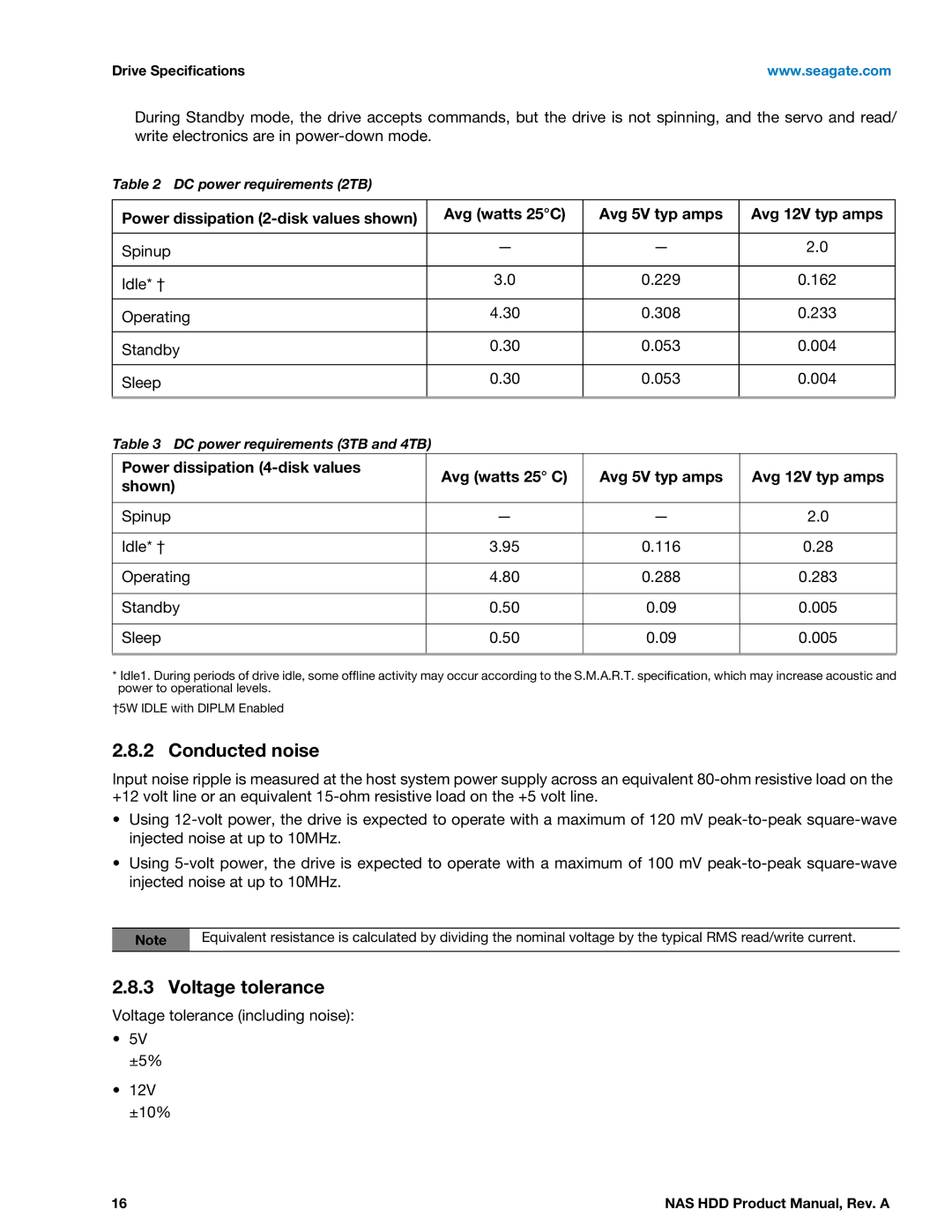
Table 2 DC power requirements (2TB)
Power dissipation |
| Avg (watts 25°C) | Avg 5V typ amps | Avg 12V typ amps | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Spinup |
| — | — | 2.0 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Idle* † |
| 3.0 | 0.229 | 0.162 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating |
| 4.30 | 0.308 | 0.233 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standby |
| 0.30 | 0.053 | 0.004 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sleep |
| 0.30 | 0.053 | 0.004 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 3 DC power requirements (3TB and 4TB) |
|
|
| ||
Power dissipation |
|
| Avg (watts 25° C) | Avg 5V typ amps | Avg 12V typ amps |
shown) |
|
| |||
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
| |
Spinup |
|
| — | — | 2.0 |
|
|
|
|
| |
Idle* † |
|
| 3.95 | 0.116 | 0.28 |
|
|
|
|
| |
Operating |
|
| 4.80 | 0.288 | 0.283 |
|
|
|
|
| |
Standby |
|
| 0.50 | 0.09 | 0.005 |
|
|
|
|
| |
Sleep |
|
| 0.50 | 0.09 | 0.005 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
*Idle1. During periods of drive idle, some offline activity may occur according to the S.M.A.R.T. specification, which may increase acoustic and power to operational levels.
†5W IDLE with DIPLM Enabled
2.8.2 Conducted noise
Input noise ripple is measured at the host system power supply across an equivalent
•Using
•Using
Note | Equivalent resistance is calculated by dividing the nominal voltage by the typical RMS read/write current. |
|
|
2.8.3 Voltage tolerance
Voltage tolerance (including noise):
•5V
±5%
•12V
±10%
16 | NAS HDD Product Manual, Rev. A |