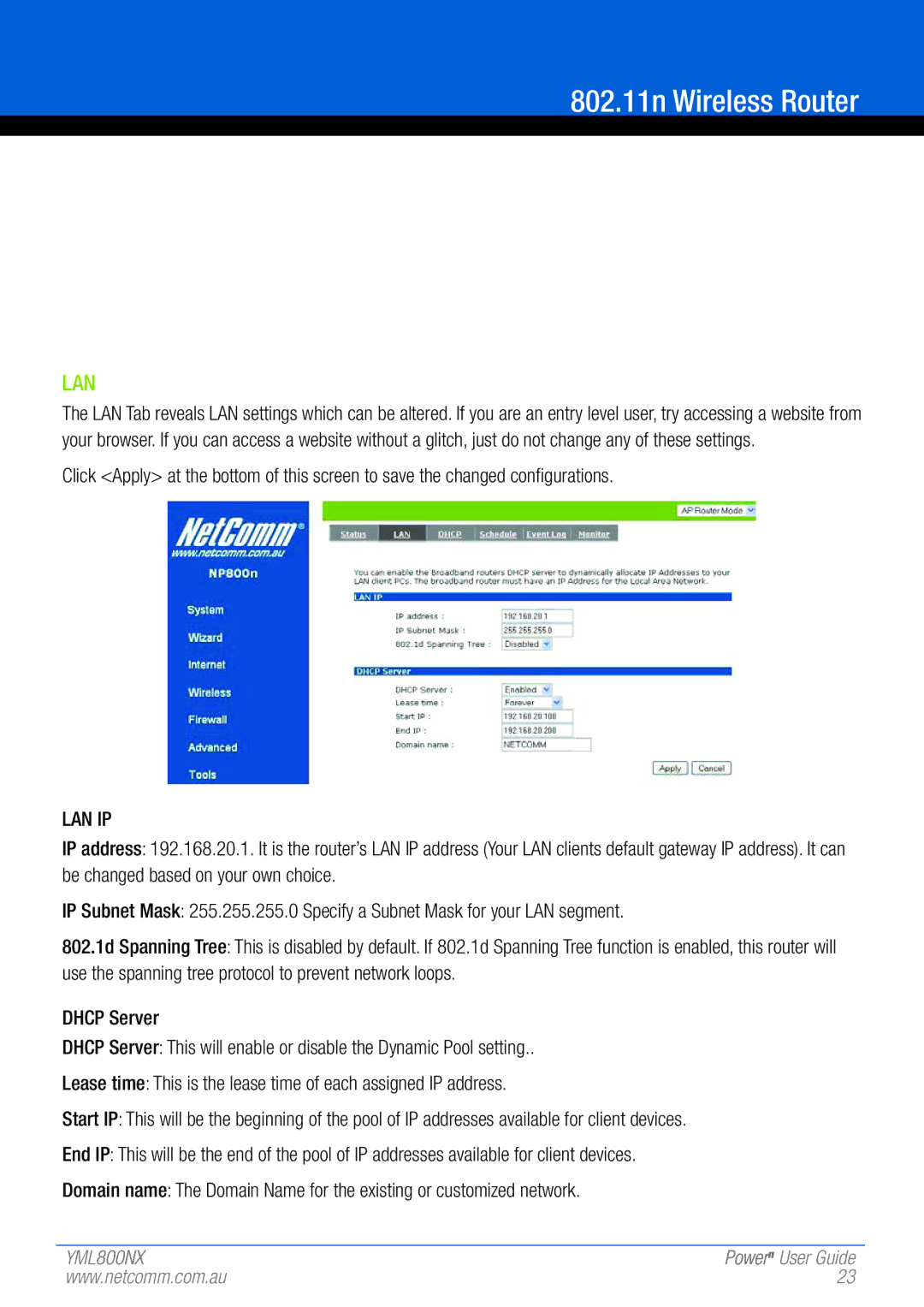
802.11 specifications
NetComm 802.11 refers to the standards established under the IEEE 802.11 family, which governs wireless networking technologies. This set of protocols enables wireless communication between devices, including computers, smartphones, and IoT devices, providing the foundation for Wi-Fi technology. Understanding the main features, technologies, and characteristics of NetComm 802.11 is essential for leveraging its potential in modern networking.One of the primary features of NetComm 802.11 is its ability to support various frequency bands, primarily operating in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The 2.4 GHz band offers extensive coverage and is ideal for penetrating walls and obstacles, catering to a more extensive range of devices. In contrast, the 5 GHz band provides faster data rates and less interference from other household devices, making it suitable for high-bandwidth applications like video streaming and online gaming.
Technically, the 802.11 standard has evolved through multiple amendments, with notable versions including 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6). 802.11n introduced Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) technology, which utilizes multiple antennas for transmitting and receiving data, significantly enhancing throughput and coverage. 802.11ac further increased data rates with wider channels and advanced modulation techniques, achieving speeds up to 1 Gbps or more. The latest 802.11ax, or Wi-Fi 6, optimizes performance in congested environments through technologies like Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and improved MIMO capabilities.
Another characteristic of NetComm 802.11 is its implementation of security protocols. The standard provides several encryption methods, including WEP, WPA, and WPA2, which have evolved to provide more robust security against unauthorized access. WPA3 is the latest standard that enhances protection against brute-force attacks and improves user experience with simplified device onboarding.
In addition to security, NetComm 802.11 supports Quality of Service (QoS) protocols, which prioritize bandwidth for critical applications, ensuring smoother performance for voice and video communications. The introduction of mesh networking capabilities has further revolutionized how Wi-Fi networks can be deployed, allowing for seamless coverage across large areas without dead spots.
In summary, NetComm 802.11 underpins the essential functionalities of wireless networking. Its versatility in frequency bands, progressive technological advancements, strong focus on security, and support for QoS make it a vital standard for modern connectivity, catering to the increasing demands for speed, reliability, and security in a degital world.