Blood pressure is measured in millimeters (mm) of mercury (Hg) and is generally recorded with the systolic pressure (120) listed first and the diastolic pressure (80) listed second. The numbers are typically separated by a slash mark (/) as shown.
Both pressure readings, the SYSTOLIC and DIASTOLIC, are necessary for a physician to evaluate the status of a patient’s blood pressure.
Please contact your physician for specific information regarding your own blood pressure.
What Influences Blood Pressure?
Many factors such as genetics, age, sex, altitude, physical activity, anxiety, muscular devel- opment, certain medications or even the time of day can influence blood pressure. Influences such as sleep or relaxation decrease blood pressure, while anxiety or exercise increase blood pressure.
WHO Blood Pressure Classifications
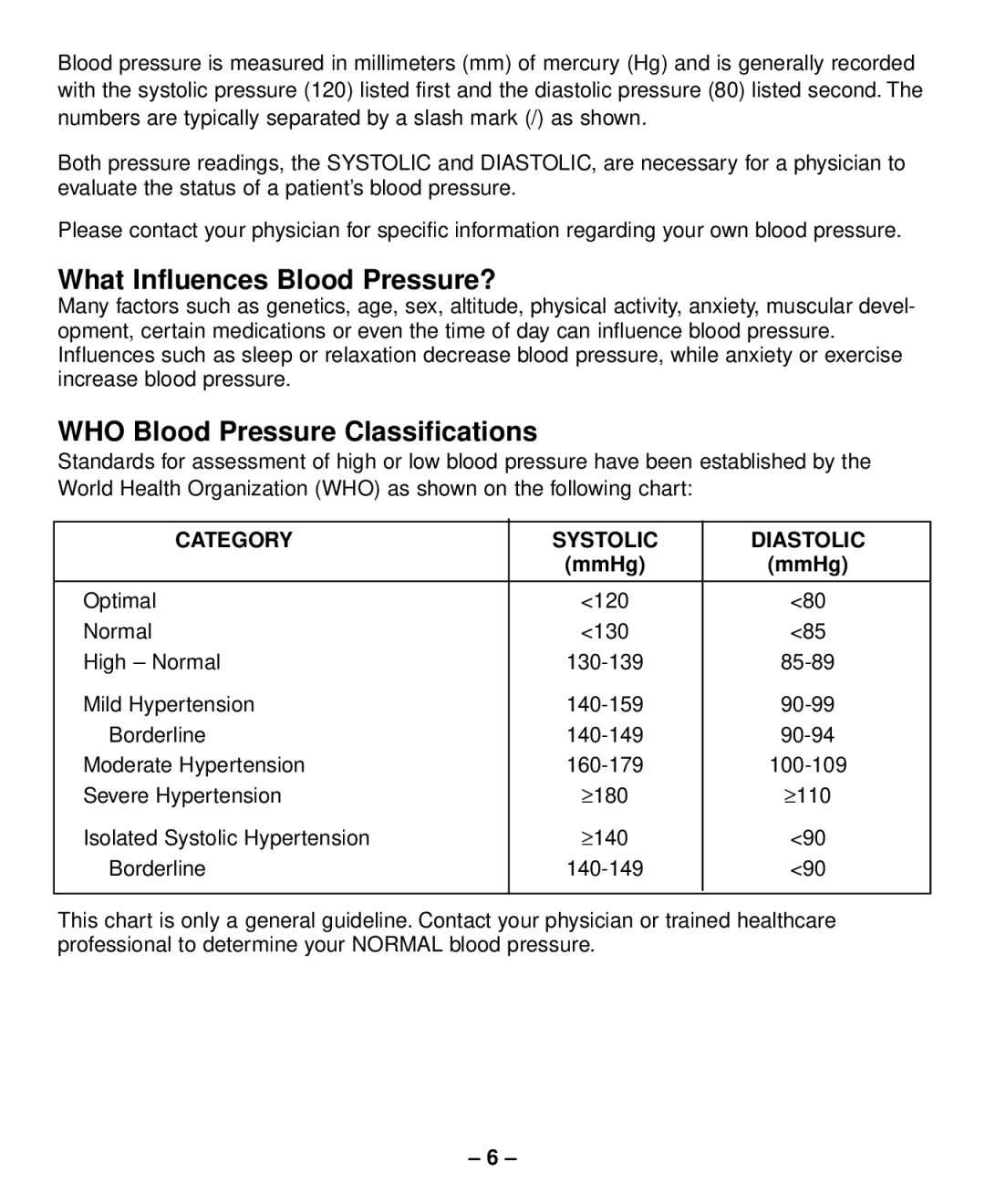
Standards for assessment of high or low blood pressure have been established by the World Health Organization (WHO) as shown on the following chart:
CATEGORY | SYSTOLIC | DIASTOLIC |
| (mmHg) | (mmHg) |
|
|
|
Optimal | <120 | <80 |
Normal | <130 | <85 |
High – Normal | ||
Mild Hypertension | ||
Borderline | ||
Moderate Hypertension | ||
Severe Hypertension | ≥ 180 | ≥ 110 |
Isolated Systolic Hypertension | ≥ 140 | <90 |
Borderline | <90 | |
|
|
|
This chart is only a general guideline. Contact your physician or trained healthcare professional to determine your NORMAL blood pressure.
– 6 –