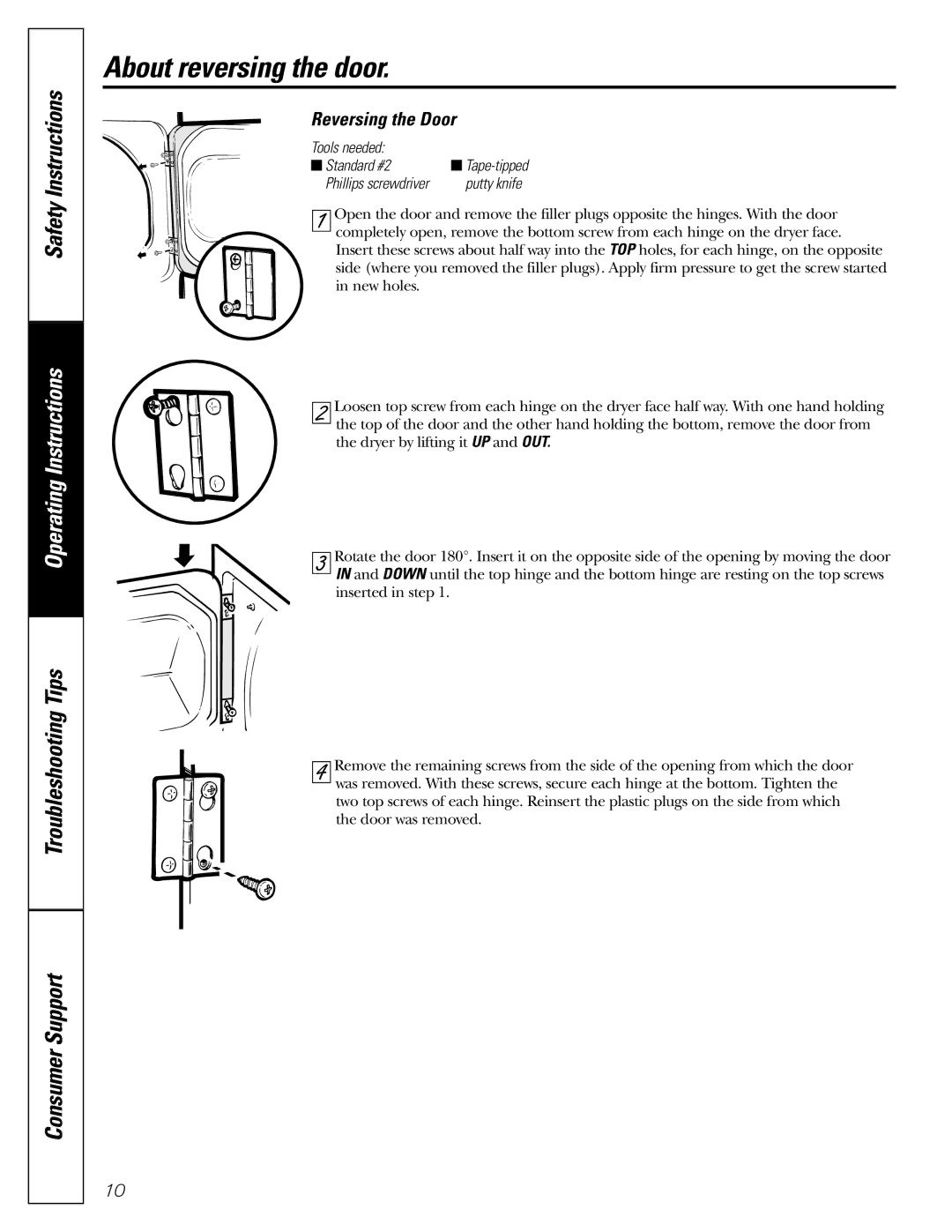
DRSR483, DLSR483, EGD4500, DBXR463, EED4500 specifications
The GE DX2300 and DX4500 are advanced digital x-ray systems designed to enhance imaging capabilities in medical diagnostics. Both systems are known for their innovative technologies, high-quality imaging, and user-friendly interfaces, making them essential tools in modern radiology.The GE DX2300 is a versatile digital X-ray system that serves as an ideal solution for a variety of clinical settings. It combines a robust design with advanced imaging technologies to deliver high-resolution images efficiently. Key features of the DX2300 include a digital flat-panel detector, which significantly improves image quality while minimizing radiation exposure for patients. The system's software algorithms provide automatic image processing and enhancements, allowing for clearer, more detailed images that facilitate accurate diagnoses. Additionally, its compact design and mobility make it suitable for both fixed and mobile applications, contributing to greater flexibility in diverse clinical environments.
On the other hand, the GE DX4500 is designed for larger healthcare facilities that require high throughput and efficiency. Its more advanced features include a larger flat-panel detector that enables imaging of larger anatomical areas in a single exposure, thus increasing patient comfort and workflow productivity. The DX4500 also incorporates digital image storage and retrieval capabilities, allowing for seamless integration into hospital networks and improving the overall management of patient data. The system's intuitive touchscreen interface simplifies operation, making it easier for technicians to navigate through various imaging protocols and settings.
Both systems utilize GE's cutting-edge imaging technologies, such as the ability to customize contrast and exposure levels based on the specific needs of each patient. These features not only enhance the quality of the images produced but also help clinicians make informed decisions more quickly and effectively.
In summary, the GE DX2300 and DX4500 represent two of the most important advancements in digital x-ray technology. With their focus on delivering high-quality images, minimizing radiation exposure, and providing user-friendly functionalities, these systems are setting new standards in diagnostic imaging. Their contributions to improved patient care and operational efficiency make them vital assets in today's healthcare landscape.