Surge Protective Devices
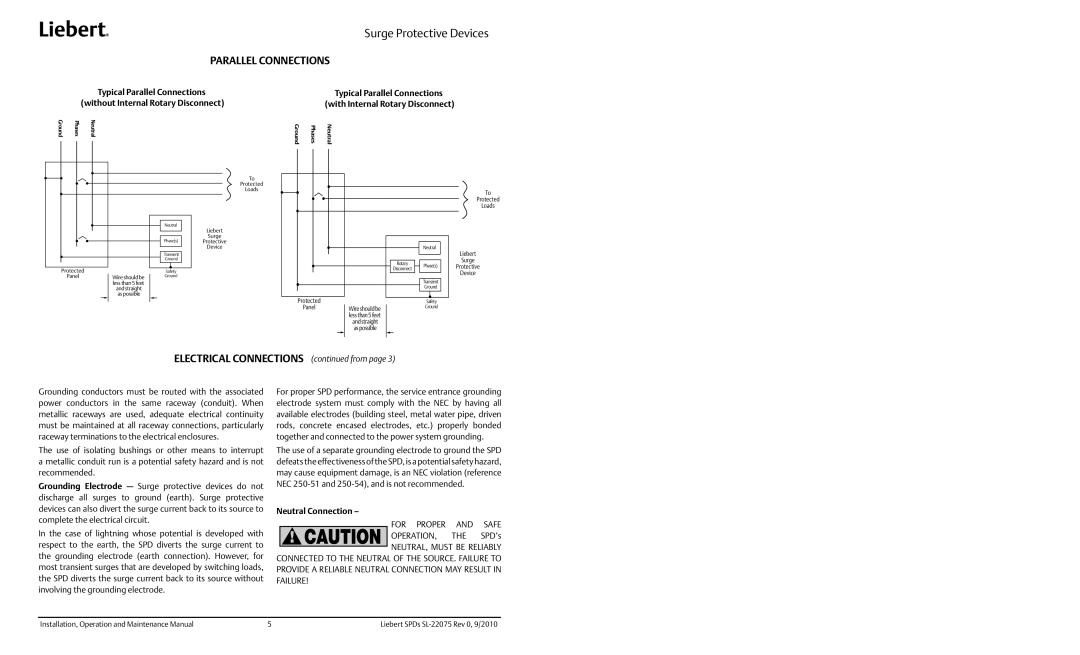
PARALLEL CONNECTIONS
Typical Parallel Connections |
(without Internal Rotary Disconnect) |
Typical Parallel Connections (with Internal Rotary Disconnect)
Ground | Phases | Neutral |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| To |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Protected |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Loads |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Neutral |
| Liebert | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Surge | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Phase(s) |
| Protective | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Device | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Transient |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Ground |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Protected |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Safety |
|
| ||||
|
| Panel |
|
|
|
| Wire should be |
|
|
| Ground |
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| less than 5 feet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| and straight |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| as possible |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ground | Phases | Neutral |
|
|
|
|
|
| Neutral |
|
|
| Rotary | Phase(s) |
|
|
| Disconnect | |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| Transient |
|
|
|
| Ground |
Protected |
|
| Safety | |
| Panel | Wire should be |
| Ground |
|
| less than 5 feet |
|
|
|
| and straight |
|
|
|
| as possible |
|
|
To
Protected
Loads
Liebert
Surge
Protective
Device
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS (continued from page 3)
Grounding conductors must be routed with the associated power conductors in the same raceway (conduit). When metallic raceways are used, adequate electrical continuity must be maintained at all raceway connections, particularly raceway terminations to the electrical enclosures.
The use of isolating bushings or other means to interrupt a metallic conduit run is a potential safety hazard and is not recommended.
Grounding Electrode — Surge protective devices do not discharge all surges to ground (earth). Surge protective devices can also divert the surge current back to its source to complete the electrical circuit.
In the case of lightning whose potential is developed with respect to the earth, the SPD diverts the surge current to the grounding electrode (earth connection). However, for most transient surges that are developed by switching loads, the SPD diverts the surge current back to its source without involving the grounding electrode.
For proper SPD performance, the service entrance grounding electrode system must comply with the NEC by having all available electrodes (building steel, metal water pipe, driven rods, concrete encased electrodes, etc.) properly bonded together and connected to the power system grounding.
The use of a separate grounding electrode to ground the SPD defeats the effectiveness of the SPD, is a potential safety hazard, may cause equipment damage, is an NEC violation (reference NEC
Neutral Connection –
FOR PROPER AND SAFE
OPERATION, THE SPD’s
NEUTRAL, MUST BE RELIABLY CONNECTED TO THE NEUTRAL OF THE SOURCE. FAILURE TO PROVIDE A RELIABLE NEUTRAL CONNECTION MAY RESULT IN FAILURE!
Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual | 5 | Liebert SPDs |