BEVEL RIPPING
This cut is the same as ripping except the blade bevel angle is set to an angle other than "0".
![]() WARNING
WARNING
Cut only with the workpiece and the fence on the right side of the blade.
RIPPING SMALL PIECES
![]() WARNING
WARNING
Avoid injury from the blade contact. Never make through saw cuts narrower than 1/2" wide.
1.It is unsafe to rip small pieces. Instead, rip a larger piece to obtain the size of the desired piece.
2.When a small width is to be ripped and your hand cannot be safely put between the blade and the rip fence, use one or more push sticks to move the workpiece.
CROSSCUTTING (Fig. Y)
![]() WARNING
WARNING
To prevent serious injury:
Do not allow familiarity or frequent use of your table saw to cause careless mistakes. Remember that even a careless fraction of a second is enough to cause a severe injury.
Keep both hands away from the blade and the path of the blade.
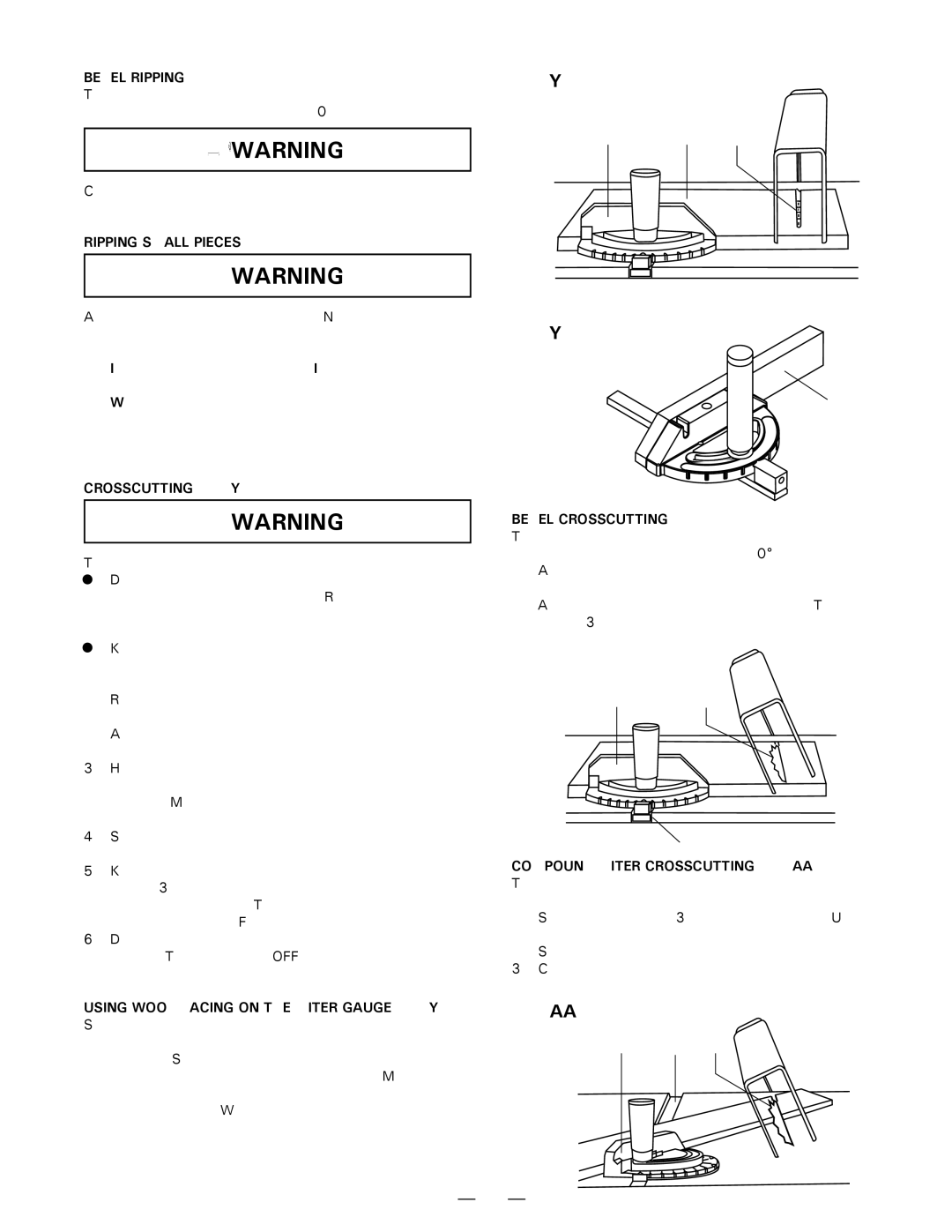
1.Remove the rip fence and place the miter gauge in the left side groove.
2.Adjust the blade height so it is 1/8" higher than the top of the workpiece.
3.Hold the workpiece firmly against the miter gauge with the blade path in line with the desired cut location. Move the workpiece to one inch distance from the blade.
4.Start the saw and wait for the blade (1) to come up to full speed.
5.Keep the workpiece (2) against the face of the miter gauge (3) and flat against the face of the gauge and flat against the table. Then slowly push the workpiece through the blade. (Fig. Y)
6.Do not try to pull the workpiece back with the blade turning. Turn the switch OFF, and carefully slide the workpiece out when the blade is completely stopped.
USING WOOD FACING ON THE MITER GAUGE (Fig.
Fig. Y
3 |
|
| 2 | 1 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig. Y-1
![]() 1
1
BEVEL CROSSCUTTING (Fig. Z)
This cutting operation is the same as crosscutting except the blade is at bevel angle other than 0![]() .
.
1.Adjust the blade (1) to the desired angle, and tighten the blade bevel lock knob.
2.Always work to the left side of the blade. The miter gauge (3) must be in the left side groove (2).
Fig. Z
31
![]() 2
2
COMPOUND MITER CROSSCUTTING (Fig. AA)
This sawing operation is combining a miter angle with a bevel angle.
1.Set the miter gauge (3) to the desired angle. Use only the left side groove (2).
2.Set the blade (1) bevel to the desired angle.
3.Carefully push the miter gauge to begin the cutting operation.
Fig. AA
3 2 1
— 19 —