SM 2610957105
|
| Assembly and adjustments |
|
| General cutting |
|
|
|
|
| Use scrap lumber to check the settings and to get the feel of operating the band saw |
| ! WARNING | |
|
| before attempting regular work. |
|
|
•Do not turn the power on before all adjustments have been made. Check to make sure the upper guide is in place. Always keep the upper blade guide close to your work, approximately 1/8" (3.2 mm) above the workpiece.
•Do not force the workpiece against the blade. Light contact permits easier cutting and prevents unwanted friction and heating of the blade.
•Sharp saw blades need little pressure for cutting. Steadily move the workpiece against the blade without forcing it.
Use the band saw for straight line operations such as
To avoid twisting the blade, do not turn sharp corners; instead, saw around corners.
A band saw is basically a
!Do not use this band saw to cut WARNING ferrous metals.
Cutting curves
When cutting curves, carefully turn the workpiece so the blade follows without twisting. If the curve
is so sharp that you repeatedly back up and cut new kerf, use a narrower blade, or a blade with more set (teeth further apart). When a blade has more set, the workpiece turns easier but the cut is rougher.
When changing a cut, do not withdraw the workpiece from the blade. The blade may get drawn off the wheels. To change a cut, turn the workpiece and saw out through the scrap material area.
When cutting long curves, make relief cuts as you go along.
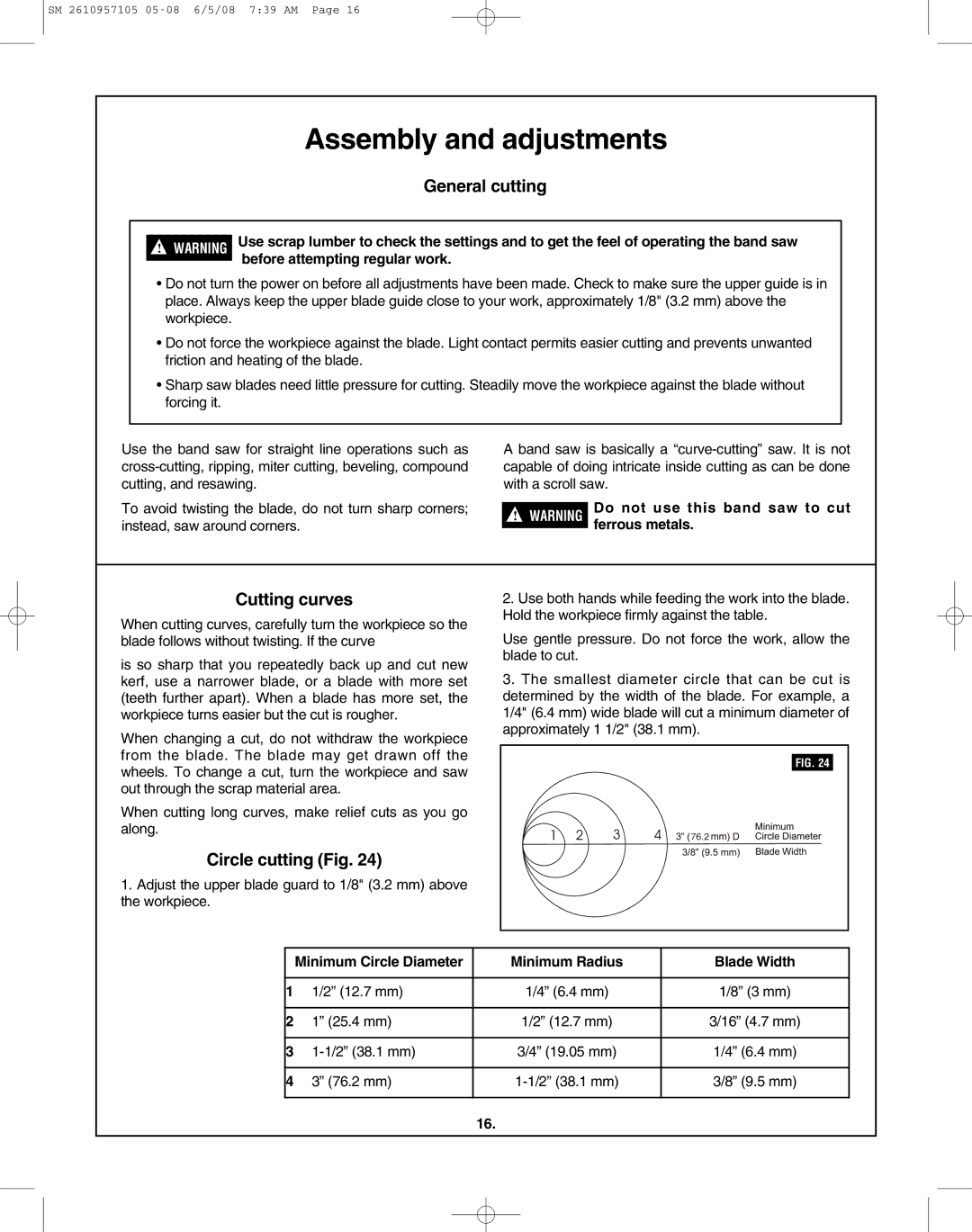
Circle cutting (Fig. 24)
1.Adjust the upper blade guard to 1/8" (3.2 mm) above the workpiece.
2.Use both hands while feeding the work into the blade. Hold the workpiece firmly against the table.
Use gentle pressure. Do not force the work, allow the blade to cut.
3.The smallest diameter circle that can be cut is determined by the width of the blade. For example, a 1/4" (6.4 mm) wide blade will cut a minimum diameter of approximately 1 1/2" (38.1 mm).
FIG. 24 |
76.2 |
| Minimum Circle Diameter | Minimum Radius | Blade Width |
|
|
|
|
1 | 1/2” (12.7 mm) | 1/4” (6.4 mm) | 1/8” (3 mm) |
|
|
|
|
2 | 1” (25.4 mm) | 1/2” (12.7 mm) | 3/16” (4.7 mm) |
|
|
|
|
3 | 3/4” (19.05 mm) | 1/4” (6.4 mm) | |
|
|
|
|
4 | 3” (76.2 mm) | 3/8” (9.5 mm) | |
|
|
|
|
16.