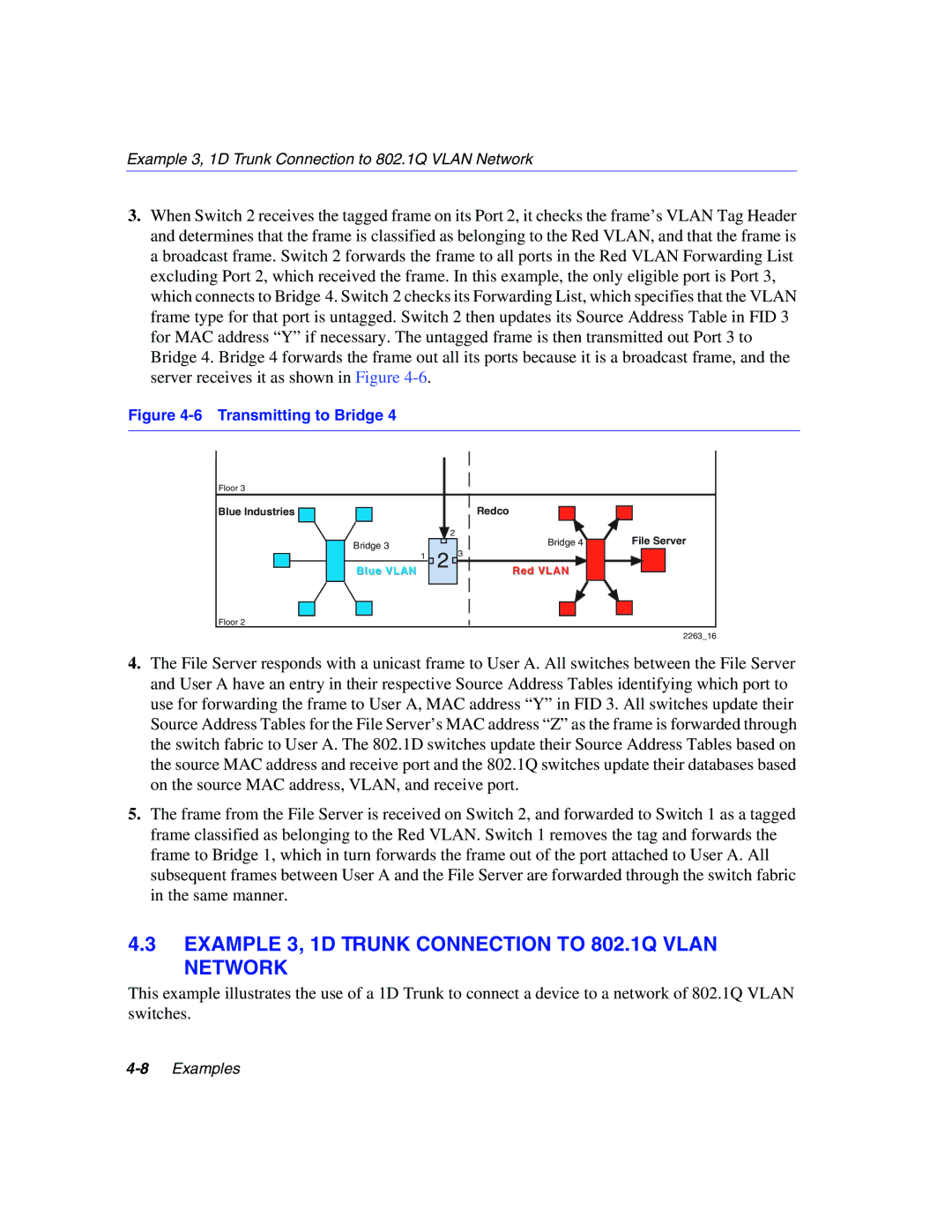
802.1Q specifications
Enterasys Networks, a subsidiary of the Siemens Group, is widely recognized for its comprehensive networking solutions, with a strong emphasis on security, reliability, and performance. One of the key technologies offered by Enterasys is 802.1Q, a critical component of Ethernet networking that establishes standards for VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) tagging. This technology is essential for enhancing network performance and managing traffic efficiently.The primary feature of 802.1Q is its ability to create VLANs, which segment a physical network into multiple logical networks. This segmentation improves network security by isolating sensitive data and restricting access to specific users or devices. With VLANs, organizations can reduce broadcast traffic, thereby enhancing overall network efficiency. Different departments within an organization can operate on their own VLAN, ensuring that their traffic is kept separate from others.
One significant technological aspect of 802.1Q is its tagging method. When a frame passes through a switch port configured for IEEE 802.1Q, the switch appends a VLAN tag to the frame. This tag contains important information, such as the VLAN ID, enabling switches and devices throughout the network to identify which VLAN the frame belongs to. This tagging is especially critical in environments where multiple VLANs share the same physical infrastructure.
Another characteristic of Enterasys Networks' implementation of 802.1Q is interoperability with existing network standards and protocols. This means that organizations can implement VLAN tagging without requiring major upgrades or replacements of their switch hardware. Enterasys ensures that its switches are compliant with various industry standards, making it easier for enterprises to integrate these solutions into their existing network settings.
Security is another vital feature of Enterasys Networks’ 802.1Q offering. By leveraging VLANs, organizations can enforce stricter access controls and policies, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive network segments. This is particularly beneficial for industries with stringent compliance requirements, such as finance and healthcare.
In summary, Enterasys Networks' 802.1Q technology plays a pivotal role in modern networking by facilitating VLAN creation, enabling efficient traffic management, ensuring interoperability, and bolstering network security. As organizations increasingly rely on connected devices and data-driven processes, technologies like 802.1Q are essential for building robust, scalable, and secure networking environments.