Http Server for AS/400 Web Programming Guide
Page
Http Server for AS/400 Web Programming Guide
Fifth Edition May
Contents
Enabling your AS/400 to run
AS/400 Operations Navigator
Conventions in this book
Prerequisite and related information
Installing Operations Navigator
How to send your comments
About Http Server for AS/400 Web Programming Guide GC41-5435
Viii Web Programming Guide V4R5
Overview of the CGI
Writing Common Gateway Interface Programs
CGI and Dynamic Documents
Overview
Uses for CGI
CGI process
Following Html form illustrates the various types of fields
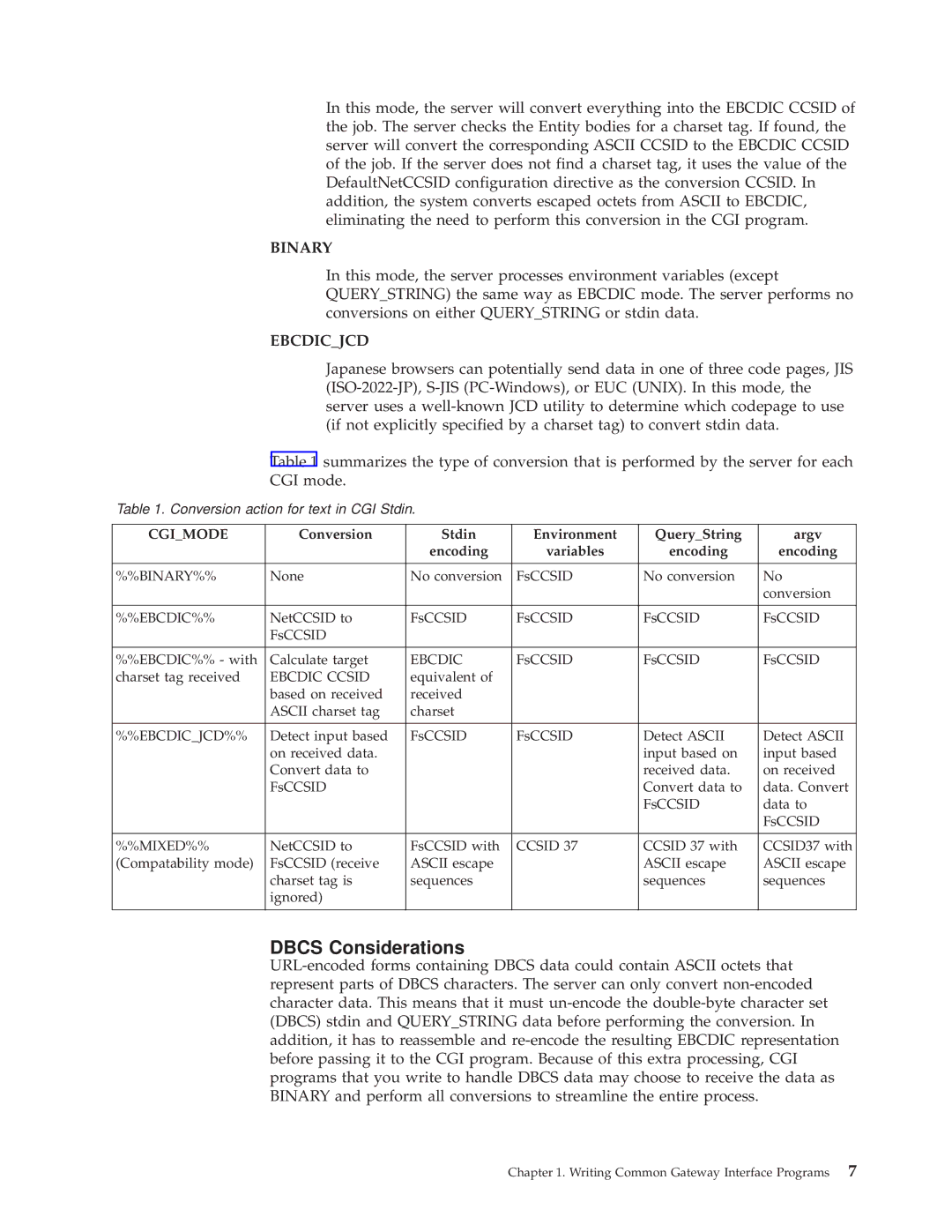
Data Conversions on CGI Input and Output
Sending Information to the Server
BINARY/EBCDIC%% BINARY/BINARY%%
EBCDIC/EBCDIC%%
EBCDICJCD/EBCDIC%%
Mixed
Ebcdicjcd
Binary
IBM PC
CGI Output Conversion Modes
BINARY%%
MIXED%%
EBCDIC%%
Returning Output from the Server
Parsing
How CGI Programs Work
Environment variables
Httpaccept
Gatewayinterface
Httpuseragent
Ibmccsidvalue
Passing SSL Environment Variables to a CGI Program
Requests from Standard Search Isindex Documents
Httpsclientcertissuercountry
Httpsclientcertissuercommonname
Httpsclientcertissuerlocality
Httpsclientcertissuerstateorprovince
AS/400 Activation Groups
CGI Programs and AS/400 Activation Groups
Httpsclientcertstateorprovince
Httpskeysize
CGI Considerations
Activation Group Problem Examples
Writing Common Gateway Interface Programs
Web Programming Guide V4R5
Writing Common Gateway Interface Programs
Web Programming Guide V4R5
Application Programming Interfaces
APIs for CGI applications
Get Environment Variable QtmhGetEnv API
CPF24B4 E
Put Environment Variable QtmhPutEnv API
CPF3C17 E
CPF3C19 E
Read from Stdin QtmhRdStin API
Length or response available
Length of data variable
Write to Stdout QtmhWrStout API
Data variable
Dbcs
Convert to DB QtmhCvtDB API
Input string
Qualified database file name
Length of input string
Response variable
CPF9822 E
CPF9810 E
CPF9812 E
Keywords
Command string
Form
Read
Post
Length of Target Buffer
Target Buffer
Produce Full Http Response QzhbCgiUtils API
Noel
Nodate
Status nnn
Length nnn
Convert URL to Path QzhbCvtURLtoPath API
Configuration APIs
URL
Name of Configuration
Length of the URL
Path to physical resource
HTPA104 E
Retrieve Directive QzhbRetrieveDirective API
Length of the directive name
Name of the directive
Number of values returned
Format name
Bufsize INPUTBINARY4
Buf
Bufactlen OUTPUTBINARY4
Errcode
HTPA001 E
Create a Configuration QzhbCreateConfig API
Errcode I/OCHAR
Delete a Configuration QzhbDeleteConfig API
CPFB602 E
HTPA105 E
Writelock INPUTBINARY4
Read a Configuration File into Memory QzhbOpenConfig API
Write
Free a Configuration File from Memory QzhbCloseConfig API
Cfg
Value
Search for a Main Directive QzhbFindDirective API
HTPA106 E
Startdir INPUTBINARY4
Valuelen INPUTBINARY4
Casesens INPUTBINARY4
Dir
HTPA108 E
HTPA107 E
HTPA110 E
Maindir INPUTBINARY4
HTPA109 E
Hassubdirs OUTPUTBINARY4
CPF3C1D E
Add a Main Directive or Subdirective QzhbAddDirective API
Issubdir OUTPUTBINARY4
Newdir OUTPUTBINARY4
Position INPUTBINARY4
Reldir INPUTBINARY4
HTPA111 E
Length of the value string must be greater than or equal to
Outputvoid
Server instance APIs
INSN0100 Format
Format INPUTCHAR8
Instance name
Running status
Bufactlen
Look up Server Instance Data QzhbGetInstanceData API
Running OUTPUTBINARY4
Configuration
Autostart
Min threads
HTPA101 E
Change Server Instance Data QzhbChangeInstanceData API
Ccsid
Idatasize INPUTBINARY4
Idata
HTPA103 E
Create a Server Instance QzhbCreateInstance API
HTPA102 E
Delete a Server Instance QzhbDeleteInstance API
Create a new Group File QzhbCreateGroupList API
Group file APIs
Pathlen INPUTBINARY4
Read a Group File into Memory QzhbOpenGroupList API
Grplist OUTPUTBINARY4
HTPA202 E
HTPA201 E
Writelock
HTPA203 E
Free Group File from Memory QzhbCloseGroupList API
Grplist INPUTBINARY4
Grp
Prevgrp INPUTBINARY4
HTPA204 E
HTPA206 E
Grouplen INPUTBINARY4
Locate a named group in a Group List QzhbFindGroupInList
Group Inputchar
Buflen OUTPUTBINARY4
Retrieve the Name of a Group QzhbGetGroupName API
Group name to add to the list
Remove a Group from a Group List QzhbRemoveGroupFromList API
Usr
Retrieve the next User in the Group QzhbGetNextUser API
Prevusr INPUTBINARY4
HTPA205 E
Locate a User in a Group QzhbFindUserInGroup API
HTPA207 E
Userlen INPUTBINARY4
Retrieve the Name of a User QzhbGetUserString API
Buflen INPUTBINARY4
Add a new user to the end of a Group QzhbAddUserToGroup
Required Parameter Group Grplist Input Binary4 Usr
Errcode Char Threadsafe Yes
Overview of Net.Data
Using Net.Data to Write CGI Programs for You
Web Programming Guide V4R5
Overview of Persistent CGI
Using Persistent CGI Programs
Named Activation Groups
Accept-HTSession CGI Header
Considerations for using Persistent CGI Programs
HTTimeout CGI Header
Persistent CGI Program Example
Web Programming Guide V4R5
Enabling your AS/400 to run CGI programs
How to enable the server to run CGI programs
Using directives for security and access control
Explicit CGI enablement
Default fail rule
Server runs only CGI programs
CGI program considerations
Protection Example1 AuthType Basic Userid
Example of Java language CGI program
Sample programs in Java, C, and RPG
Samplejava String userMethod String cl Cl = new String
Sample programs in Java, C, and RPG
Web Programming Guide V4R5
Sample programs in Java, C, and RPG
Example of C language CGI program
Sample programs in Java, C, and RPG
Web Programming Guide V4R5
Sample programs in Java, C, and RPG
Environment variable
Example of RPG language CGI program
Create the *PGM object called Samplecrtrpgmod and Crtpgm
INZ
CZ-ADD 16QUSBPRV
Subst
Cat Htmli0 BufOut
Example of a C language server configuration API program
Web Programming Guide V4R5
Sample programs in Java, C, and RPG
Web Programming Guide V4R5
Writing Server API programs
General procedure for writing Server API programs
Overview of the Server API
Guidelines
Basic server request process
Application functions
Service
Data Filter
PostExit
Name Translation
Log
Error
Http return codes and values
Value Return code
Predefined functions and macros
HTTPDextract
HTTPDauthenticate
HTTPDattributes
HTTPDset
HTTPDreversetranslate
HTTPDtranslate
HTTPDread
HTTPDexec
HTTPDwrite
HTTPDlogerror
HTTPDlogtrace
HTTPDrestart
Return codes
Httpdparametererror
Server API directives and syntax
Server API configuration directives
Server API usage notes
URL templete
Server API directive variables
Specific URL
Porting CGI programs
Authentication and Authorization
Compatibility with other APIs
Environment variables
Server API variables
Password
Errorinfo
Proxyaccess
Proxycontenttype
Requestcontenttype
Proxycontentlength
Responsecontentlength
Proxymethod
Example
Ssiroot
Userid
Username
Web Programming Guide V4R5
Overview of servlets
Writing Java Servlets
Web Programming Guide V4R5
Considerations for using server-side includes
Using Server-Side Includes
Preparing to use server-side includes
Examples
Format for server-side includes
Result 1K Default ″abbrev″
Directives for server-side includes
Result Example
Specifier Meaning
Specifier Meaning
Content-encoding
Content-type
Dategmt
Datelocal
Result 1K
Last-modified
Directive Formats
#flastmod virtual=&PARENTURI
Alert bell
Symptom
Troubleshooting your CGI programs
Web Programming Guide V4R5
Troubleshooting your CGI programs
Put the CGI programs in a separate library
Symptom
Web Programming Guide V4R5
145
Trademarks
Programming Interface Information
Page
Web Programming Guide V4R5
How satisfied are you that the information in this book is
Readers’ Comments We’d Like to Hear from You
Business Reply Mail
Page
GC41-5435-04
Web Programming Guide V4R5