Transmission of
Video Signals
A CCTV signal contains a wide range of frequencies from around 30 hertz to around 10 Megahertz. As a result special circuits are required to cope with the wide
Because signals from CCTV cameras often have to travel long distances to reach the control centre, the choice of transmission medium depends upon the particular installation and its requirements.
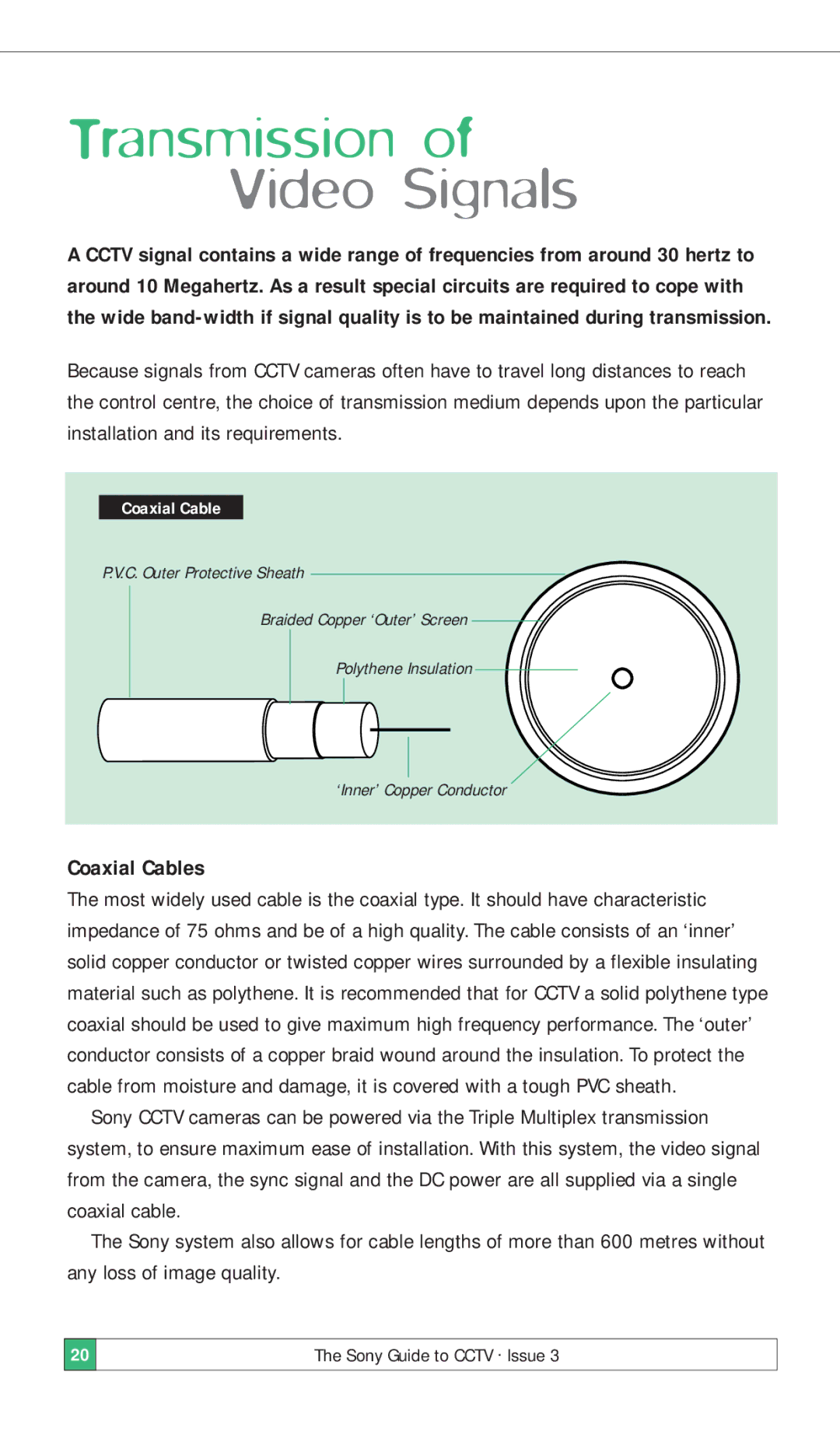
Coaxial Cable
P.V.C. Outer Protective Sheath
Braided Copper ‘Outer’ Screen
Polythene Insulation
‘Inner’ Copper Conductor
Coaxial Cables
The most widely used cable is the coaxial type. It should have characteristic impedance of 75 ohms and be of a high quality. The cable consists of an ‘inner’ solid copper conductor or twisted copper wires surrounded by a flexible insulating material such as polythene. It is recommended that for CCTV a solid polythene type coaxial should be used to give maximum high frequency performance. The ‘outer’ conductor consists of a copper braid wound around the insulation. To protect the cable from moisture and damage, it is covered with a tough PVC sheath.
Sony CCTV cameras can be powered via the Triple Multiplex transmission system, to ensure maximum ease of installation. With this system, the video signal from the camera, the sync signal and the DC power are all supplied via a single coaxial cable.
The Sony system also allows for cable lengths of more than 600 metres without any loss of image quality.
20
The Sony Guide to CCTV . Issue 3