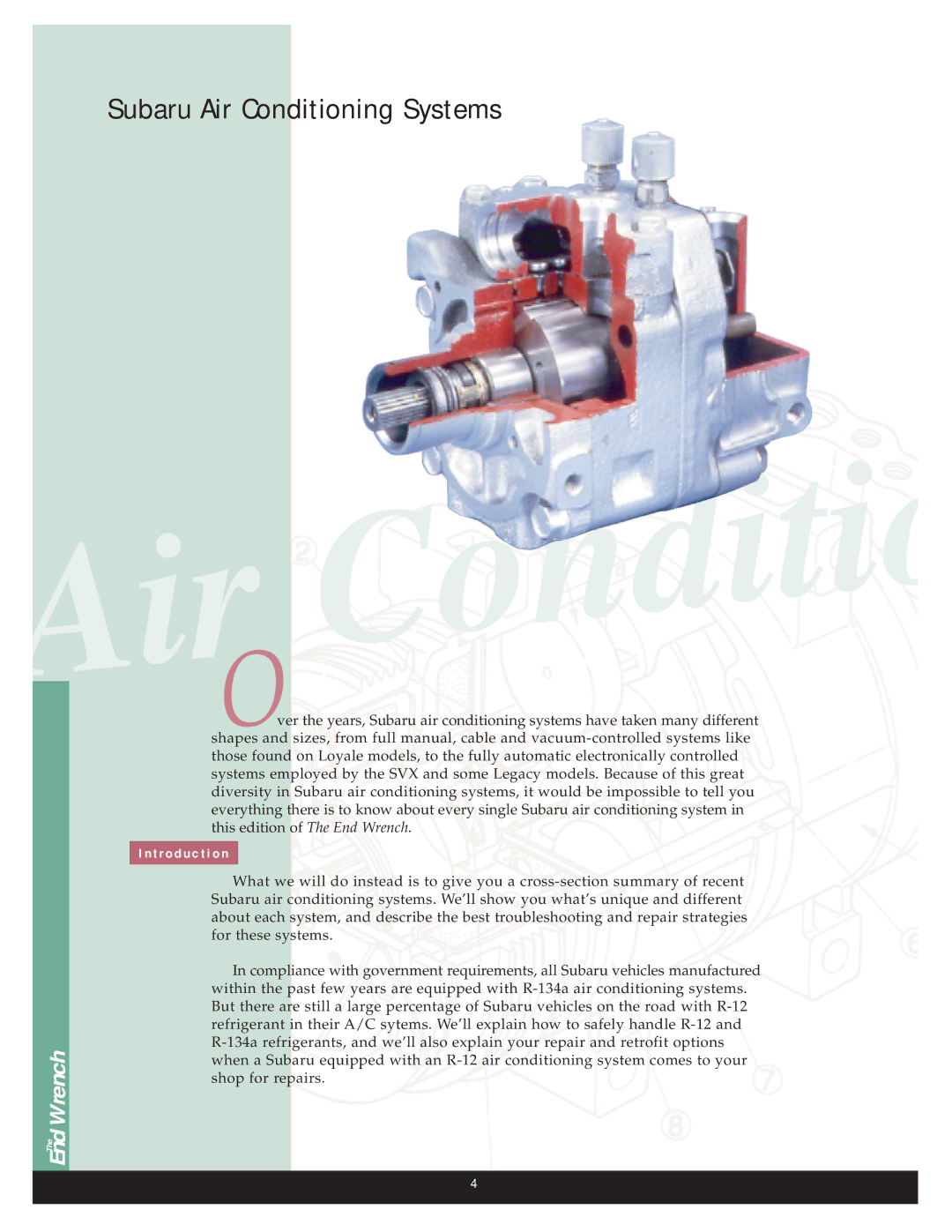
R-12, R-134A specifications
Subaru, a renowned automotive manufacturer, has made significant advancements in its air conditioning refrigerant technologies, particularly in its use of R-12 and R-134A. Understanding these refrigerants is crucial for enthusiasts and technicians alike, as they are integral to Subaru's climate control systems.R-12, also known as dichlorodifluoromethane, was commonly used in automotive air conditioning systems until the late 20th century. It is a chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) that proved to be highly efficient in cooling systems, offering optimal performance in various conditions. However, environmental concerns over ozone depletion led to a phasedown of its use. Subaru vehicles produced before the early 1990s often utilized R-12, characterized by its stable properties and excellent thermodynamic performance. Despite its effectiveness, the negative environmental impact of R-12 has rendered it obsolete in modern automotive applications.
Adapting to these challenges, Subaru transitioned to R-134A, or tetrafluoroethane, in the 1990s. R-134A is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) that does not deplete the ozone layer, making it a more environmentally friendly alternative to R-12. This transition coincided with Subaru's commitment to sustainability and compliance with international regulations. R-134A boasts several advantages, including lower global warming potential and improved efficiency in cooling performance. Its thermodynamic properties provide effective heat absorption, ensuring that Subaru drivers can rely on consistent climate control, regardless of external temperatures.
Subaru has integrated R-134A into its vehicle technology without compromising performance. Newer models utilize advanced HVAC systems that maximize refrigerant efficiency while maintaining comfort. Features such as variable compressor speed control enhance overall system performance, allowing for quicker cooling response and reduced energy consumption. Additionally, Subaru employs meticulous system designs to minimize refrigerant leakage, further supporting environmental initiatives.
The transition from R-12 to R-134A exemplifies Subaru's responsiveness to both performance and environmental concerns. As regulations continue to evolve, it's expected that Subaru will continue to innovate in refrigerant technology, prioritizing sustainability while delivering reliable and efficient climate control for its drivers. As vehicle technology advances, it's clear that Subaru remains committed to adapting its systems for a cleaner, more efficient future.