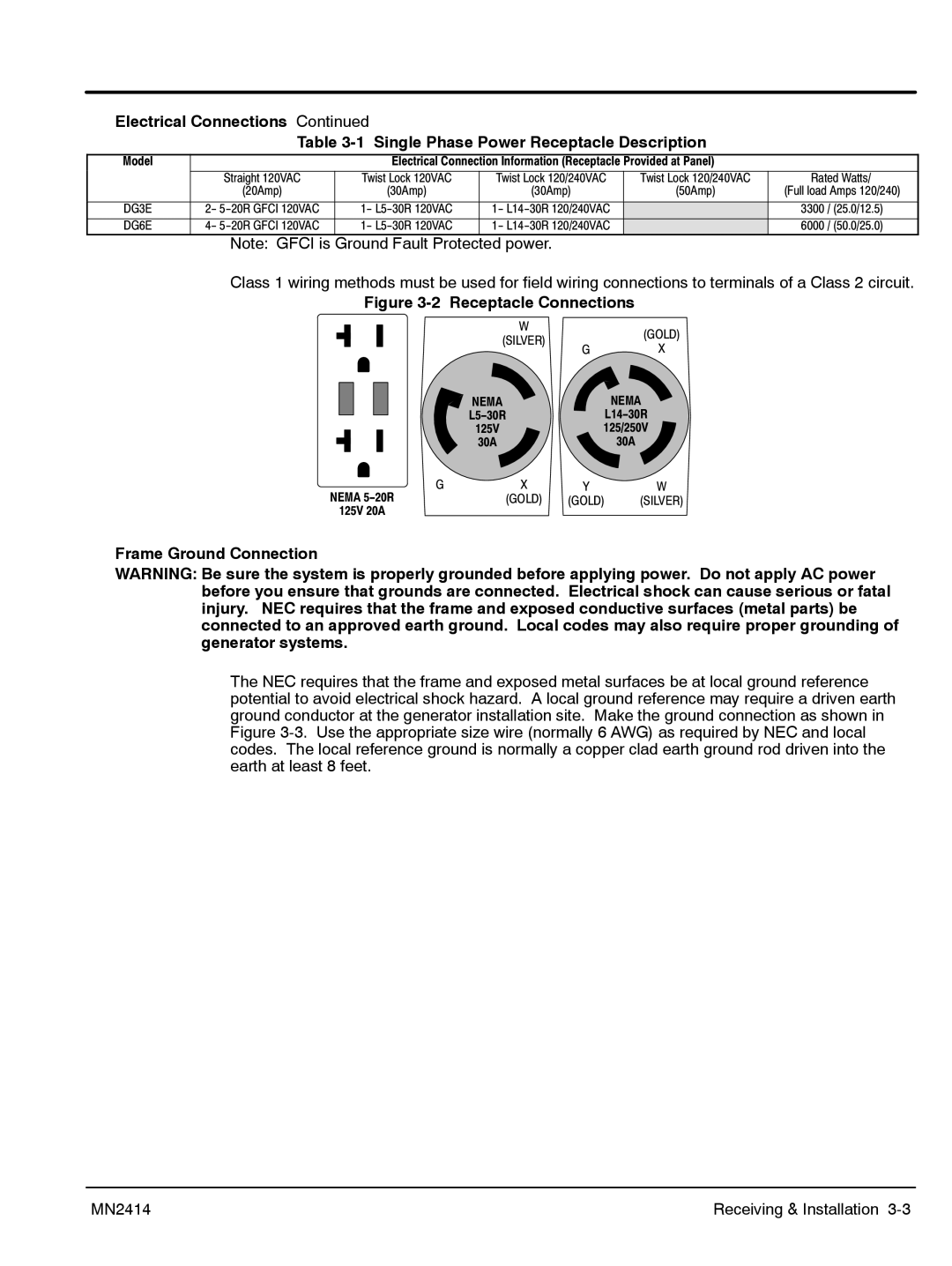
Electrical Connections Continued
Table
Model |
| Electrical Connection Information (Receptacle Provided at Panel) |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Straight 120VAC | Twist Lock 120VAC | Twist Lock 120/240VAC | Twist Lock 120/240VAC | Rated Watts/ |
| (20Amp) | (30Amp) | (30Amp) | (50Amp) | (Full load Amps 120/240) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
DG3E | 2− 5−20R GFCI 120VAC | 1− L5−30R 120VAC | 1− L14−30R 120/240VAC |
| 3300 / (25.0/12.5) |
DG6E | 4− 5−20R GFCI 120VAC | 1− L5−30R 120VAC | 1− L14−30R 120/240VAC |
| 6000 / (50.0/25.0) |
Note: GFCI is Ground Fault Protected power.
Class 1 wiring methods must be used for field wiring connections to terminals of a Class 2 circuit.
Figure 3-2 Receptacle Connections
| W |
| (GOLD) |
| (SILVER) |
| |
| G | X | |
|
| ||
| NEMA |
| NEMA |
| L5−30R |
| L14−30R |
| 125V | 125/250V | |
| 30A |
| 30A |
G | X | Y | W |
NEMA 5−20R | (GOLD) | (GOLD) | (SILVER) |
125V 20A |
|
|
|
Frame Ground Connection
WARNING: Be sure the system is properly grounded before applying power. Do not apply AC power before you ensure that grounds are connected. Electrical shock can cause serious or fatal injury. NEC requires that the frame and exposed conductive surfaces (metal parts) be connected to an approved earth ground. Local codes may also require proper grounding of generator systems.
The NEC requires that the frame and exposed metal surfaces be at local ground reference potential to avoid electrical shock hazard. A local ground reference may require a driven earth ground conductor at the generator installation site. Make the ground connection as shown in Figure
MN2414 | Receiving & Installation |