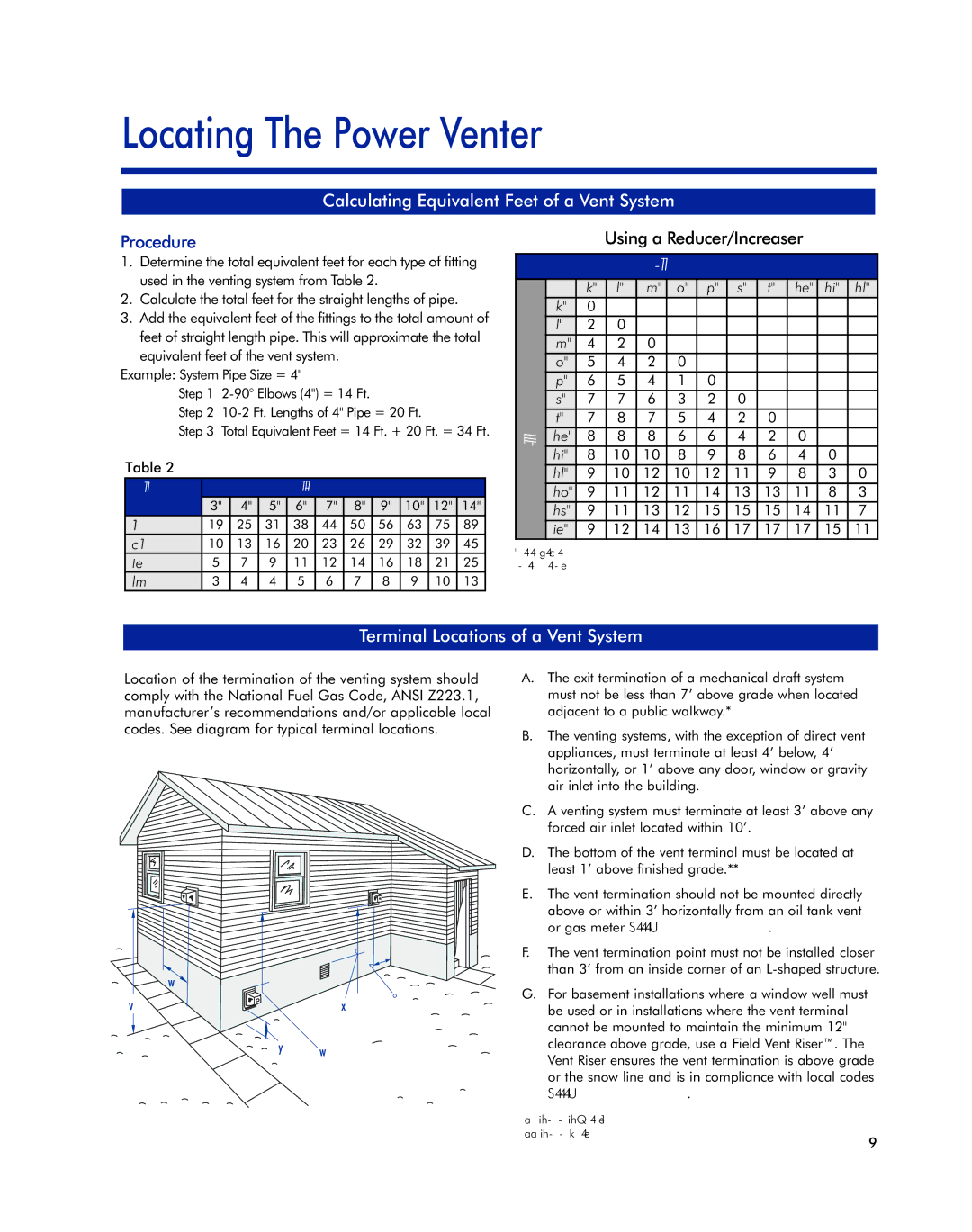
Oil Venting Systems specifications
Field Controls Oil Venting Systems are engineered to enhance the efficiency and safety of oil heating applications while ensuring environmental compliance. These systems are designed to facilitate the venting of combustion gases, preventing the buildup of harmful substances and maintaining optimal performance of oil-fueled heating appliances.A standout feature of Field Controls Oil Venting Systems is their adaptability. They can be seamlessly integrated with a variety of oil-fired heating units, including furnaces and boilers. This versatility allows homeowners and businesses to upgrade or replace their existing venting systems with minimal hassle, leading to improved energy efficiency and reduced operational costs.
The technology that underpins these venting systems is designed to optimize airflow and minimize pressure drop, allowing for efficient exhaust of combustion gases. Field Controls employs advanced materials that are resistant to corrosive gases, ensuring a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements. Additionally, their systems utilize a unique multi-hinge design, which enhances flexibility during installation, ensuring a perfect fit in a diverse range of configurations.
Field Controls also focuses on safety with features such as backdraft dampers and safety switches. These elements prevent backflow of exhaust gases into the living space, providing peace of mind for users. The systems are rigorously tested to comply with national safety standards, ensuring a reliable and secure installation for residential and commercial applications alike.
Moreover, Field Controls Oil Venting Systems prioritize efficiency by optimizing the venting process. This results in reduced energy consumption and lower emissions, aligning with modern environmental standards and helping users transition to more sustainable heating options.
In summary, Field Controls Oil Venting Systems represent a robust solution for oil heating applications, combining safety, efficiency, and adaptability. With their innovative design and commitment to quality, they provide users with a reliable means to manage oil venting, ensuring both comfort and compliance with environmental regulations. By investing in a Field Controls system, customers can enhance their heating systems while contributing to a cleaner and more efficient future.