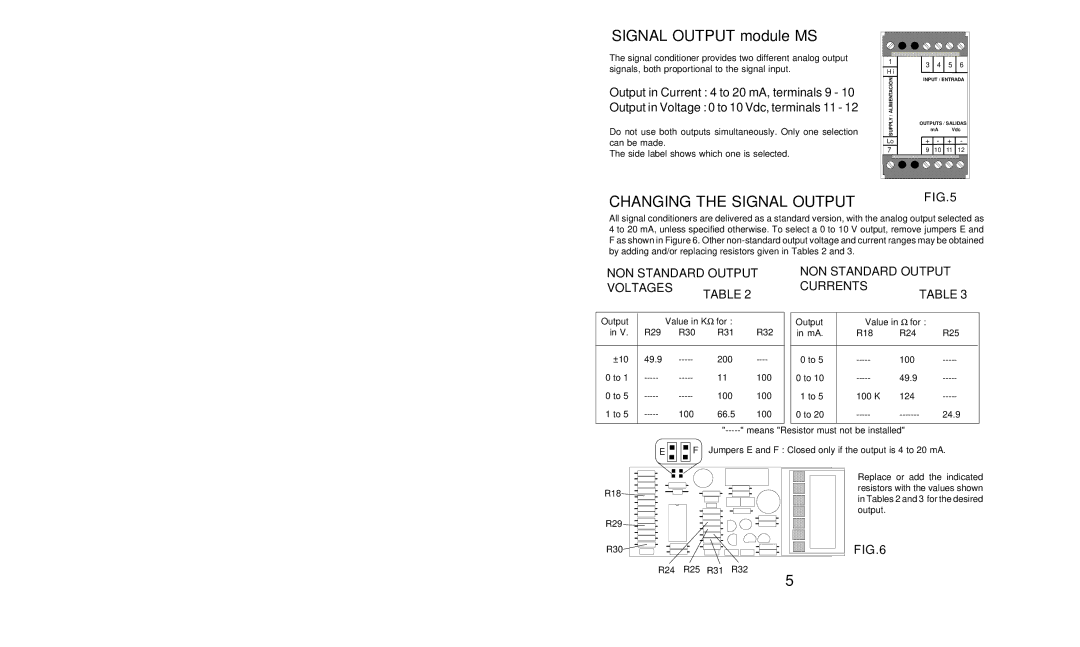
SIGNAL OUTPUT module MS
The signal conditioner provides two different analog output signals, both proportional to the signal input.
Output in Current : 4 to 20 mA, terminals 9 - 10
Output in Voltage : 0 to 10 Vdc, terminals 11 - 12
Do not use both outputs simultaneously. Only one selection can be made.
The side label shows which one is selected.
1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
H i |
|
|
|
| |
/ ALIMENTACION | INPUT / ENTRADA | ||||
|
|
|
| ||
SUPPLY | OUTPUTS / SALIDAS | ||||
| mA | Vdc | |||
+ | - | + | - | ||
Lo | |||||
7 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
CHANGING THE SIGNAL OUTPUT | FIG.5 |
All signal conditioners are delivered as a standard version, with the analog output selected as 4 to 20 mA, unless specified otherwise. To select a 0 to 10 V output, remove jumpers E and F as shown in Figure 6. Other
NON STANDARD OUTPUT |
| NON STANDARD OUTPUT | ||||||||
VOLTAGES | TABLE 2 |
|
| CURRENTS | TABLE 3 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Output |
| Value in KΩ | for : |
|
| Output | Value in Ω for : |
| ||
in V. | R29 |
| R30 | R31 | R32 |
| in mA. | R18 | R24 | R25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
±10 | 49.9 |
| 200 |
| 0 to 5 | 100 | ||||
0 to 1 |
| 11 | 100 |
| 0 to 10 | 49.9 | ||||
0 to 5 |
| 100 | 100 |
| 1 to 5 | 100 K | 124 | |||
1 to 5 |
| 100 | 66.5 | 100 |
| 0 to 20 | 24.9 | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
E ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() F Jumpers E and F : Closed only if the output is 4 to 20 mA.
F Jumpers E and F : Closed only if the output is 4 to 20 mA.
| Replace or add the indicated | |
R18 | resistors with the values shown | |
in Tables 2 and 3 for the desired | ||
| ||
| output. | |
R29 |
|
R30 |
|
| FIG.6 |
R24 | R25 | R31 | R32 |
5