Overview of IBM Networking
STUN and BSTUN
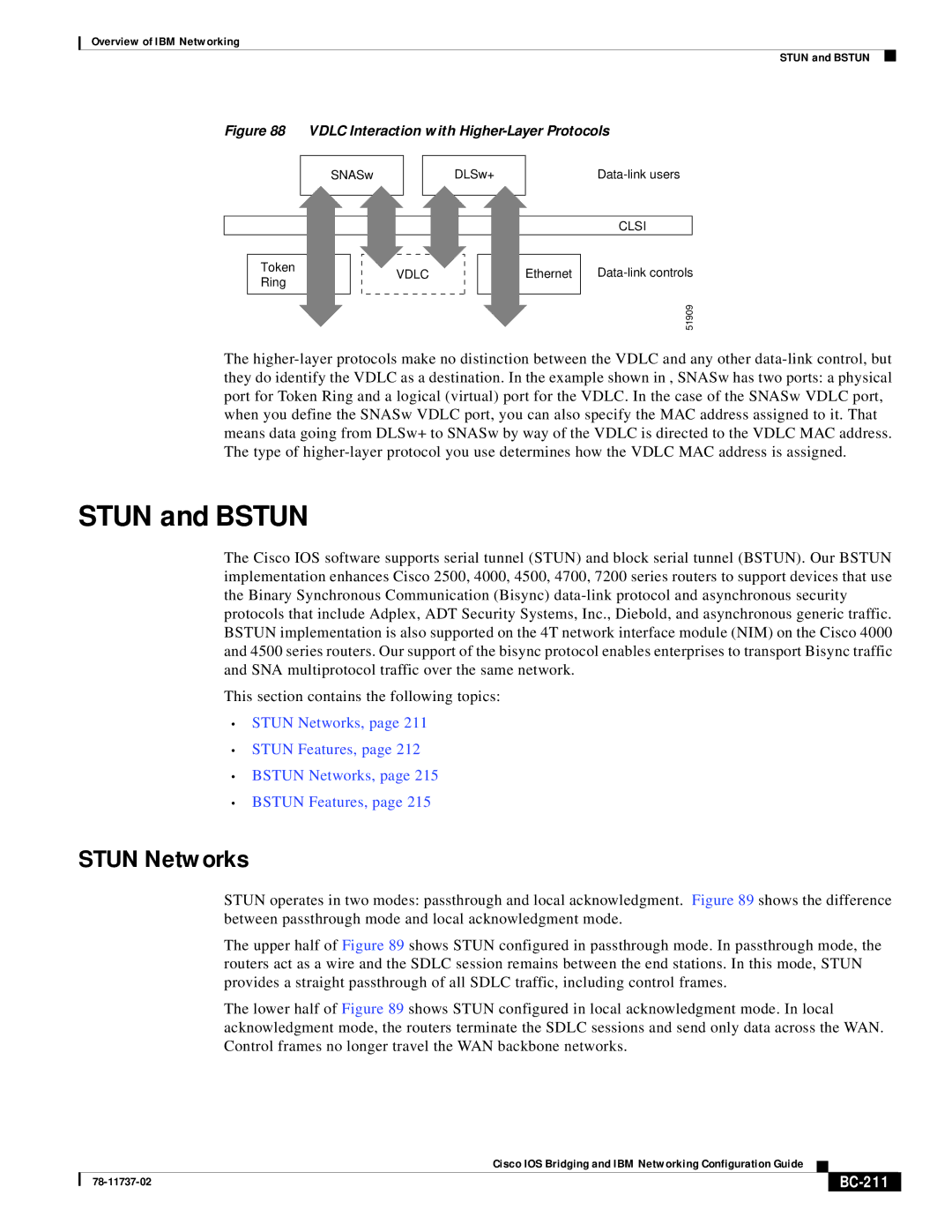
Figure 88 VDLC Interaction with Higher-Layer Protocols
SNASw
DLSw+
|
|
|
| CLSI |
|
|
|
|
|
| Token | VDLC | Ethernet | |
| Ring | |||
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| 51909 |
|
|
|
|
The
STUN and BSTUN
The Cisco IOS software supports serial tunnel (STUN) and block serial tunnel (BSTUN). Our BSTUN implementation enhances Cisco 2500, 4000, 4500, 4700, 7200 series routers to support devices that use the Binary Synchronous Communication (Bisync)
This section contains the following topics:
•STUN Networks, page 211
•STUN Features, page 212
•BSTUN Networks, page 215
•BSTUN Features, page 215
STUN Networks
STUN operates in two modes: passthrough and local acknowledgment. Figure 89 shows the difference between passthrough mode and local acknowledgment mode.
The upper half of Figure 89 shows STUN configured in passthrough mode. In passthrough mode, the routers act as a wire and the SDLC session remains between the end stations. In this mode, STUN provides a straight passthrough of all SDLC traffic, including control frames.
The lower half of Figure 89 shows STUN configured in local acknowledgment mode. In local acknowledgment mode, the routers terminate the SDLC sessions and send only data across the WAN. Control frames no longer travel the WAN backbone networks.
|
| Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|