Physical data (continued)
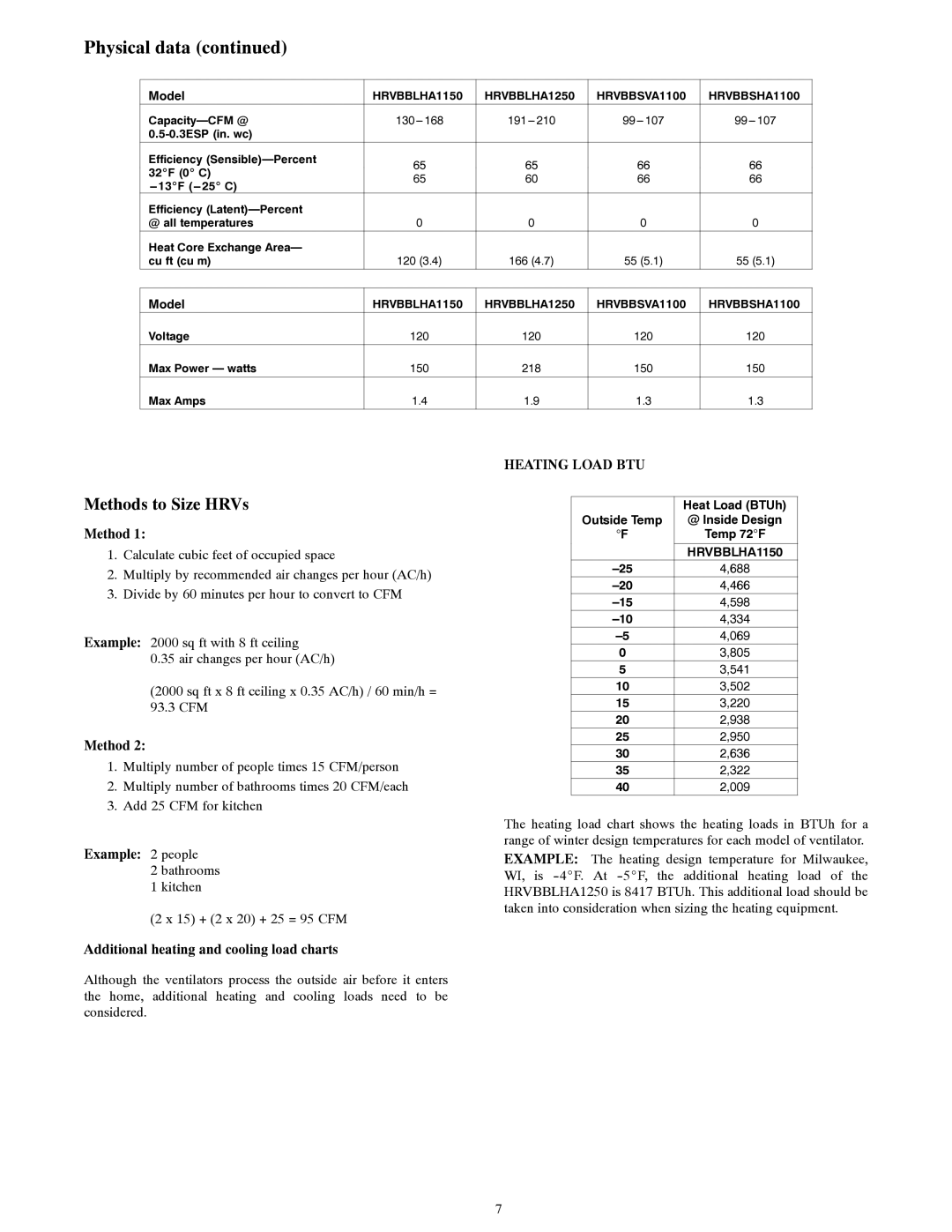
Model | HRVBBLHA1150 | HRVBBLHA1250 | HRVBBSVA1100 | HRVBBSHA1100 | |
|
|
|
| ||
Efficiency | 65 | 65 | 66 | 66 | |
32_F (0_ C) | |||||
65 | 60 | 66 | 66 | ||
|
|
|
| ||
Efficiency |
|
|
|
| |
@ all temperatures | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Heat Core Exchange Area— |
|
|
|
| |
cu ft (cu m) | 120 (3.4) | 166 (4.7) | 55 (5.1) | 55 (5.1) |
Model | HRVBBLHA1150 | HRVBBLHA1250 | HRVBBSVA1100 | HRVBBSHA1100 |
Voltage | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
Max Power — watts | 150 | 218 | 150 | 150 |
Max Amps | 1.4 | 1.9 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
Methods to Size HRVs
Method 1:
1.Calculate cubic feet of occupied space
2.Multiply by recommended air changes per hour (AC/h)
3.Divide by 60 minutes per hour to convert to CFM
Example: 2000 sq ft with 8 ft ceiling 0.35 air changes per hour (AC/h)
(2000 sq ft x 8 ft ceiling x 0.35 AC/h) / 60 min/h = 93.3 CFM
Method 2:
1.Multiply number of people times 15 CFM/person
2.Multiply number of bathrooms times 20 CFM/each
3.Add 25 CFM for kitchen
Example: 2 people
2bathrooms
1kitchen
(2 x 15) + (2 x 20) + 25 = 95 CFM
Additional heating and cooling load charts
Although the ventilators process the outside air before it enters the home, additional heating and cooling loads need to be considered.
HEATING LOAD BTU
Outside Temp | Heat Load (BTUh) |
@ Inside Design | |
°F | Temp 72°F |
| HRVBBLHA1150 |
4,688 | |
4,466 | |
4,598 | |
4,334 | |
4,069 | |
0 | 3,805 |
5 | 3,541 |
10 | 3,502 |
15 | 3,220 |
20 | 2,938 |
25 | 2,950 |
30 | 2,636 |
35 | 2,322 |
40 | 2,009 |
The heating load chart shows the heating loads in BTUh for a range of winter design temperatures for each model of ventilator.
EXAMPLE: The heating design temperature for Milwaukee, WI, is
7