LFD Display
Table of contents
Sound Adjustment
Support
Specifications
Table of contents
Copyright
Before Using the Product
Cleaning
Safety Precautions
Symbols
Power off the product and computer
Storage
Electricity and Safety
Installation
Install the product in a kitchen or near a kitchen counter
Sloped surface, etc
Product or cause a fire
Operation
Product failure, an electric shock or fire may result
Output ports, etc
Page
Preparations
Checking the Contents
Warranty card
Checking the Components
Components
Items sold separately
RCA stereo cable P.54 RCA cable P.51
Audio adapter P.51
DP-DVI cable
Control Panel
Parts
Panel Key
Buttons Description
Control menu
Return
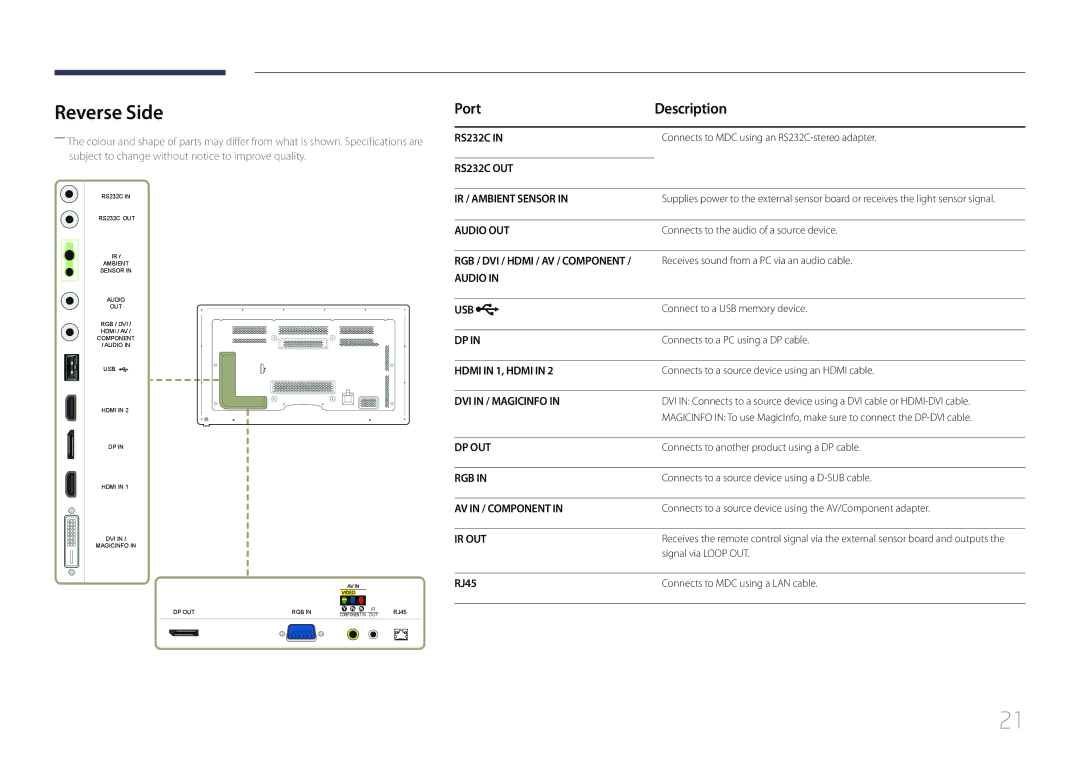
Reverse Side
Port Description
RJ45
Assembling the Holder-Wire stand
Contents Home Launch Button
Remote Control
Quickly select frequently used functions
To place batteries in the remote control
Return to the previous menu
PC, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort
Remote Control Reception Range
Adjusting the OSD with the Remote Control
ButtonsDescription
Select from Picture, Sound, Network, System or
Products 1
Connection Using an IR Stereo Cable Sold separately
Installation on a Perpendicular Wall
Tilting Angle and Rotation
Ventilation
Installation on an Indented Wall
Dimensions
Plane view
Model name
Installing the Wall Mount
Preparing before installing Wall-Mount
Installing the Wall Mount Kit
400 × 400 15.7 ×
Wall Mount Kit Specifications Vesa
Pin Signal
Remote Control RS232C
Cable Connection
RS232C Cable
RS232C cable Connector 9-Pin D-Sub to Stereo Cable
Pin No Standard Colour Signal
LAN Cable
Female
Signal
Connector RJ45
Direct LAN cable PC to HUB
Cross LAN cable PC to PC
Connection
Connection
Controlling Set control command
Viewing control state Get control command
Command
Command type Value range
Volume control
Power control
Setting the input source Set Input Source
Input source control
Input Source An input source code to be set on a product
Screen mode control
PIP On/Off control
Auto adjustment control PC and BNC only
Video Wall Mode Control
Safety Lock
Full Natural
Set Video Wall On/Off
Video Wall On
WallOn Same as above Nak
Set Video Wall
Off
10x10 Video Wall Model
Set Number
10x10 Video Wall Model 1 ~
Connecting and Using a Source Device
Before Connecting
Pre-connection Checkpoints
Connection using the D-SUB cable Analogue type
Connecting to a PC
Connection Using an HDMI-DVI Cable
Connection using a DVI cable Digital type
Connection Using an Hdmi Cable
Connection Using an DP Cable
Precautions for using DP
Changing the Resolution
Changing the Resolution on Windows XP
Changing the Resolution on Windows Vista
Changing the Resolution on Windows
Connecting an External Monitor
Connection Using the AV Cable
Connecting to a Video Device
Connection Using the component Cable
Using an Hdmi cable or Hdmi to DVI Cable up to 1080p
Connecting to an Audio System
Entering MagicInfo mode
Connecting the network box Sold separately
Press Source on the remote control, and select MagicInfo
MagicInfo
Select TCP/IP step
BackB Apply Finish Cancel
Plug In Module
Menu m → Support → Contents Home → Source → Enter E
What is Intel WiDi?
Changing the Input source
Source
Usage Conditions
WiDi Connection
Using MDC
Configuring Settings for Multi Control
Configuring settings for Multi Control
DisplayPort daisy chain
Uninstallation
MDC Programme Installation/Uninstallation
Connecting to MDC
What is MDC?
Using MDC via RS-232C serial data communications standards
Monitor Computer
Connection using a direct LAN cable
Using MDC via Ethernet
Connection using a cross LAN cable
Connection Management
Launching the programme displays the user login window
User Login
Auto Set ID
Cloning
Command Retry
Getting Started with MDC
Menu Bar
Main Screen Layout Menus
Input Source Change the input source
Channel Change the channel
Alert
Volume
Custom
Screen Adjustment
Adjust the tint for the selected display device
Adjust the colours for the selected display device
Adjust the Hdmi Black Level for the selected display device
Color
Reduces Mpeg noise to provide improved picture quality
Size
Controls the LED backlight to maximize picture clarity
You can view details of the selected screen size
3D Control
Advanced features
Adjust the primary colour intensity
Adjust the screen contrast
Adjust the colour temperature for a more natural picture
Adjust each colour red, green, blue darkness
System Setup
Sound Adjustment
Adjust the bass for the selected display
Adjust the treble for the selected display
View the PIP Size of the current display
Select the format to display the split screen
Select a PIP input source
Channel can be changed if PIP Source is TV
Set the product to automatically power on
General Fan & Temperature
Select a method to configure the fan speed
Configure the fan speed
Security OSD Display
Lock the on-screen menus
Lock the buttons on the display device
Time
On Time Set the time to power on the selected display device
Screen Burn Protection
End Time Set end time to display screen saver
Start Time Set start time to display screen saver
Safety Screen Lamp Control
Enter a message to display on the screen
Enable or disable Ticker
Security Reset
Tool Settings
Options Edit Column
Edit Column
View the programme information
Monitor Window Information
Resizing a Window
Other Functions
Create groups and manage the list of sets on a group basis
Group Management
Deleting Groups
Renaming Groups
Schedule Management
Creating Schedules
Edit Group window displayed, click Rename
Deleting a Schedule
Schedule Modification
To modify a schedule, select the schedule and click Edit
To delete a schedule, select the schedule and click Delete
IssueSolution
Troubleshooting Guide
Remote control does not work
Following message appears
Page
Picture Mode
Screen Adjustment
If the input source is PC, DVI or DisplayPort
If the input source is AV, Component, HDMI1, HDMI2
Input source Picture Mode Adjustable options
100
MENUm → Picture → Entere
Screen Adjustment
Screen Adjustment
MENUm → Picture → Screen Adjustment → Entere
101
102
Picture Sizes available by Input Source
Input Source Picture Size
103
Position
Zoom/Position
PC Screen Adjustment
104
Screen Size
MENUm → Picture → Auto Adjustment → Entere
Auto Adjustment
Available resolutions Off / 1024x768 / 1280x768 / 1360x768
105
Aspect Ratio
Rotation
106
MENUm → Picture → Rotation → Entere
Advanced Settings
Advanced Settings
Input Source Picture Mode Advanced Settings
MENUm → Picture → Advanced Settings → Entere
108
White Balance
109
10p White Balance
Gamma
110
Expert Pattern
Motion Lighting
Picture Options
Input source Picture Mode Picture Options
111
Picture Options
Colour Tone
112
Colour Temp
Digital Noise Filter
113
Film Mode
Hdmi Black Level
Motion Plus
MENUm → Picture → Reset Picture → Entere
Reset Picture
Resets your current picture mode to its default settings
114
Sound Mode
Sound Adjustment
MENUm → Sound → Sound Mode → Entere
115
116
Sound Effect
MENUm → Sound → Speaker Settings → Entere
Speaker Settings
Auto Volume Off / Normal / Night
117
Reset all sound settings to the factory defaults
Reset Sound
MENUm → Sound → Reset Sound → Entere
118
Connecting to a Wired Network
Network Settings
Menu m → Network → Network Settings → Enter E
Network
120
Automatic Network Settings
Wired Network Settings
Getting the Network Connection Values
Manual Network Settings
123
Connecting to a Wireless Network
Automatic Network Setup
Wireless Network Setting
125
Manual Network Setup
126
How to set up manually
Go to Network Settings screen
How to set up using Wpspbc
If your router has a Wpspbc button, follow these steps
Select WPSPBC, press E, and then press E again
Network Status
You can check the current network and Internet status
Menu m → Network → Network Status → Enter E
Menu m → Network → Wi-Fi Direct → Enter E
Wi-Fi Direct
Menu m → Network → Soft AP → Enter E
Soft AP
Soft AP
Security Key
Using the AllShare Play Function
AllShare Settings
Menu m → Network → AllShare Settings → Enter E
Device Name
Multi Control
System
132
Multi Control
Time
Sleep Timer
133
Clock Set
On Timer
On Timer1 ~ On Timer7
134
Off Timer
135
Holiday Management
136
Menu Language
System
MENUm → System → Menu Language → Entere
Rotate menu
137
MENUm → System → Rotate menu → Entere
138
Eco Solution
Security
Safety Lock
139
Button Lock
140
PIP Settings
Main picture Sub picture
PC , DVI , HDMI1 , HDMI2 , DisplayPort , MagicInfo
141
Auto Protection Time
MENUm → System → Auto Protection Time → Entere
Off / 2 hours / 4 hours / 8 hours / 10 hours
Screen Burn Protection
Available Pixel Shift Settings and Optimum Settings
142
Pixel Shift
Timer
Timer
143
Immediate display
144
Rolling bar / Fading screen
Off / Light / Dark
145
Ticker
MENUm → System → Ticker → Entere
Vertical Top / Middle / Bottom
146
Video Wall
Video Wall
Format
147
Vertical
Screen Position
148
Source AutoSwitch Settings
149
General
150
Auto Power
Sound Feedback
Standby Control
Temperature Control
Power On Adjustment
151
Lamp Schedule
152
Anynet+ HDMI-CEC
Anynet+ HDMI-CEC
Anynet+ HDMI-CEC
153
Switching between Anynet+ Devices
Auto Turn Off
No / Yes
Problem Possible Solution
Troubleshooting for Anynet+
MessageDisconnecting
154
Problem
155
Connected device is not displayed
Play Mode
DivX Video On Demand
156
Magic Clone
Reset System
157
Magic Clone
PC module power
Reset All
Synced power-on
Synced power-off
MENUm → Support → Software Update → Entere
Software Update
Support
159
Contact Samsung
160
MENUm → Support → Contact Samsung → Entere
Contents Home
162
MENUm → Support → Contents Home → Source → Entere
AllShare Play
Edit Name
AllShare Play
What is AllShare Play?
163
USB HDD greater than 2TB is not supported
164
Compatible devices with AllShare Play
File system and formats
Connecting a USB device
Using a USB device
MENUm → Support → Contents Home → AllShare Play → Entere
165
Connecting to a PC over a network
Background Music On and Background Music Setting features
166
167
Using the AllShare Play features
168
Using the Basic AllShare Play Features
Sorting the file lists
Sort Criteria Operation Videos Photos Music
Playing Selected Files
169
Copying Files
Creating a Playlist
170
My list
My list options
Option Name Operations Recently played Whats new Playlist
Videos
Using the Play Continuously Function Resume Play
171
Playing a Video
Photos
172
Viewing a Photo or Slide Show
Music
173
Playing Music
Videos / Photos / Music Play Option menu
174
Option Name Operations Videos Photos Music
175
Supported Subtitle and AllShare Play file formats
Supported image resolutions
176
Subtitle
Supported music file formats
177
Supported Video Formats
File Extension Type Codec Comments
178
Read before using MagicInfo Lite player
MagicInfo Lite
179
180
Contents
Video Audio
181
Flash
182
183
3D Shadow Effects not supported
Vertical text
Access the server you have assigned to your device
Approving a connected device from the server
184
185
Device Group Select
To specify the group
186
MagicInfo Lite
MagicInfo Lite player
Network schedule
187
Local schedule
Internal Auto Play
USB Device Auto Play
188
189
Local Schedule Manager
Registering a Local schedule
Duration
190
Modifying a Local schedule
191
Deleting a Local schedule
192
Select Edit
Next, select Delete
Running a Local schedule
193
Stopping a Local schedule
Select Stop
194
Viewing the details of a Local schedule
Details of the schedule will be displayed
195
Copying a Local schedule
Device. Select Yes to copy the files
Copying content
Content manager
Select Content manager in the MagicInfo Lite menu screen
196
197
Deleting content
Server Network Settings
Settings
198
Active / Passive
199
When Content is Running
Viewing the details of the content that is running
200
PIP Off / On
201
Activate or deactivate the PIP function
Background Music Off / On
MagicInfo Premium S
Read before using MagicInfo Premium S Player
File Formats Compatible with MagicInfo Premium S Player
202
Fade1, Fade2, Blind, Spiral, Checker, Linear, Stairs, Wipe
203
Charts Vertical text
Flash Power Point
Masked Image, Tiled Image content not supported
204
Template files
205
Creation/editing/playback are only available
Template Manager Supported in USB Device Auto Play
Network Schedule Multiframe
206
Template files and LFD.lfd files
More than one sound output cannot be used
Others
207
208
209
MagicInfo Premium S
210
MagicInfo Premium S Player
Template Player
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
Template Manager
Registering a Template
221
Contents
Select sound or background music
222
223
224
To run MagicInfo Premium S, connect to a network
225
226
Copy Deployed Folders
Manual / Auto
227
228
MagicInfo Videowall S
Read before using MagicInfo Videowall S Player
File Formats Compatible with MagicInfo Videowall S Player
229
Video
230
Restrictions
231
Only one video Videos file can be played per client
Available
MENUm → Support → Contents Home → MagicInfo Videowall S →
Default Storage
MagicInfo Videowall S
232
233
Testing the Product
Troubleshooting Guide
Checking the Resolution and Frequency
234
Screen issue
Installation issue PC mode
Not Optimum Mode is displayed
235
236
Adjust Brightness and Contrast
Sharpness
237
Sound issue
238
Go to Sound and change Speaker Select to Internal
Source device issue
Remote control issue
There is audible sound when the volume is muted
239
Can I update the software driver while in WiDi mode?
Intel WiDi connection issue
240
Unable to establish a WiDi connection
241
Do not change the wireless LAN settings while in WiDi mode
Want to change the size of the WiDi screen
How can I obtain the WiDi software driver?
Menu is enabled or disabled depending on the Source mode
Other issue
242
Small particles are found on the edges of the product
243
There is no sound in Hdmi mode
DVI-HDMI cable is connected
Device with YCbCr output
244
PC display settings cannot be saved
How can I change the resolution?
Settings
245
Question Answer
How do I set powersaving mode?
246
Question
247
Specifications
248
249
Power Indicator
PowerSaver
Power Consumption
250
Preset Timing Modes
251
Vertical Frequency Pixel Clock Sync Polarity KHz MHz
252
Appendix
Contact Samsung World Wide
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
0685 88 99
261
0800 300
211350370
262
Product damage caused by customers fault
Not a product defect
Others
263
Correct disposal of batteries in this product
Applicable in countries with separate collection systems
Optimum Picture Quality and Afterimage Burn-in Prevention
264
Optimum Picture Quality
265
What is afterimage burn-in?
Prevention of Afterimage Burn-in
Preventing afterimage burn-in
Move and change text every 30 minutes as shown below
266
267
Licence
268
Terminology