DV135
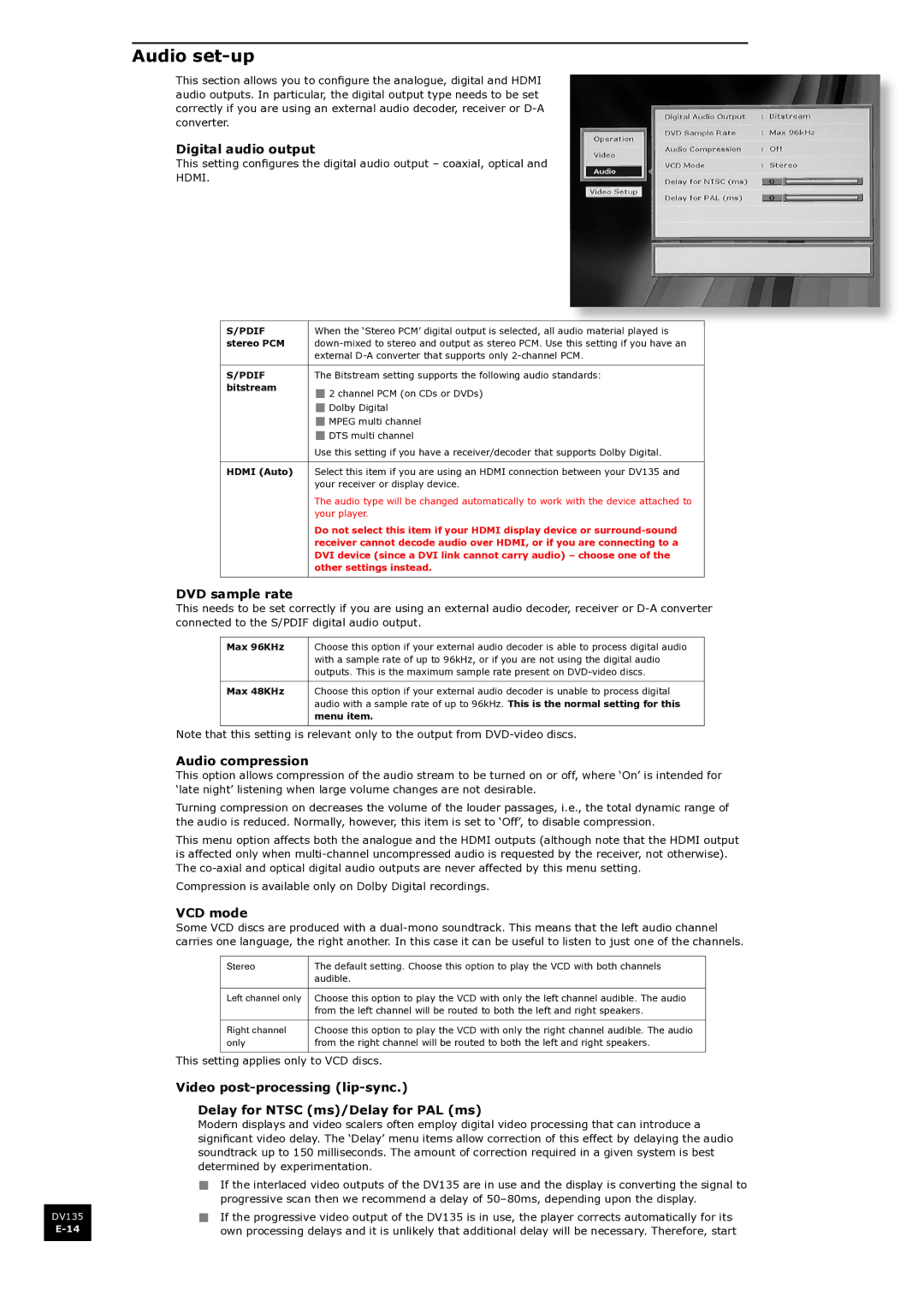
Audio set-up
This section allows you to configure the analogue, digital and HDMI audio outputs. In particular, the digital output type needs to be set correctly if you are using an external audio decoder, receiver or
Digital audio output
This setting configures the digital audio output – coaxial, optical and
HDMI.
|
|
|
|
S/PDIF | When the ‘Stereo PCM’ digital output is selected, all audio material played is |
| |
| |||
stereo PCM |
| ||
| external |
| |
|
|
|
|
S/PDIF | The Bitstream setting supports the following audio standards: |
| |
bitstream | < 2 channel PCM (on CDs or DVDs) |
| |
|
| ||
| < Dolby Digital |
| |
| < MPEG multi channel |
| |
| < DTS multi channel |
| |
| Use this setting if you have a receiver/decoder that supports Dolby Digital. |
| |
|
|
|
|
HDMI (Auto) | Select this item if you are using an HDMI connection between your DV135 and |
| |
| your receiver or display device. |
| |
| The audio type will be changed automatically to work with the device attached to |
| |
| your player. |
| |
| Do not select this item if your HDMI display device or |
| |
| receiver cannot decode audio over HDMI, or if you are connecting to a |
| |
| DVI device (since a DVI link cannot carry audio) – choose one of the |
| |
| other settings instead. |
| |
|
|
|
|
DVD sample rate
This needs to be set correctly if you are using an external audio decoder, receiver or
Max 96KHz | Choose this option if your external audio decoder is able to process digital audio |
| with a sample rate of up to 96kHz, or if you are not using the digital audio |
| outputs. This is the maximum sample rate present on |
|
|
Max 48KHz | Choose this option if your external audio decoder is unable to process digital |
| audio with a sample rate of up to 96kHz. This is the normal setting for this |
| menu item. |
|
|
Note that this setting is relevant only to the output from
Audio compression
This option allows compression of the audio stream to be turned on or off, where ‘On’ is intended for ‘late night’ listening when large volume changes are not desirable.
Turning compression on decreases the volume of the louder passages, i.e., the total dynamic range of the audio is reduced. Normally, however, this item is set to ‘Off’, to disable compression.
This menu option affects both the analogue and the HDMI outputs (although note that the HDMI output is affected only when
Compression is available only on Dolby Digital recordings.
VCD mode
Some VCD discs are produced with a
Stereo | The default setting. Choose this option to play the VCD with both channels |
| audible. |
|
|
Left channel only | Choose this option to play the VCD with only the left channel audible. The audio |
| from the left channel will be routed to both the left and right speakers. |
|
|
Right channel | Choose this option to play the VCD with only the right channel audible. The audio |
only | from the right channel will be routed to both the left and right speakers. |
|
|
This setting applies only to VCD discs.
Video
Delay for NTSC (ms)/Delay for PAL (ms)
Modern displays and video scalers often employ digital video processing that can introduce a significant video delay. The ‘Delay’ menu items allow correction of this effect by delaying the audio soundtrack up to 150 milliseconds. The amount of correction required in a given system is best determined by experimentation.
<If the interlaced video outputs of the DV135 are in use and the display is converting the signal to progressive scan then we recommend a delay of
<If the progressive video output of the DV135 is in use, the player corrects automatically for its own processing delays and it is unlikely that additional delay will be necessary. Therefore, start