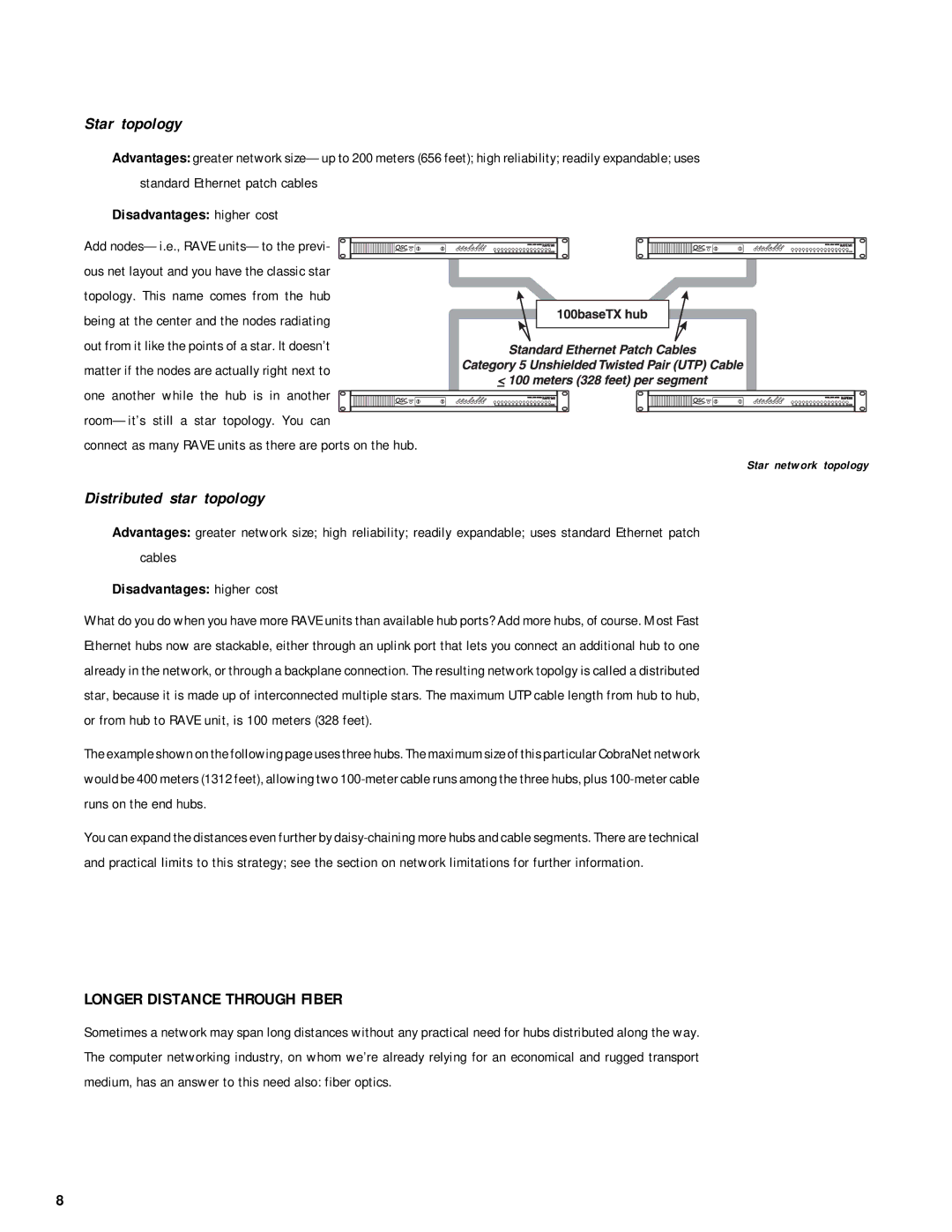
RAVE 88, RAVE 81, RAVE 161, RAVE 160, RAVE 80 specifications
QSC Audio has been a leading name in professional audio equipment, known for its innovative technologies and high-performance solutions. The RAVE series is one of their hallmark offerings, designed specifically for a variety of sound reinforcement applications. The main models in the RAVE lineup include the RAVE 81, RAVE 188, RAVE 88, RAVE 160, and RAVE 80, each catering to distinct needs while embodying QSC's commitment to quality and reliability.The RAVE 81 is a powered loudspeaker delivering impressive sound reinforcement capabilities. With a robust 8-inch woofer and a high-frequency driver, the RAVE 81 ensures full-range audio reproduction. It features integrated QSC amplifiers, which optimize performance for both live sound and installed applications. The speaker also includes versatile input options, making it easy to connect various audio sources, whether in a concert hall or a corporate event.
For larger venues, the RAVE 188 excels with its dual 18-inch woofers, providing deep, powerful bass response crucial for bass-heavy genres. This subwoofer is built with advanced DSP (Digital Signal Processing), ensuring precise tuning for various acoustical environments. The RAVE 188's rugged construction makes it ideal for both touring and fixed installations, ensuring durability under challenging conditions.
The RAVE 88 is a versatile solution featuring dual 8-inch woofers. This model is perfect for applications requiring clear vocal reproduction and balanced sound across a wide range of frequencies. The RAVE 88 is equipped with QSC's intelligent EQ algorithms, which allow users to tailor the sound according to specific venue acoustics, enhancing the overall listening experience.
The RAVE 160 is engineered for high-traffic installations, providing a compact form factor without compromising audio quality. With a full-range design, it combines an efficient woofer and tweeter configuration, making it suitable for both speech and music applications. The RAVE 160 is particularly popular in educational settings and retail spaces due to its unobtrusive design and exceptional intelligibility.
Finally, the RAVE 80 rounds out the series as a highly portable loudspeaker. Its lightweight design makes it easy to transport and set up, which is ideal for mobile DJs, smaller venues, or casual outdoor events. Despite its size, the RAVE 80 delivers impressive audio performance, with a clear and balanced sound that belies its compact nature.
In conclusion, the QSC RAVE series, including the RAVE 81, RAVE 188, RAVE 88, RAVE 160, and RAVE 80, showcases a blend of advanced technologies, thoughtful design, and exceptional audio performance, making them suitable for a wide range of applications in the professional audio landscape. Whether for touring, installation, or portable use, the RAVE models represent robust solutions in sound reinforcement.