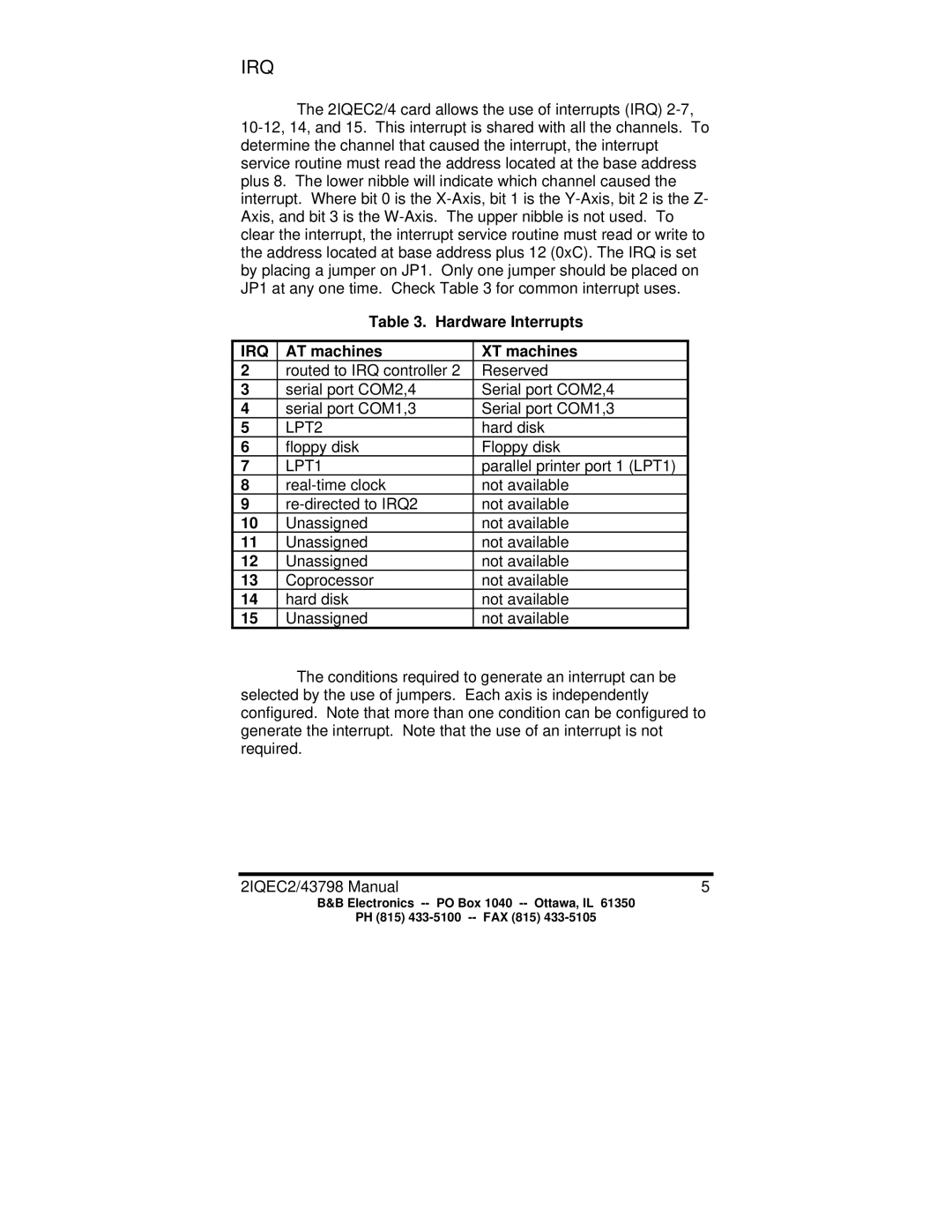
2IQEC2, 2IQEC4 specifications
B&B Electronics has long been a key player in the field of industrial communication and networking solutions, and their 2IQEC4 and 2IQEC2 devices stand as reflective examples of their innovation and dedication to quality. These devices are part of the company's extensive range designed to facilitate communication in diverse industrial settings, ensuring reliability and efficiency.The 2IQEC4 is a robust 4-port Ethernet switch, while the 2IQEC2 serves as a 2-port variant. Both models are integrated with advanced technologies to deliver seamless connectivity in environments where durability and performance are critical. One of the standout features of these devices is their compatibility with Power over Ethernet (PoE), which allows for simpler installations by eliminating the need for separate power sources for each connected device.
These Ethernet switches are engineered for industrial applications, meaning they can withstand harsh conditions, including extreme temperatures, vibration, and electromagnetic interference. Their rugged design ensures reliable operation in demanding environments, making them ideal for industries such as manufacturing, transportation, and utility management.
Both the 2IQEC4 and 2IQEC2 come equipped with advanced security features including VLAN support and IGMP snooping, which help to optimize traffic performance and enhance overall network security. These functionalities are crucial in preventing unauthorized access, managing bandwidth efficiently, and minimizing potential network congestion.
In terms of installation and management, B&B Electronics has designed these devices for user-friendliness. The web-based management interface allows for straightforward configuration and monitoring, empowering users to manage their networks with ease. Additionally, diagnostic LEDs provide real-time feedback on device status, facilitating quick troubleshooting and maintenance.
The Ethernet switches also support a wide range of networking protocols, which ensures compatibility with various industrial devices and systems. This flexibility makes them suitable for integrating with existing infrastructure while also enabling future scalability as a network grows or evolves.
In summary, B&B Electronics' 2IQEC4 and 2IQEC2 models offer a reliable, efficient, and secure solution for industrial networking. With their robust construction, advanced features, and user-friendly management capabilities, these Ethernet switches are well-equipped to meet the challenges of modern industrial environments, making them invaluable assets in enhancing communication and operational efficiency.