DCS 700 specifications
The Kodak DCS 700 series, introduced in 1996, marked a significant milestone in the evolution of digital photography. Targeted at professional photographers, this groundbreaking camera system was one of the first digital single-lens reflex (DSLR) cameras to deliver high-quality images comparable to traditional film cameras.One of the standout features of the Kodak DCS 700 series was its remarkable resolution for the time. It boasted a 6.2-megapixel sensor, allowing photographers to capture images with stunning clarity and detail. This high resolution was ideal for various applications, from commercial photography to scientific imaging. The DCS 700 utilized a charged-coupled device (CCD) sensor, which was known for its excellent light sensitivity and image quality, especially in low-light conditions.
The DCS 700 was designed with a robust construction, resembling traditional film cameras, which made it more comfortable for professionals accustomed to using film. It featured a familiar layout, including a mirror reflex mechanism that allowed photographers to view exactly what the lens was capturing. This design ensured that transitioning to digital photography felt natural for many users.
Another key feature of the DCS 700 series was its ability to shoot in RAW format, enabling photographers to store images with minimal compression. This capability provided greater flexibility in post-processing, allowing for adjustments in exposure, color balance, and other critical aspects without losing image quality. Additionally, the camera came equipped with an advanced metering system to accurately gauge exposure, ensuring well-balanced images even in challenging lighting situations.
The Kodak DCS 700 series also came with integrated connectivity options, allowing users to transfer images directly to computers for quick editing and sharing. This feature was particularly appealing for professionals in fast-paced environments, where speed and efficiency were paramount.
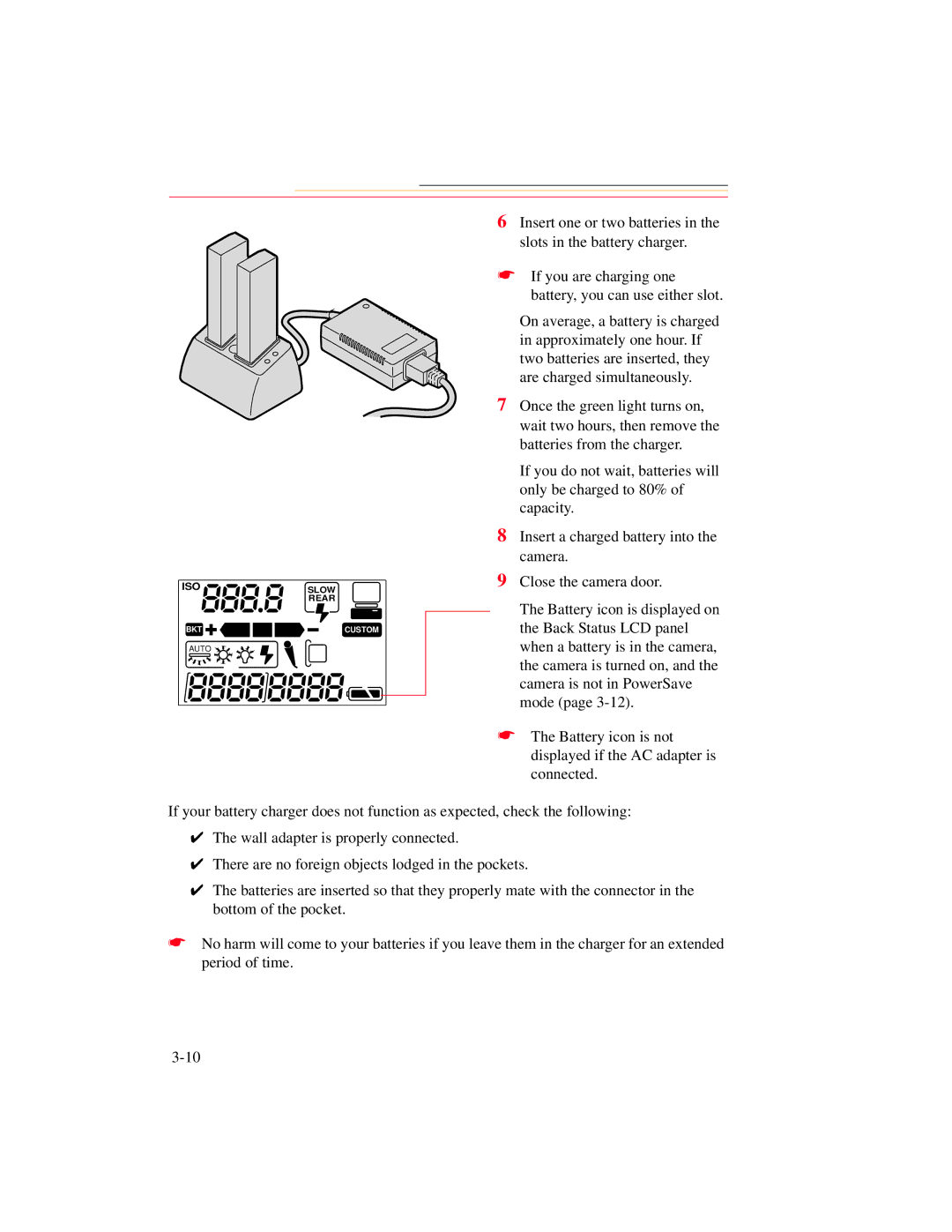
Battery life was another significant aspect, as the DCS 700 series utilized rechargeable batteries that offered extended shooting sessions, a crucial feature for those covering events or long assignments.
While the DCS 700 series might be considered outdated by today’s standards, it laid the groundwork for future DSLR innovations and is remembered as a pivotal development in the transition from film to digital photography. As a testament to its impact, many professionals still reflect on the DCS 700 series as a reliable tool in their early digital photography endeavors, showcasing Kodak's commitment to advancing imaging technologies.