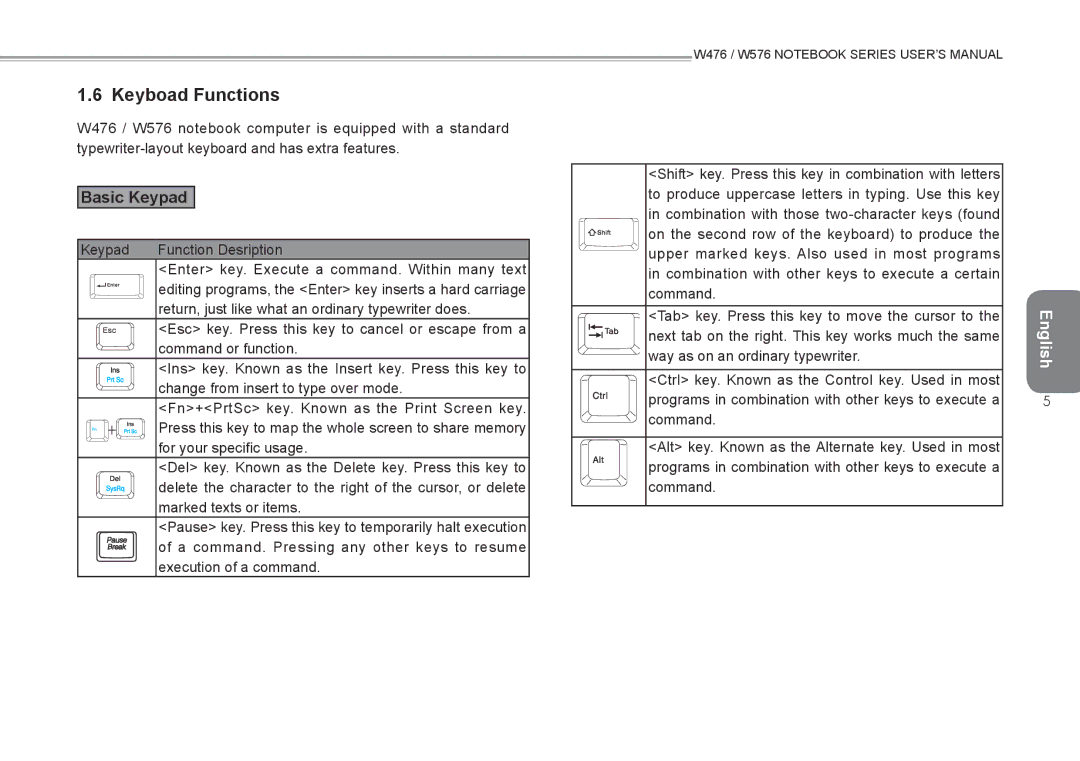
W476, W576 specifications
Intel's W576 and W476 processors are innovative additions to the company's Xeon lineup, designed specifically for high-performance computing tasks and enterprise-level applications. These processors cater to a diverse range of industries requiring robust processing power, reliability, and energy efficiency.The Intel W576 processor is equipped with 24 cores and 48 threads, featuring an impressive base clock speed of 2.6 GHz, which can boost up to 4.4 GHz with Intel Turbo Boost technology. This architecture allows for exceptional multitasking capabilities, making it suitable for data-intensive applications, virtualization, and AI workloads. The W576 supports Intel's Advanced Vector Extensions (AVX-512), which enhances its ability to perform complex calculations efficiently, vital for scientific simulations and machine learning processes.
On the other hand, the W476 processor, although slightly less powerful with its 16 cores and 32 threads, still delivers formidable performance with a base clock speed of 2.4 GHz and a turbo frequency of 4.3 GHz. The W476 is designed for workloads that do not require the same level of parallel processing as the W576 but still demand substantial computational power, making it ideal for enterprises focused on reliable performance without extreme scalability requirements.
Both processors integrate Intel's Speed Shift technology, which allows for quicker adjustments to CPU performance based on workload demands. This contributes to improved power efficiency and thermal management, ensuring that both processors operate optimally under varying workloads. They also support Intel Deep Learning Boost, which enables accelerated AI inference performance, crucial for businesses leveraging machine learning solutions.
Furthermore, these processors include features such as Intel Optane memory support, which enhances system responsiveness and storage capabilities, and support for DDR4 memory up to 3200 MT/s, allowing for faster data throughput. The W576 and W476 also possess robust security features including Intel Software Guard Extensions which provide hardware-based protection for sensitive data and applications.
In summary, the Intel W576 and W476 processors represent a significant step forward in processing technology for enterprise environments. With their advanced architectures, improved power efficiency, and support for modern workloads, they provide the versatility and performance required in today's data-driven landscape. Whether for high-demand AI applications or reliable enterprise computing, these processors stand out as powerful solutions that align with the evolving needs of the industry.