Star Hopping
Another way to find
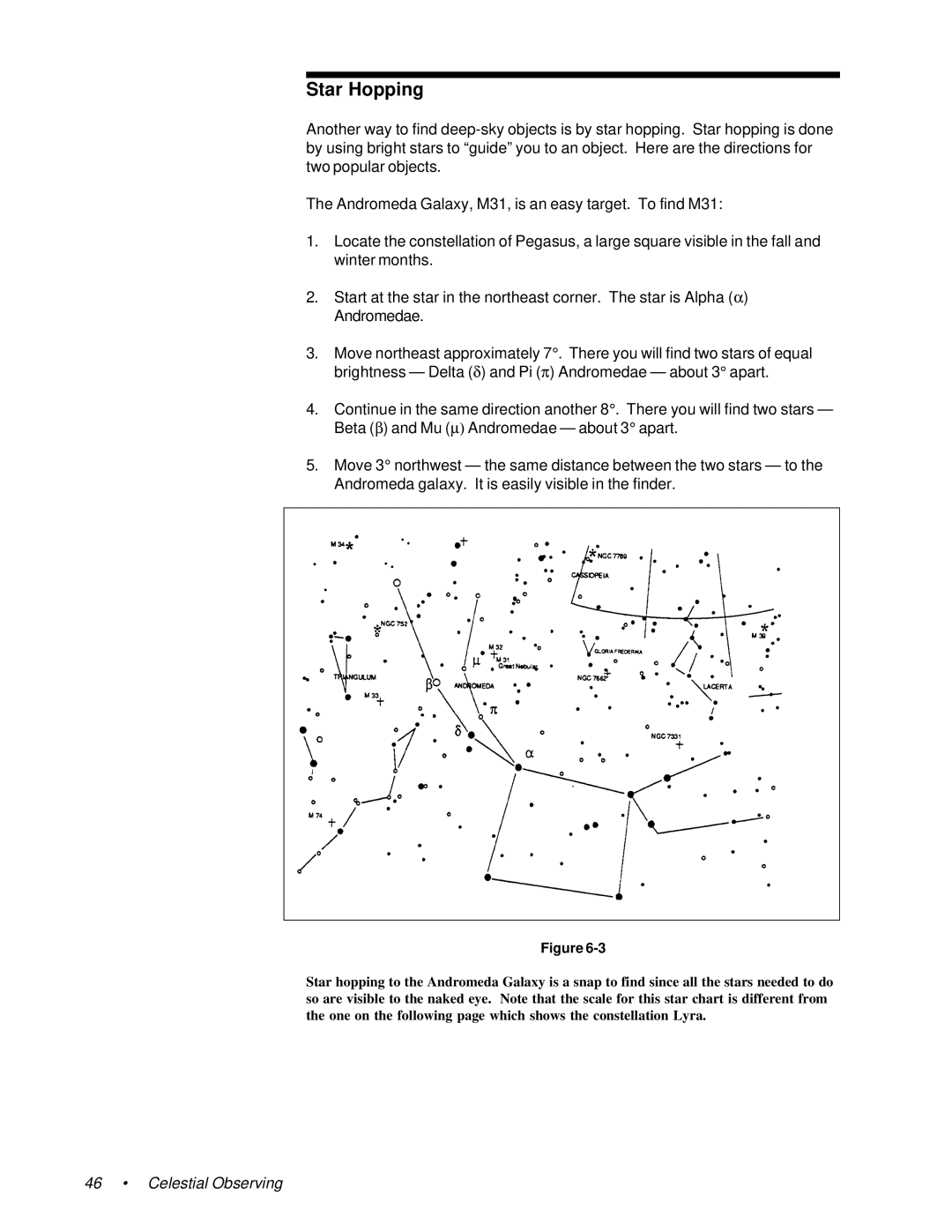
The Andromeda Galaxy, M31, is an easy target. To find M31:
1.Locate the constellation of Pegasus, a large square visible in the fall and winter months.
2.Start at the star in the northeast corner. The star is Alpha (α ) Andromedae.
3.Move northeast approximately 7°. There you will find two stars of equal brightness — Delta (δ ) and Pi (π ) Andromedae — about 3° apart.
4.Continue in the same direction another 8°. There you will find two stars — Beta (β ) and Mu (∝) Andromedae — about 3° apart.
5.Move 3° northwest — the same distance between the two stars — to the Andromeda galaxy. It is easily visible in the finder.
Figure
Star hopping to the Andromeda Galaxy is a snap to find since all the stars needed to do so are visible to the naked eye. Note that the scale for this star chart is different from the one on the following page which shows the constellation Lyra.
46 • Celestial Observing