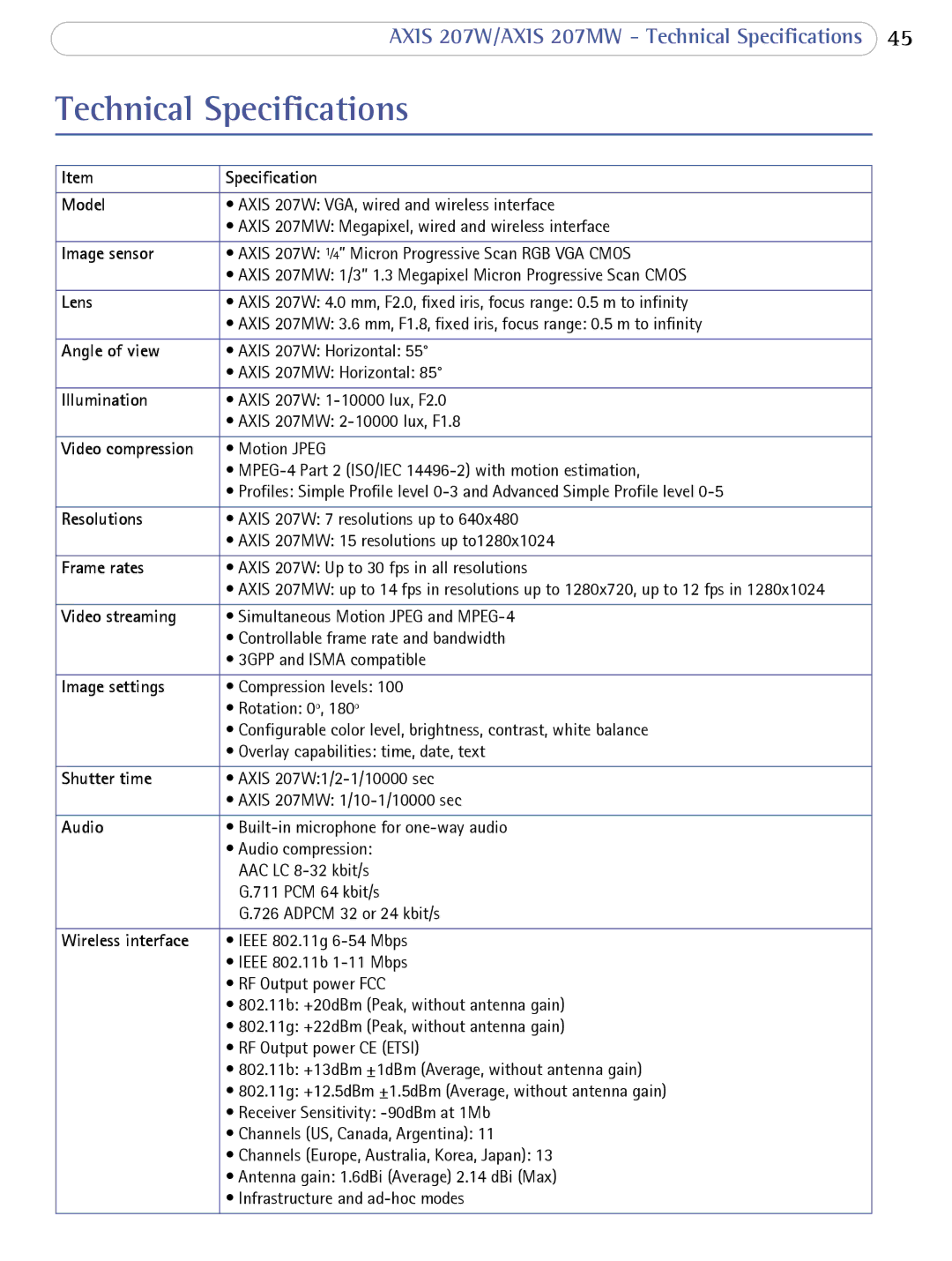
207W specifications
The Axis Communications 207W is a versatile and compact network camera designed to offer high-quality video surveillance along with ease of installation and use. A part of Axis’s extensive range of cameras, the 207W brings features you would expect from a professional-grade security camera while ensuring flexibility for small to medium-sized installations.One of the standout features of the Axis 207W is its wireless connectivity. This allows users to place the camera in locations where running cables would be challenging or impractical. The camera supports Wi-Fi connectivity, which simplifies the installation process significantly and offers greater freedom in positioning the device for optimal field of view.
Equipped with a 1/4-inch progressive scan CMOS sensor, the Axis 207W captures high-resolution video at a resolution of 640x480 pixels. The camera's frame rate supports up to 30 frames per second in standard quality, ensuring smooth video playback and reliable motion detection. This is particularly beneficial for environments where detail is crucial, such as retail stores and office spaces.
The camera also leverages Axis’s renowned Color and Day/Night technology, allowing it to automatically switch between color mode during the day and black-and-white mode at night. The infrared capability enhances nighttime surveillance, ensuring that users receive clear images even in low-light conditions, significantly improving security around the clock.
In terms of durability, the Axis 207W is designed with a solid construction, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor deployment. The camera includes a tamper-resistant feature, adding an additional layer of security.
Easy integration is another vital characteristic of the 207W. It supports various streaming protocols, including RTSP and RTP, facilitating seamless integration with existing surveillance systems or third-party applications. This versatility allows for flexible use in different environments without locking users into a specific ecosystem.
The user-friendly interface accompanying the camera enhances its accessibility for users of all experience levels, making it easy to manage and configure settings via a web-based interface. Overall, the Axis Communications 207W stands out as a powerful and flexible solution for those seeking reliable security surveillance technology. With its robust feature set, it caters to a wide range of applications, ensuring peace of mind for users.