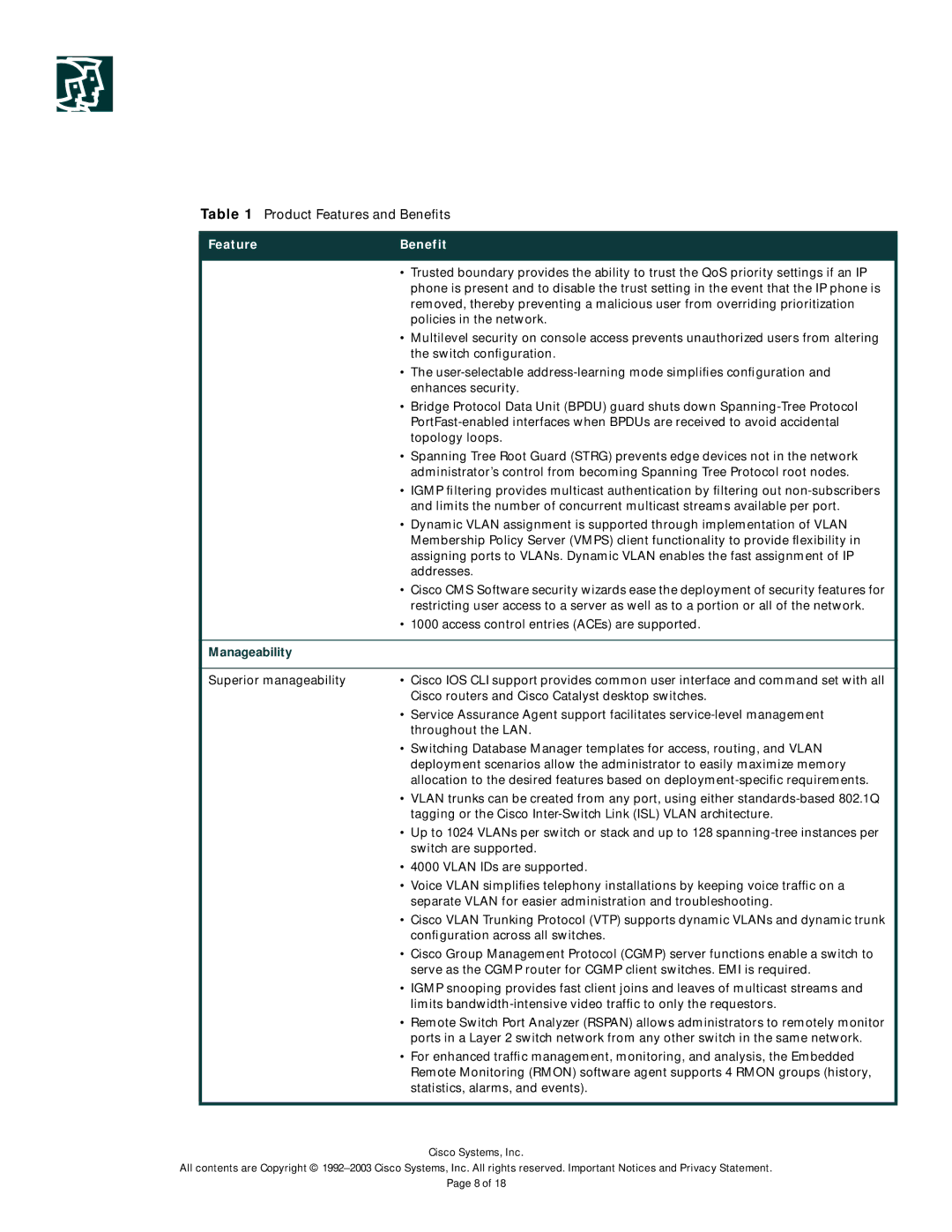
Table 1 Product Features and Benefits
Feature | Benefit |
|
|
| • Trusted boundary provides the ability to trust the QoS priority settings if an IP |
| phone is present and to disable the trust setting in the event that the IP phone is |
| removed, thereby preventing a malicious user from overriding prioritization |
| policies in the network. |
| • Multilevel security on console access prevents unauthorized users from altering |
| the switch configuration. |
| • The |
| enhances security. |
| • Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) guard shuts down |
| |
| topology loops. |
| • Spanning Tree Root Guard (STRG) prevents edge devices not in the network |
| administrator’s control from becoming Spanning Tree Protocol root nodes. |
| • IGMP filtering provides multicast authentication by filtering out |
| and limits the number of concurrent multicast streams available per port. |
| • Dynamic VLAN assignment is supported through implementation of VLAN |
| Membership Policy Server (VMPS) client functionality to provide flexibility in |
| assigning ports to VLANs. Dynamic VLAN enables the fast assignment of IP |
| addresses. |
| • Cisco CMS Software security wizards ease the deployment of security features for |
| restricting user access to a server as well as to a portion or all of the network. |
| • 1000 access control entries (ACEs) are supported. |
|
|
Manageability |
|
|
|
Superior manageability | • Cisco IOS CLI support provides common user interface and command set with all |
| Cisco routers and Cisco Catalyst desktop switches. |
| • Service Assurance Agent support facilitates |
| throughout the LAN. |
| • Switching Database Manager templates for access, routing, and VLAN |
| deployment scenarios allow the administrator to easily maximize memory |
| allocation to the desired features based on |
| • VLAN trunks can be created from any port, using either |
| tagging or the Cisco |
| • Up to 1024 VLANs per switch or stack and up to 128 |
| switch are supported. |
| • 4000 VLAN IDs are supported. |
| • Voice VLAN simplifies telephony installations by keeping voice traffic on a |
| separate VLAN for easier administration and troubleshooting. |
| • Cisco VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) supports dynamic VLANs and dynamic trunk |
| configuration across all switches. |
| • Cisco Group Management Protocol (CGMP) server functions enable a switch to |
| serve as the CGMP router for CGMP client switches. EMI is required. |
| • IGMP snooping provides fast client joins and leaves of multicast streams and |
| limits |
| • Remote Switch Port Analyzer (RSPAN) allows administrators to remotely monitor |
| ports in a Layer 2 switch network from any other switch in the same network. |
| • For enhanced traffic management, monitoring, and analysis, the Embedded |
| Remote Monitoring (RMON) software agent supports 4 RMON groups (history, |
| statistics, alarms, and events). |
|
|
Cisco Systems, Inc.
All contents are Copyright ©
Page 8 of 18