POST code checkpoints
The POST code checkpoints are the largest set of checkpoints during the BIOS
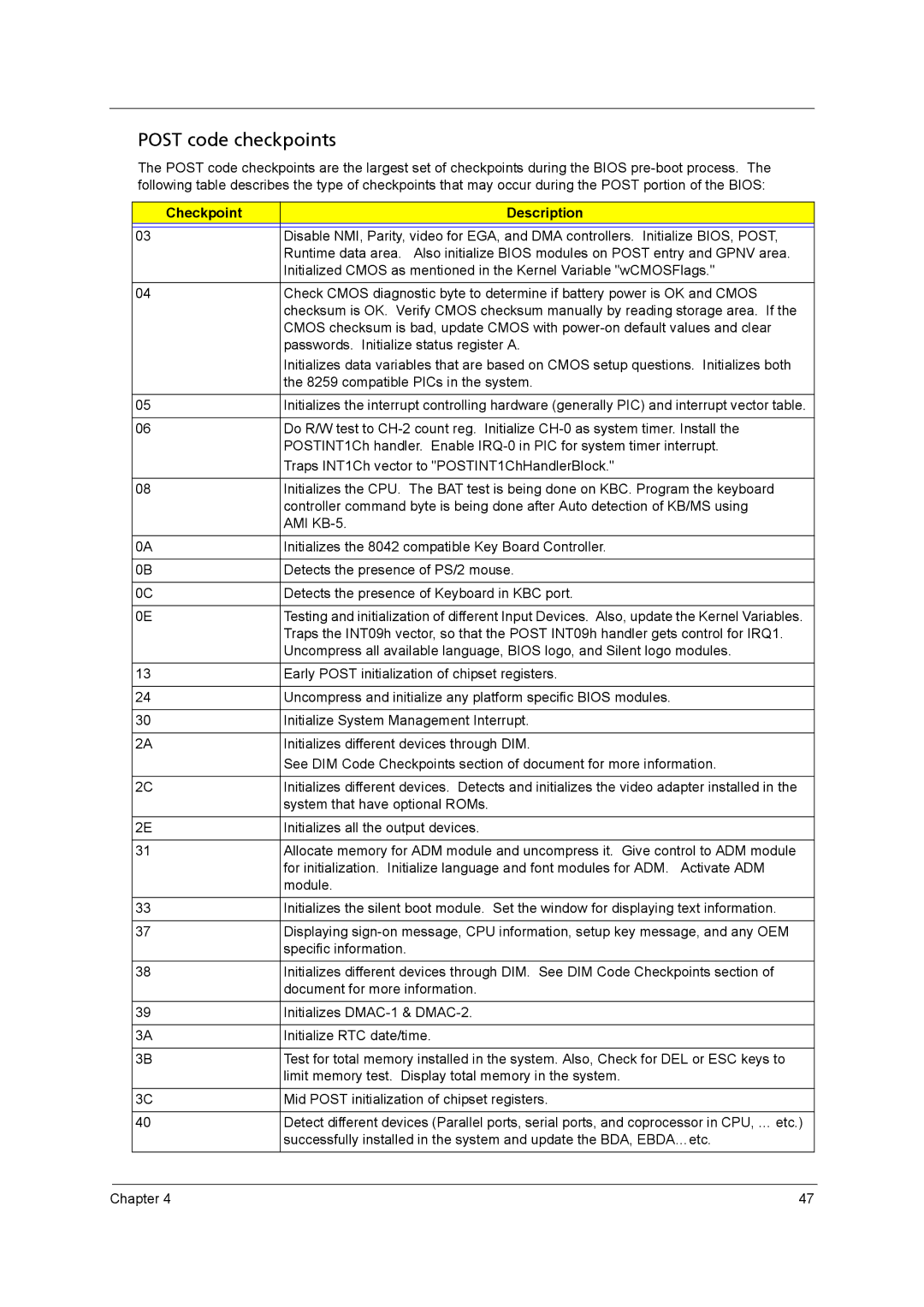
| Checkpoint | Description |
| 03 | Disable NMI, Parity, video for EGA, and DMA controllers. Initialize BIOS, POST, |
|
| Runtime data area. Also initialize BIOS modules on POST entry and GPNV area. |
|
| Initialized CMOS as mentioned in the Kernel Variable "wCMOSFlags." |
|
| |
04 | Check CMOS diagnostic byte to determine if battery power is OK and CMOS | |
|
| checksum is OK. Verify CMOS checksum manually by reading storage area. If the |
|
| CMOS checksum is bad, update CMOS with |
|
| passwords. Initialize status register A. |
|
| Initializes data variables that are based on CMOS setup questions. Initializes both |
|
| the 8259 compatible PICs in the system. |
|
| |
05 | Initializes the interrupt controlling hardware (generally PIC) and interrupt vector table. | |
|
| |
06 | Do R/W test to | |
|
| POSTINT1Ch handler. Enable |
|
| Traps INT1Ch vector to "POSTINT1ChHandlerBlock." |
|
| |
08 | Initializes the CPU. The BAT test is being done on KBC. Program the keyboard | |
|
| controller command byte is being done after Auto detection of KB/MS using |
|
| AMI |
|
|
|
| 0A | Initializes the 8042 compatible Key Board Controller. |
|
|
|
| 0B | Detects the presence of PS/2 mouse. |
|
|
|
| 0C | Detects the presence of Keyboard in KBC port. |
|
|
|
| 0E | Testing and initialization of different Input Devices. Also, update the Kernel Variables. |
|
| Traps the INT09h vector, so that the POST INT09h handler gets control for IRQ1. |
|
| Uncompress all available language, BIOS logo, and Silent logo modules. |
|
| |
13 | Early POST initialization of chipset registers. | |
|
| |
24 | Uncompress and initialize any platform specific BIOS modules. | |
|
| |
30 | Initialize System Management Interrupt. | |
|
|
|
| 2A | Initializes different devices through DIM. |
|
| See DIM Code Checkpoints section of document for more information. |
|
|
|
| 2C | Initializes different devices. Detects and initializes the video adapter installed in the |
|
| system that have optional ROMs. |
|
|
|
| 2E | Initializes all the output devices. |
|
| |
31 | Allocate memory for ADM module and uncompress it. Give control to ADM module | |
|
| for initialization. Initialize language and font modules for ADM. Activate ADM |
|
| module. |
|
| |
33 | Initializes the silent boot module. Set the window for displaying text information. | |
|
| |
37 | Displaying | |
|
| specific information. |
|
| |
38 | Initializes different devices through DIM. See DIM Code Checkpoints section of | |
|
| document for more information. |
|
| |
39 | Initializes | |
|
|
|
| 3A | Initialize RTC date/time. |
|
|
|
| 3B | Test for total memory installed in the system. Also, Check for DEL or ESC keys to |
|
| limit memory test. Display total memory in the system. |
|
|
|
| 3C | Mid POST initialization of chipset registers. |
|
| |
40 | Detect different devices (Parallel ports, serial ports, and coprocessor in CPU, … etc.) | |
|
| successfully installed in the system and update the BDA, EBDA…etc. |
|
|
|
Chapter 4 | 47 |