darker.
Display Features
Graph display
Calculation display
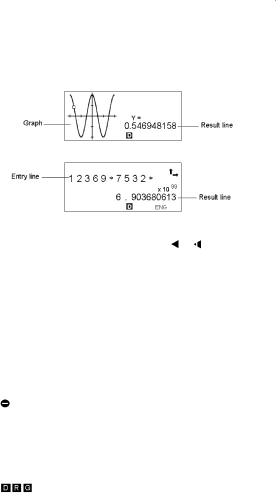
Entry line | Displays an entry of up to 76 digits. Entries with more than 11 | ||
| digits will scroll to the left. When you input the 69th digit of a | ||
| single entry, the cursor changes from | to | to let you |
| know that you are approaching the entry limit. If you need to | ||
| input more than 76 digits, you should divide your calculation | ||
| into two or more parts. |
|
|
Result line | Displays the result of a calculation. 10 digits can be displayed, | ||
| together with a decimal point, a negative sign, the x10 | ||
| indicator, and a | ||
| that exceed this limit are displayed in scientific notation. | ||
Indicators | The following indicators appear on the display to indicate the | ||
| status of the calculator. |
|
|
Indicator | Meaning |
|
|
MValues are stored in running memory
–Result is negative
Invalid action
2nd The next action will be a 2nd function
X = Y = The x- and ![]() Alphabetic keys are active
Alphabetic keys are active
STAT Statistics mode is active
PROG Program mode is active
Angle mode: Degrees, Rads, or Grads