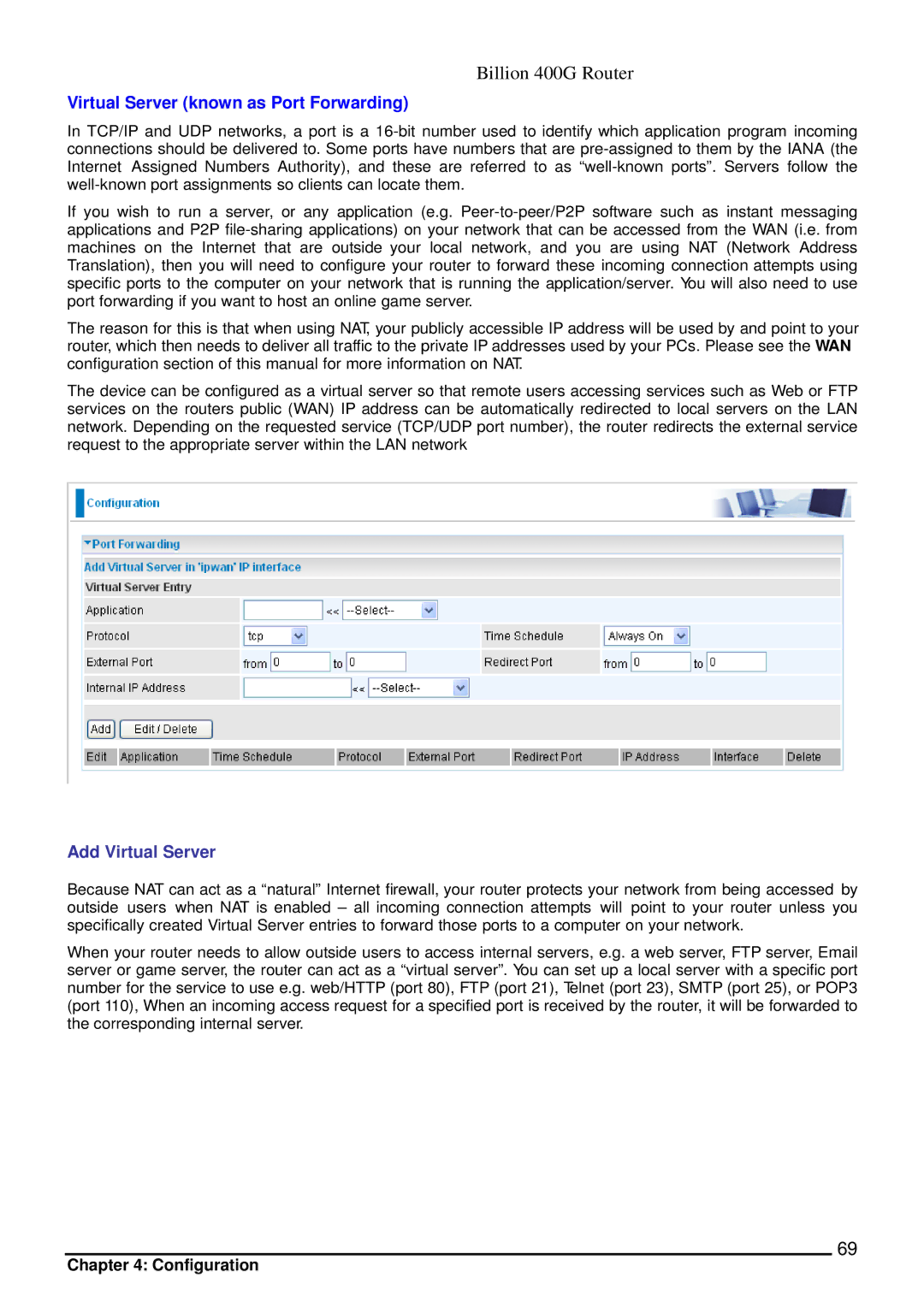
400G specifications
Billion Electric Company, a prominent player in the telecommunications and networking industry, has made significant strides with its new 400G solutions that stand out due to their innovative features and technologies. The 400G technology is designed to meet the ever-increasing demand for higher bandwidth and faster data transfer speeds, particularly in data centers, enterprise networks, and service providers.One of the main features of Billion Electric's 400G offering is its scalability. The architecture supports a range of interfaces and can be easily integrated into existing networks, allowing for smooth upgrades from lower-capacity systems. This adaptability ensures that businesses can accommodate future growth without overhauling their entire infrastructure.
The 400G solutions utilize advanced photonic technology, which enhances data transmission by reducing latency and maximizing throughput. This is particularly beneficial for applications such as cloud computing, big data analytics, and high-definition video streaming, where speed and reliability are paramount. Moreover, Billion Electric employs cutting-edge modulation techniques and optical networking solutions, ensuring robust performance even at high data rates.
Another noteworthy aspect of Billion Electric’s 400G technology is its energy efficiency. In an era where sustainability is crucial, the company has developed solutions that not only provide high performance but also minimize energy consumption. The integration of AI-based network management tools further enhances operational efficiency by optimizing resource allocation and reducing operational costs.
In terms of network resilience, Billion Electric's 400G solutions feature built-in redundancy and failover capabilities. This ensures that essential services remain uninterrupted, which is critical for industries relying on continuous connectivity. Additionally, security protocols are embedded within the system, offering enhanced protection against potential cyber threats.
Furthermore, Billion Electric provides comprehensive support and training, empowering businesses to effectively transition to 400G technology. With a focus on customer satisfaction and operational excellence, the company positions itself as a trusted partner in the ever-evolving telecommunication landscape.
In summary, Billion Electric’s 400G solutions are characterized by their scalability, advanced photonic technology, energy efficiency, network resilience, and robust support. These features collectively cater to the modern demands of high-speed networking, setting a new standard in performance and reliability for telecommunications infrastructure. As digital transformation accelerates, Billion Electric continues to innovate, leading the way in the next generation of connectivity.