What is blood pressure? | Systolic blood pressure |
| Diastolic blood pressure |
| |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hypertension guide
Systolic blood pressure |
(mmHg) |
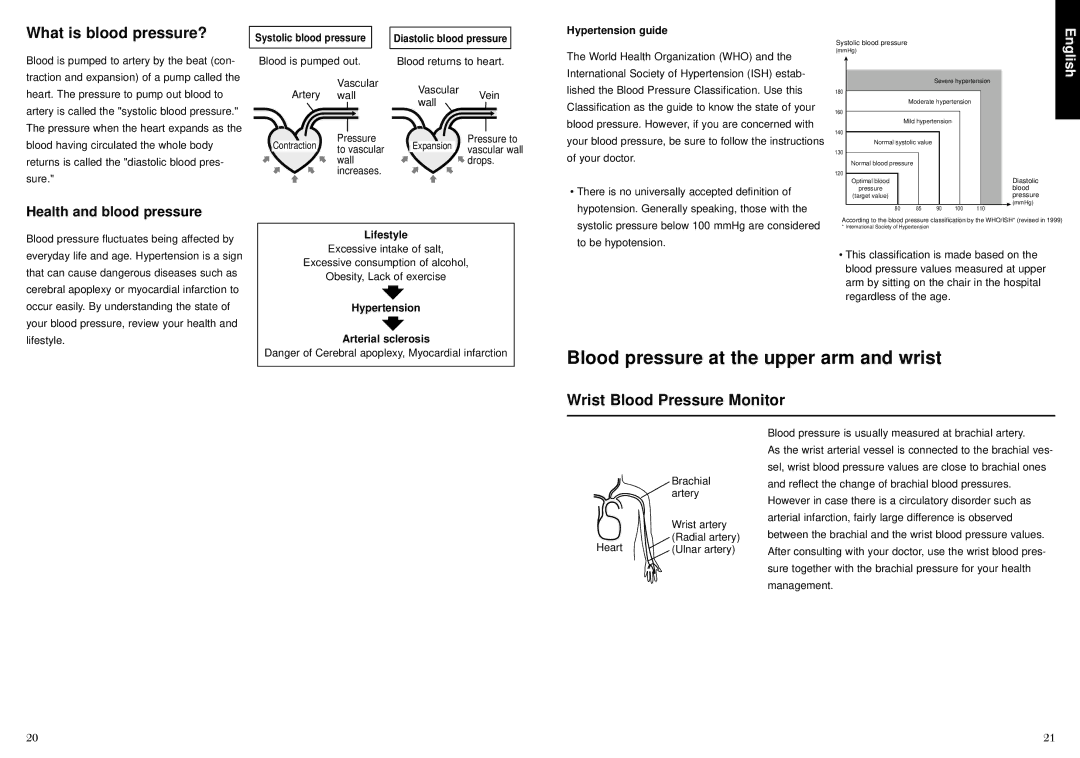
Blood is pumped to artery by the beat (con- traction and expansion) of a pump called the heart. The pressure to pump out blood to artery is called the "systolic blood pressure." The pressure when the heart expands as the blood having circulated the whole body returns is called the "diastolic blood pres- sure."
Blood is pumped out. | Blood returns to heart. | |||
Artery | Vascular | Vascular | Vein | |
wall | ||||
wall | ||||
|
|
| ||
Contraction | Pressure | Expansion | Pressure to | |
to vascular | vascular wall | |||
|
| |||
| wall |
| drops. | |
| increases. |
|
| |
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Society of Hypertension (ISH) estab- lished the Blood Pressure Classification. Use this Classification as the guide to know the state of your blood pressure. However, if you are concerned with your blood pressure, be sure to follow the instructions of your doctor.
Severe hypertension | English |
| |
180 |
|
Moderate hypertension |
|
160 |
|
Mild hypertension |
|
140 |
|
Normal systolic value |
|
130 |
|
Normal blood pressure |
|
120 |
|
Optimal blood | Diastolic |
| blood |
Health and blood pressure
Blood pressure fluctuates being affected by everyday life and age. Hypertension is a sign that can cause dangerous diseases such as cerebral apoplexy or myocardial infarction to occur easily. By understanding the state of your blood pressure, review your health and lifestyle.
Lifestyle
Excessive intake of salt,
Excessive consumption of alcohol,
Obesity, Lack of exercise
Hypertension
Arterial sclerosis
•There is no universally accepted definition of hypotension. Generally speaking, those with the systolic pressure below 100 mmHg are considered to be hypotension.
pressure |
|
|
| pressure |
(target value) |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| (mmHg) |
80 | 85 | 90 | 100 | 110 |
According to the blood pressure classification by the WHO/ISH* (revised in 1999)
*International Society of Hypertension
•This classification is made based on the blood pressure values measured at upper arm by sitting on the chair in the hospital regardless of the age.
Danger of Cerebral apoplexy, Myocardial infarction
Blood pressure at the upper arm and wrist
Wrist Blood Pressure Monitor
| Brachial |
| artery |
| Wrist artery |
Heart | (Radial artery) |
(Ulnar artery) |
Blood pressure is usually measured at brachial artery.
As the wrist arterial vessel is connected to the brachial ves- sel, wrist blood pressure values are close to brachial ones and reflect the change of brachial blood pressures. However in case there is a circulatory disorder such as arterial infarction, fairly large difference is observed between the brachial and the wrist blood pressure values. After consulting with your doctor, use the wrist blood pres- sure together with the brachial pressure for your health management.
20 | 21 |