First, the input signal is divided into its low- and
Because the
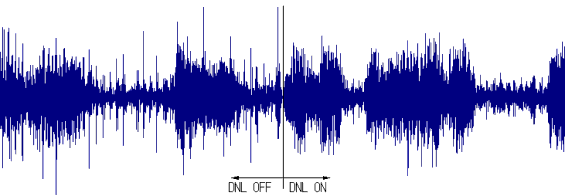
Fig.14 demonstrates how ignition noise is reduced by the DNL.
Fig. 14: The effect of DNL on ignition noise
The DNL works in SSB, CW, FSK and AM modes, and it can be used in conjunction with other interference reduction and noise elimination features.
●Noise reduction
There are two methods available for noise reduction: NR1 and NR2. NR1 is a line enhancer that employs adaptive filter technology. By shaping a filter that lets through signals with a certain amount of periodicity, as with voice and CW, it can suppress noise that falls outside the passband. NR2 employs what is known as SPAC (speech processing by auto correlation) technology. What results from looping one cycle of the RX signal’s autocorrelation coefficient is then output as the received audio. What this means is that only periodic signals found in the received audio emerge. In principle this approach can result in a small amount of noise at the “seam” where the periodic signal is looped together, but in practice it proves extremely effective at noise compression.
NR1 is a good choice for SSB and other audio signals, while NR2 is especially effective when used with single frequencies, as with a CW signal.
Figs. 15~17 demonstrate the effect of applying NR1 and NR2. For comparison purposes, the same weak sine signal was received, with the audio output monitored by an FFT analyzer.
23