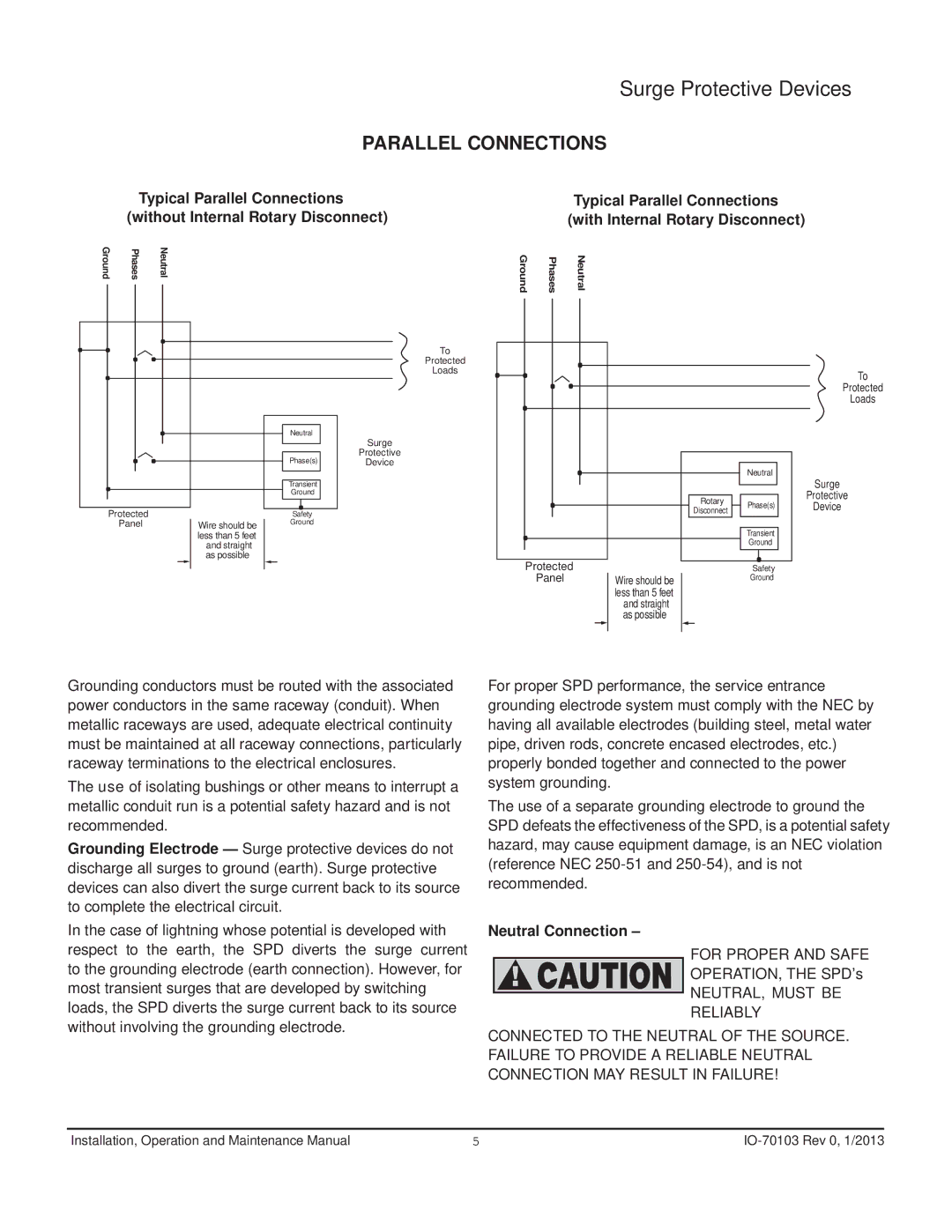
510 specifications
The Emerson 510 is a cutting-edge, versatile automation controller designed to enhance operational efficiency, improve productivity, and ensure seamless management across various industries. Known for its robust architecture, the Emerson 510 integrates a host of features and technologies that cater to the demands of modern automation processes.One of the standout characteristics of the Emerson 510 is its modular design, which allows users to customize their systems according to specific application requirements. This flexibility ensures that businesses can scale their operations without having to invest in entirely new systems. The controller supports a variety of I/O modules, communication cards, and power supplies, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial applications, from manufacturing to processing plants.
The Emerson 510 is powered by advanced technologies that promote faster data processing and enhanced connectivity. It features an intuitive user interface that simplifies programming and monitoring, allowing operators to interact with the system effortlessly. The controller also supports various programming languages, including Ladder Logic and Structured Text, catering to the preferences of different users and ensuring that system integration is as smooth as possible.
Another significant advantage of the Emerson 510 is its real-time data acquisition and processing capabilities. This functionality enables operators to monitor system performance, receive alerts, and make data-driven decisions to optimize operations. The controller’s networking capabilities allow for seamless integration into larger control systems, facilitating communication with other devices and systems, such as SCADA and HMI platforms.
Security is a critical aspect of modern industrial control systems, and the Emerson 510 addresses this concern with robust cybersecurity features. It incorporates advanced encryption protocols, user authentication, and access controls to ensure that the system remains protected against potential threats and vulnerabilities.
In conclusion, the Emerson 510 automation controller stands out in the industry with its modular design, advanced processing capabilities, user-friendly interface, and strong security features. It empowers businesses to enhance operational efficiency, streamline processes, and drive innovation, making it an invaluable asset for any organization looking to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape.