Chapter 12 Configuring EtherChannels
Understanding How EtherChannels Work
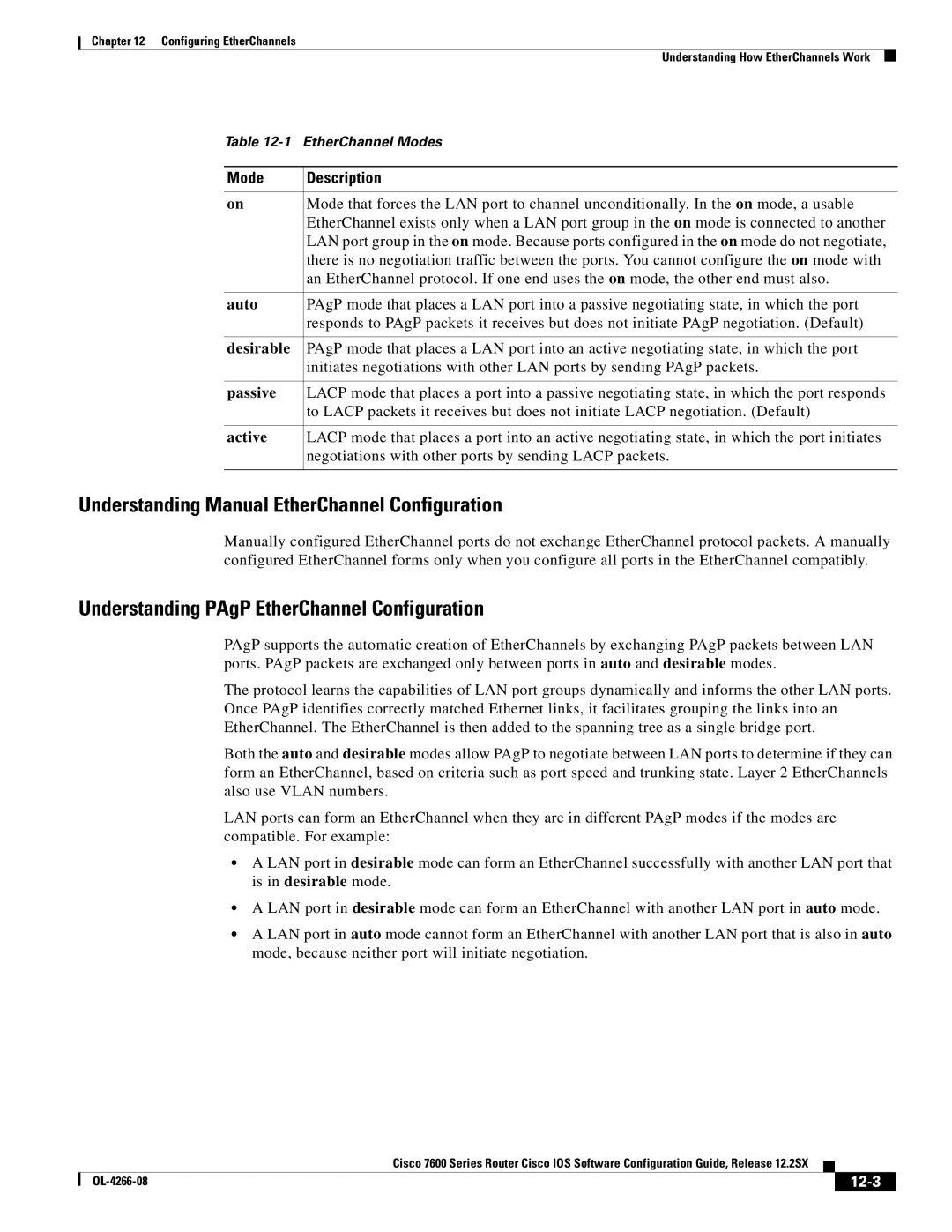
Table
Mode | Description |
|
|
on | Mode that forces the LAN port to channel unconditionally. In the on mode, a usable |
| EtherChannel exists only when a LAN port group in the on mode is connected to another |
| LAN port group in the on mode. Because ports configured in the on mode do not negotiate, |
| there is no negotiation traffic between the ports. You cannot configure the on mode with |
| an EtherChannel protocol. If one end uses the on mode, the other end must also. |
|
|
auto | PAgP mode that places a LAN port into a passive negotiating state, in which the port |
| responds to PAgP packets it receives but does not initiate PAgP negotiation. (Default) |
|
|
desirable | PAgP mode that places a LAN port into an active negotiating state, in which the port |
| initiates negotiations with other LAN ports by sending PAgP packets. |
|
|
passive | LACP mode that places a port into a passive negotiating state, in which the port responds |
| to LACP packets it receives but does not initiate LACP negotiation. (Default) |
|
|
active | LACP mode that places a port into an active negotiating state, in which the port initiates |
| negotiations with other ports by sending LACP packets. |
|
|
Understanding Manual EtherChannel Configuration
Manually configured EtherChannel ports do not exchange EtherChannel protocol packets. A manually configured EtherChannel forms only when you configure all ports in the EtherChannel compatibly.
Understanding PAgP EtherChannel Configuration
PAgP supports the automatic creation of EtherChannels by exchanging PAgP packets between LAN ports. PAgP packets are exchanged only between ports in auto and desirable modes.
The protocol learns the capabilities of LAN port groups dynamically and informs the other LAN ports. Once PAgP identifies correctly matched Ethernet links, it facilitates grouping the links into an EtherChannel. The EtherChannel is then added to the spanning tree as a single bridge port.
Both the auto and desirable modes allow PAgP to negotiate between LAN ports to determine if they can form an EtherChannel, based on criteria such as port speed and trunking state. Layer 2 EtherChannels also use VLAN numbers.
LAN ports can form an EtherChannel when they are in different PAgP modes if the modes are compatible. For example:
•A LAN port in desirable mode can form an EtherChannel successfully with another LAN port that is in desirable mode.
•A LAN port in desirable mode can form an EtherChannel with another LAN port in auto mode.
•A LAN port in auto mode cannot form an EtherChannel with another LAN port that is also in auto mode, because neither port will initiate negotiation.
Cisco 7600 Series Router Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide, Release 12.2SX
|
|
| |
|
|