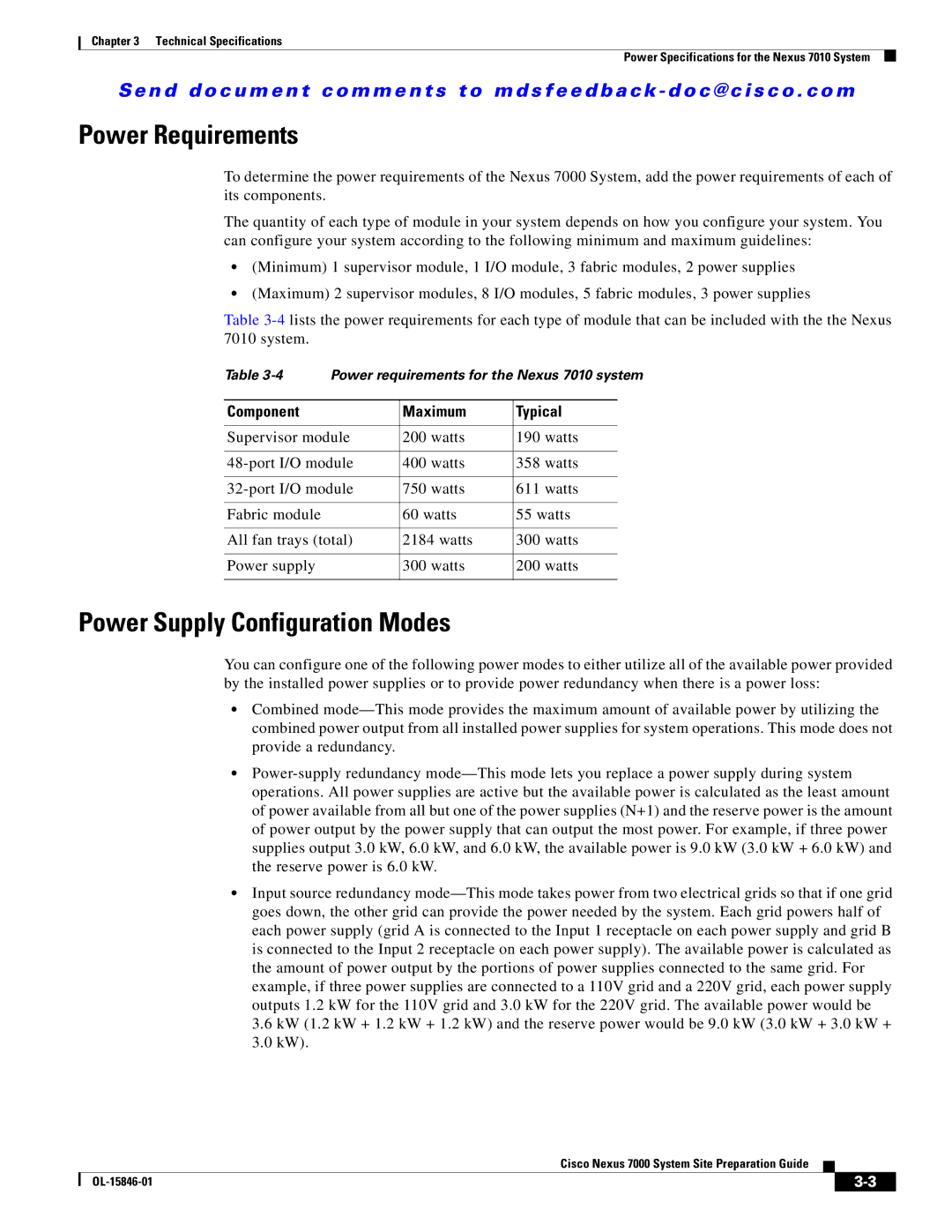
7000 specifications
Cisco Systems 7000 series routers are pivotal in the landscape of networking, providing high-performance, reliable solutions for enterprise environments and service providers. These routers were designed to support the growing demands of digital communication, offering robust features that enhance connectivity and streamline network operations.One of the primary characteristics of the Cisco 7000 series is its modular architecture. This allows for the integration of various interface modules and processing units, enabling organizations to customize their routers according to specific networking needs. The modularity supports scalability, as businesses can upgrade or replace components as their requirements evolve without having to replace the entire system.
The Cisco 7000 series incorporates advanced routing protocols, ensuring efficient data packet management and traffic flow. It supports multiple protocols, including OSPF, BGP, and EIGRP, facilitating seamless integration into a variety of network environments. This flexibility is essential in modern networks, where diverse communication protocols are in use.
Load balancing capabilities are another significant feature of the Cisco 7000 series. This functionality allows for the optimal distribution of network traffic across multiple paths, enhancing performance and redundancy. By ensuring that no single route is overwhelmed, organizations can maintain uptime and improve overall user experience.
Security is a top priority for many businesses, and the Cisco 7000 series addresses this need with built-in security features. It supports Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and access control lists (ACL) to provide secure remote access and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. This capability is vital in today’s threat landscape, where data breaches can have far-reaching consequences.
The series also boasts high throughput and low latency, making it suitable for bandwidth-intensive applications like video conferencing and cloud computing. Coupled with Quality of Service (QoS) features, the Cisco 7000 ensures that critical applications receive the bandwidth they need, thereby enhancing overall network performance.
In terms of manageability, the Cisco 7000 routers come equipped with advanced monitoring and diagnostic tools. Network administrators can easily track performance metrics and identify potential issues before they escalate, minimizing downtimes and maintaining business continuity.
In summary, the Cisco Systems 7000 series routers are a sophisticated solution for organizations seeking to optimize their networking infrastructure. With modularity, robust routing protocols, load balancing, security features, high performance, and comprehensive manageability, the Cisco 7000 series stands out as a reliable foundation for successful network operations in an increasingly connected world.