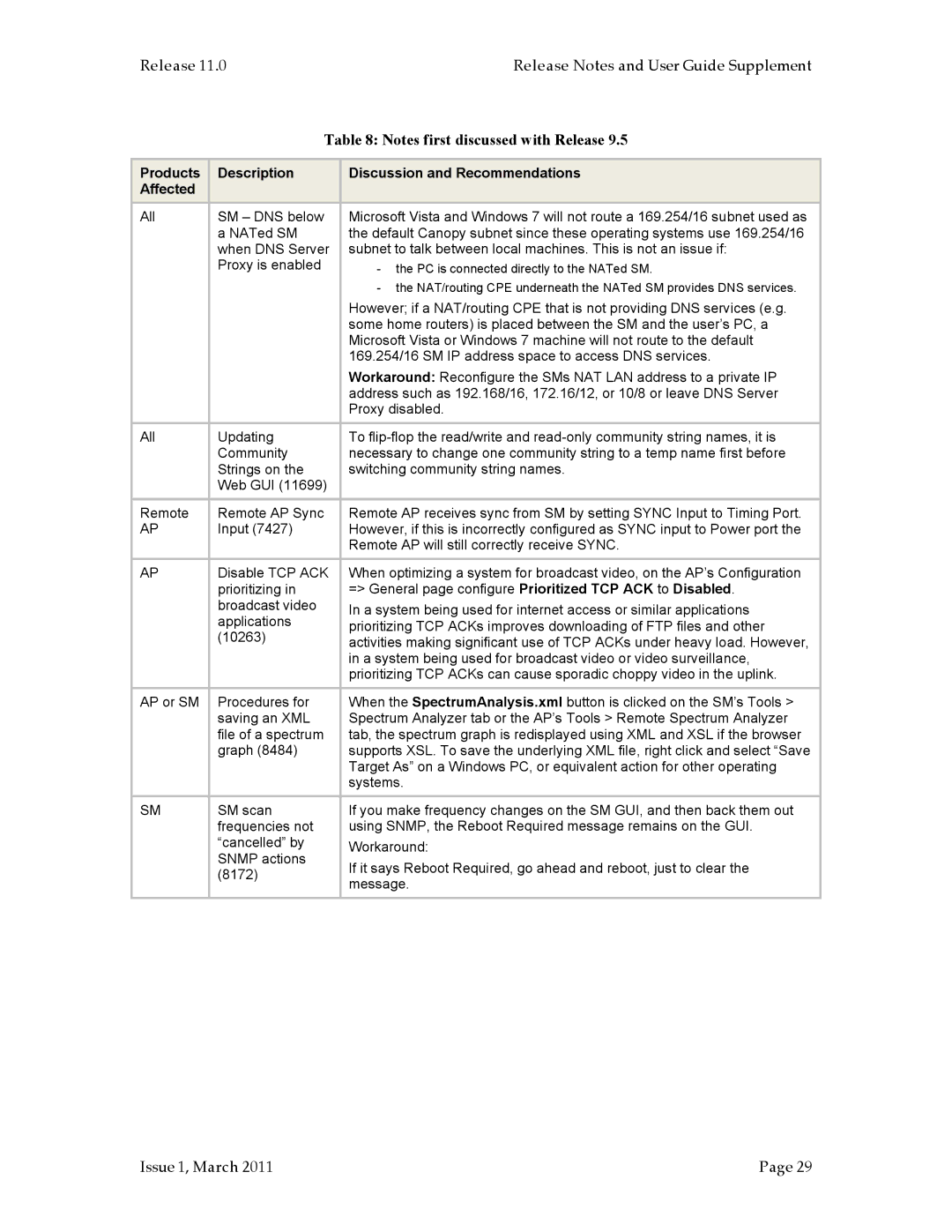
PTP 100 (FSK), PMP 400, PTP 200 (OFDM, PMP 100 specifications
Motorola has long been a key player in the wireless communications market, known for its innovative solutions that cater to various connectivity needs. Among its diverse product range, the Motorola PMP 100 and PTP 200 series stand out as robust solutions for both point-to-multipoint (PMP) and point-to-point (PTP) applications, utilizing advanced modulation technologies such as OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing) and FSK (Frequency Shift Keying).The Motorola PMP 100 series is designed for wireless broadband access, enabling operators to provide high-speed internet connectivity to rural and underserved areas. Its capability to support multiple users makes it an ideal choice for ISPs looking to deliver last-mile connectivity. The PMP 100 operates in the 2.4 GHz and 5.7 GHz frequency bands, ensuring flexibility and compliance with various regulatory requirements. One of its key features is the use of OFDM technology, which enhances spectral efficiency and minimizes interference, resulting in reliable data transmission even in challenging environments.
On the other hand, the PTP 200 series focuses on point-to-point communication, offering high-capacity backhaul links between two locations. The PTP 200 is optimized for performance in line-of-sight scenarios, featuring advanced antenna options and narrow beam width capabilities. This product also leverages OFDM technology, which provides increased data rates and improved capacity, supporting applications such as video surveillance, voice over IP, and enterprise connectivity.
In addition to the PMP and PTP 200 series, Motorola also offers the PMP 400 and PTP 100, which utilize FSK modulation. The PMP 400 series further advances the capabilities of wireless broadband access, featuring enhanced error correction, allowing for better performance in adverse conditions. This series is particularly well-suited for environments with high noise levels, making it a reliable choice for industrial applications. The PTP 100 series, on the other hand, operates effectively in point-to-point scenarios with lower bandwidth requirements, ensuring cost-effective solutions for dedicated leased line services.
In summary, the Motorola PMP and PTP series represent a comprehensive suite of wireless communication solutions, utilizing advanced modulation technologies like OFDM and FSK to deliver high-speed, reliable connectivity. These products demonstrate Motorola's commitment to innovation, addressing the diverse needs of users ranging from ISPs to enterprise customers, all while ensuring robust performance and ease of deployment in various environments.