Telco and ISP Dial Scenarios and Configurations
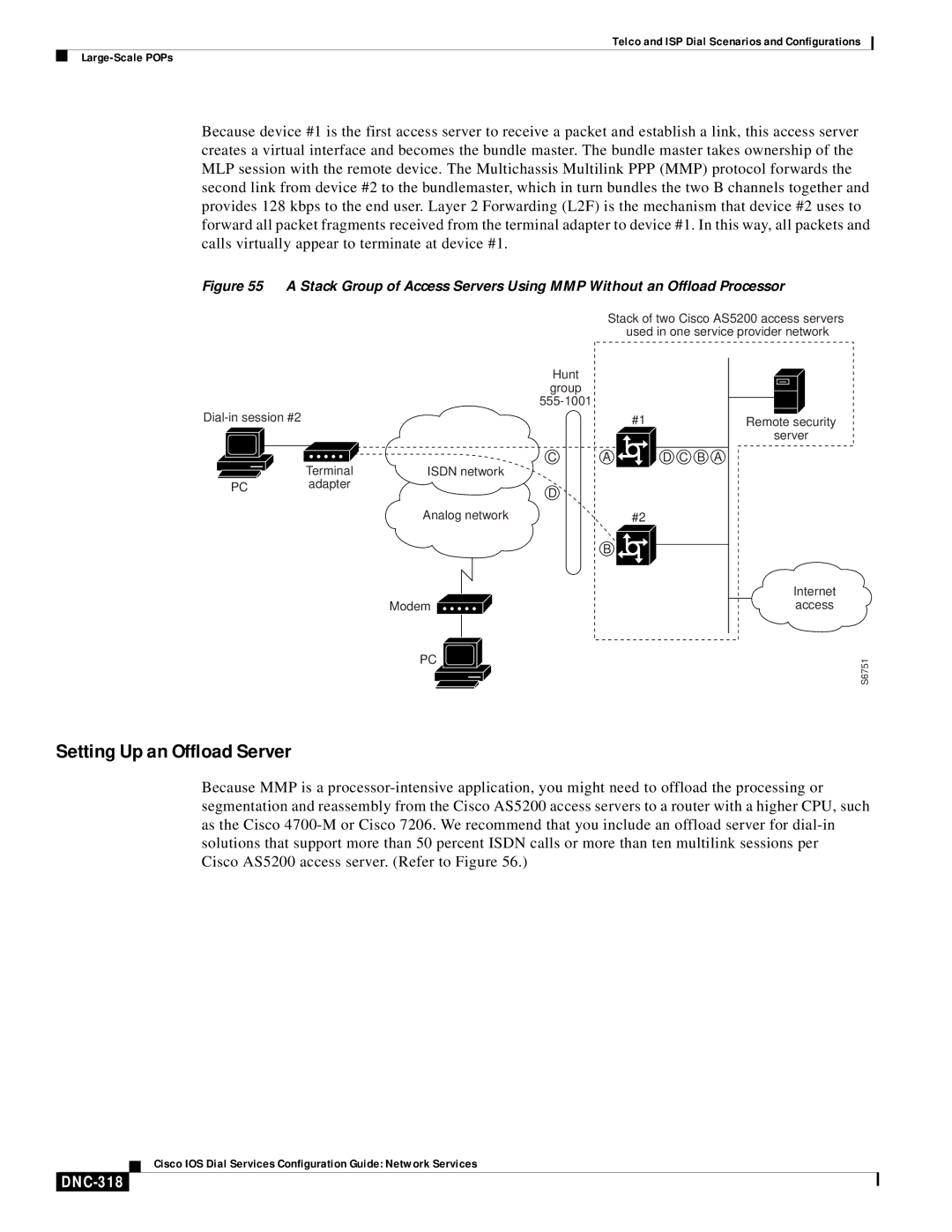
Because device #1 is the first access server to receive a packet and establish a link, this access server creates a virtual interface and becomes the bundle master. The bundle master takes ownership of the MLP session with the remote device. The Multichassis Multilink PPP (MMP) protocol forwards the second link from device #2 to the bundlemaster, which in turn bundles the two B channels together and provides 128 kbps to the end user. Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F) is the mechanism that device #2 uses to forward all packet fragments received from the terminal adapter to device #1. In this way, all packets and calls virtually appear to terminate at device #1.
Figure 55 A Stack Group of Access Servers Using MMP Without an Offload Processor
Stack of two Cisco AS5200 access servers used in one service provider network
|
| Hunt |
|
|
| group |
|
|
|
| |
|
| #1 | |
| Terminal | C | A |
| ISDN network |
| |
PC | adapter | D |
|
|
|
| |
|
| Analog network | #2 |
|
|
| B |
|
| Modem |
|
|
| PC |
|
D C B A
Remote security
server
Internet access
S6751
Setting Up an Offload Server
Because MMP is a
Cisco IOS Dial Services Configuration Guide: Network Services