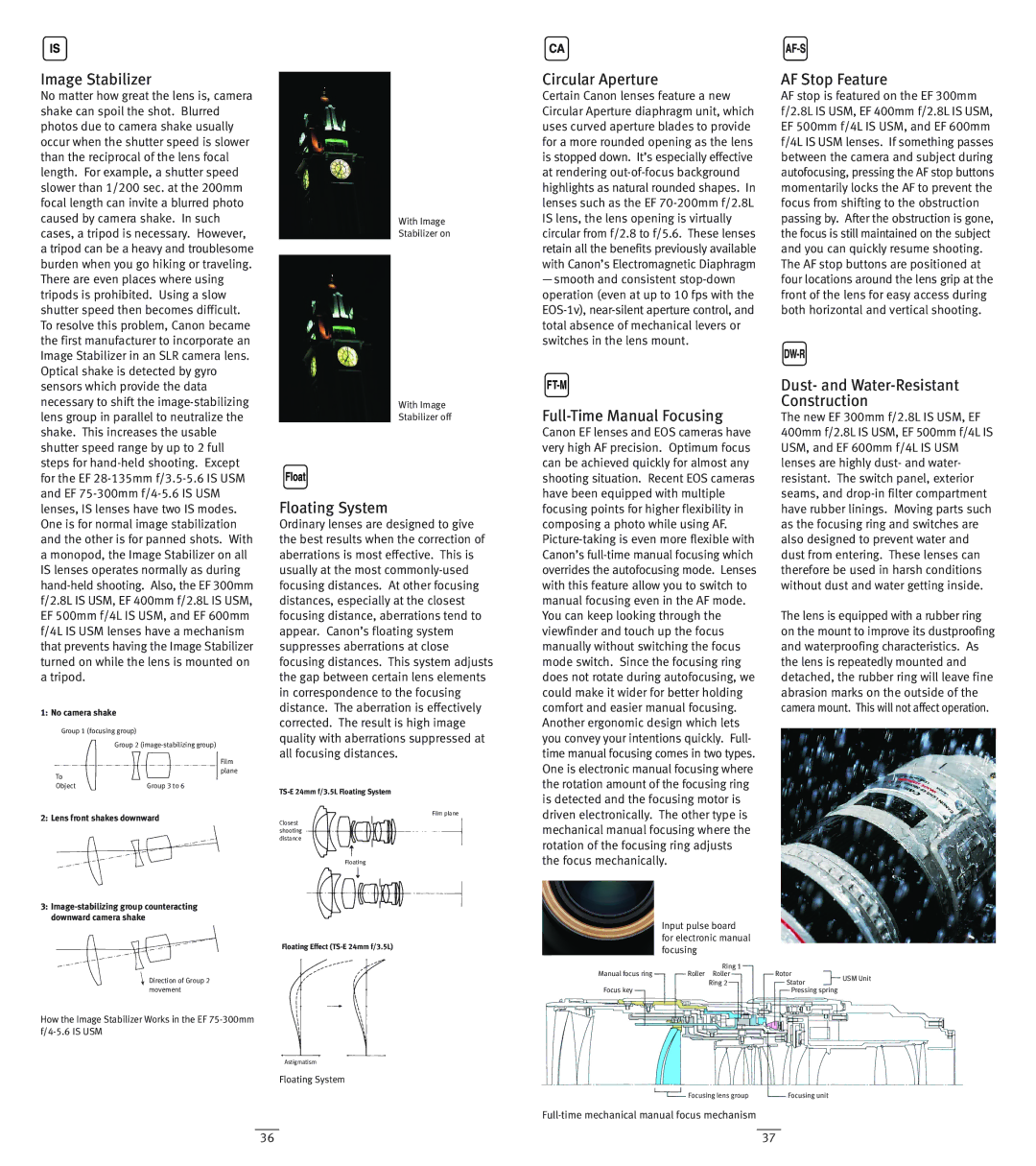
Image Stabilizer
No matter how great the lens is, camera shake can spoil the shot. Blurred photos due to camera shake usually occur when the shutter speed is slower than the reciprocal of the lens focal length. For example, a shutter speed slower than 1/200 sec. at the 200mm focal length can invite a blurred photo caused by camera shake. In such cases, a tripod is necessary. However, a tripod can be a heavy and troublesome burden when you go hiking or traveling. There are even places where using tripods is prohibited. Using a slow shutter speed then becomes difficult. To resolve this problem, Canon became the first manufacturer to incorporate an Image Stabilizer in an SLR camera lens. Optical shake is detected by gyro
With Image Stabilizer on
Circular Aperture
Certain Canon lenses feature a new Circular Aperture diaphragm unit, which uses curved aperture blades to provide for a more rounded opening as the lens is stopped down. It’s especially effective at rendering
—smooth and consistent
AF Stop Feature
AF stop is featured on the EF 300mm f/2.8L IS USM, EF 400mm f/2.8L IS USM, EF 500mm f/4L IS USM, and EF 600mm f/4L IS USM lenses. If something passes between the camera and subject during autofocusing, pressing the AF stop buttons momentarily locks the AF to prevent the focus from shifting to the obstruction passing by. After the obstruction is gone, the focus is still maintained on the subject and you can quickly resume shooting. The AF stop buttons are positioned at four locations around the lens grip at the front of the lens for easy access during both horizontal and vertical shooting.
sensors which provide the data necessary to shift the
1: No camera shake
Group 1 (focusing group)
Group 2
Film plane
To |
|
Object | Group 3 to 6 |
2: Lens front shakes downward
With Image
Stabilizer off
Floating System
Ordinary lenses are designed to give the best results when the correction of aberrations is most effective. This is usually at the most
Film plane
Closest shooting distance
Floating
Full-Time Manual Focusing
Canon EF lenses and EOS cameras have very high AF precision. Optimum focus can be achieved quickly for almost any shooting situation. Recent EOS cameras have been equipped with multiple focusing points for higher flexibility in composing a photo while using AF.
Dust- and Water-Resistant Construction
The new EF 300mm f/2.8L IS USM, EF 400mm f/2.8L IS USM, EF 500mm f/4L IS USM, and EF 600mm f/4L IS USM lenses are highly dust- and water- resistant. The switch panel, exterior seams, and
The lens is equipped with a rubber ring on the mount to improve its dustproofing and waterproofing characteristics. As the lens is repeatedly mounted and detached, the rubber ring will leave fine abrasion marks on the outside of the camera mount. This will not affect operation.
3:
Floating Effect
Direction of Group 2 movement
How the Image Stabilizer Works in the EF
Astigmatism
Floating System
Input pulse board for electronic manual focusing
| Ring 1 |
|
|
Manual focus ring | Roller Roller | Rotor | USM Unit |
| Ring 2 | Stator | |
|
| ||
Focus key |
| Pressing spring |
|
Focusing lens group | Focusing unit |
36 | 37 |