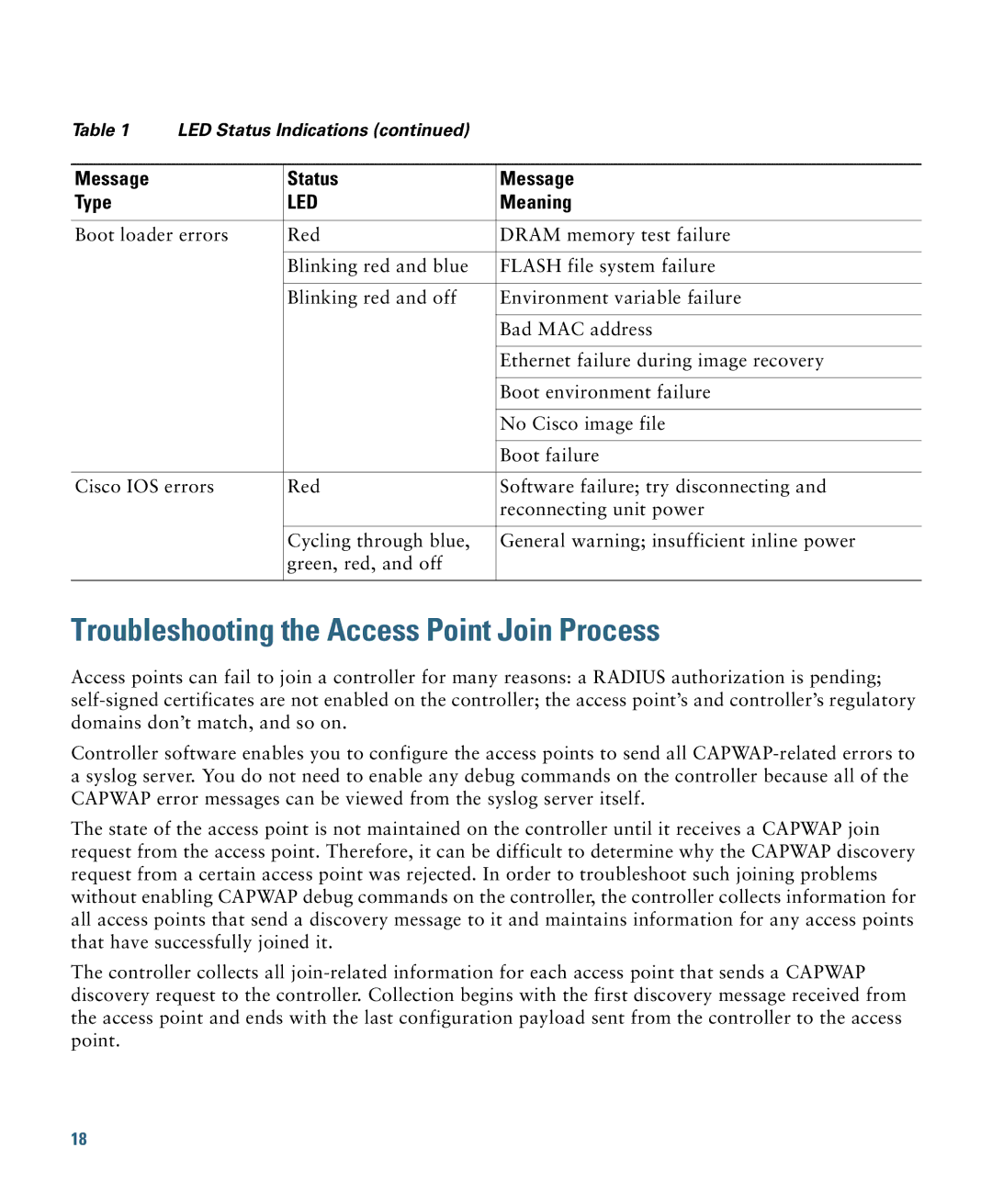
Table 1 | LED Status Indications (continued) |
| |
|
|
|
|
Message |
| Status | Message |
Type |
| LED | Meaning |
|
|
| |
Boot loader errors | Red | DRAM memory test failure | |
|
|
|
|
|
| Blinking red and blue | FLASH file system failure |
|
|
|
|
|
| Blinking red and off | Environment variable failure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Bad MAC address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Ethernet failure during image recovery |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Boot environment failure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| No Cisco image file |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Boot failure |
|
|
| |
Cisco IOS errors | Red | Software failure; try disconnecting and | |
|
|
| reconnecting unit power |
|
|
|
|
|
| Cycling through blue, | General warning; insufficient inline power |
|
| green, red, and off |
|
|
|
|
|
Troubleshooting the Access Point Join Process
Access points can fail to join a controller for many reasons: a RADIUS authorization is pending;
Controller software enables you to configure the access points to send all
The state of the access point is not maintained on the controller until it receives a CAPWAP join request from the access point. Therefore, it can be difficult to determine why the CAPWAP discovery request from a certain access point was rejected. In order to troubleshoot such joining problems without enabling CAPWAP debug commands on the controller, the controller collects information for all access points that send a discovery message to it and maintains information for any access points that have successfully joined it.
The controller collects all
18