Overview of IBM Networking
NCIA
After the peer session has been established, the NDLC protocol establishes the circuit between the client and server. This circuit is used to transfer
In the NCIA server only peer keepalive is maintained. There is no keepalive at circuit level.
The NCIA server acts as a
Advantages of the Client/Server Model
The client/server model used in the NCIA Server feature extends the scalability of NCIA. In addition, it provides support for both the installed base of RSRB routers and the growing number of DLSw+ routers.
Extended Scalability
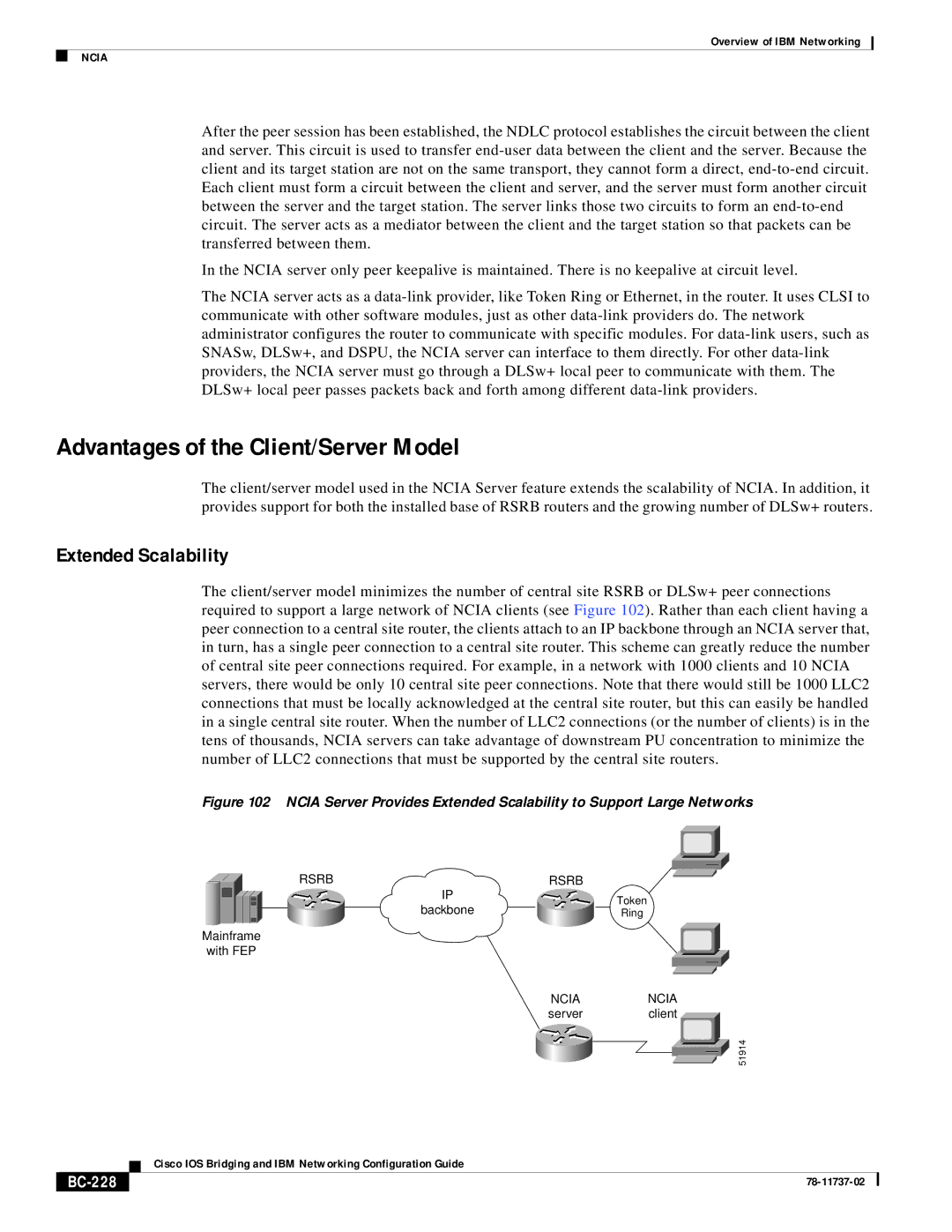
The client/server model minimizes the number of central site RSRB or DLSw+ peer connections required to support a large network of NCIA clients (see Figure 102). Rather than each client having a peer connection to a central site router, the clients attach to an IP backbone through an NCIA server that, in turn, has a single peer connection to a central site router. This scheme can greatly reduce the number of central site peer connections required. For example, in a network with 1000 clients and 10 NCIA servers, there would be only 10 central site peer connections. Note that there would still be 1000 LLC2 connections that must be locally acknowledged at the central site router, but this can easily be handled in a single central site router. When the number of LLC2 connections (or the number of clients) is in the tens of thousands, NCIA servers can take advantage of downstream PU concentration to minimize the number of LLC2 connections that must be supported by the central site routers.
Figure 102 NCIA Server Provides Extended Scalability to Support Large Networks
RSRB | RSRB | |
IP | Token | |
backbone | ||
Ring |
Mainframe
with FEP
NCIANCIA
server client ![]()
51914
| Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide |
|