Choosing a Camera
developed a range of
solutions, the most popular of which include
hybrid cameras that operate in colour when lighting is adequate, switching to monochrome as darkness falls. Some
cameras operate in low light by reducing the
number of frames captured to produce a
brighter picture although this causes problems when there is movement within the image.
Sony has developed a more radical approach by improving the sensitivity
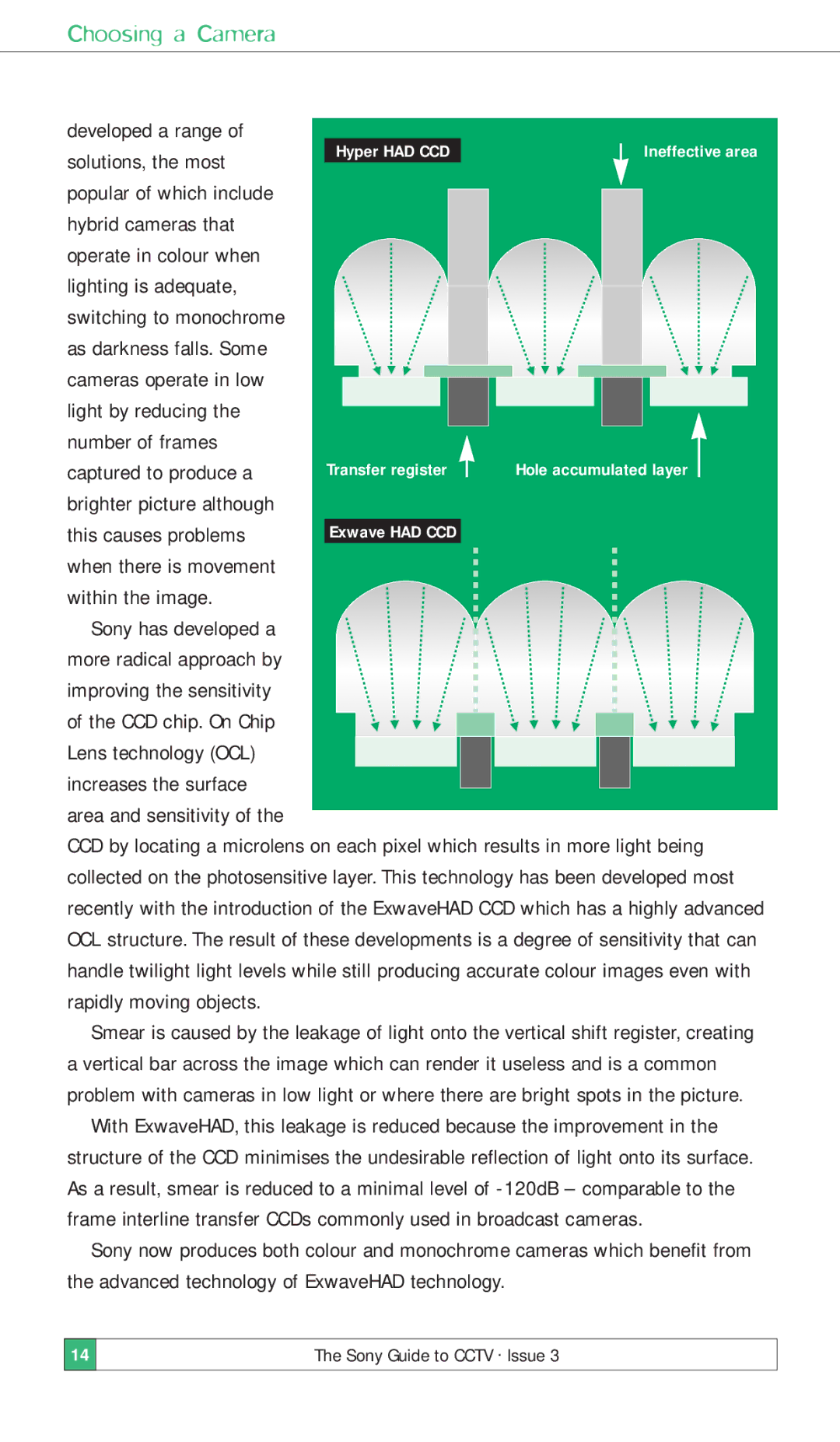
of the CCD chip. On Chip Lens technology (OCL) increases the surface
area and sensitivity of the
CCD by locating a microlens on each pixel which results in more light being collected on the photosensitive layer. This technology has been developed most recently with the introduction of the ExwaveHAD CCD which has a highly advanced OCL structure. The result of these developments is a degree of sensitivity that can handle twilight light levels while still producing accurate colour images even with rapidly moving objects.
Smear is caused by the leakage of light onto the vertical shift register, creating a vertical bar across the image which can render it useless and is a common problem with cameras in low light or where there are bright spots in the picture.
With ExwaveHAD, this leakage is reduced because the improvement in the structure of the CCD minimises the undesirable reflection of light onto its surface. As a result, smear is reduced to a minimal level of
Sony now produces both colour and monochrome cameras which benefit from the advanced technology of ExwaveHAD technology.
14
The Sony Guide to CCTV . Issue 3